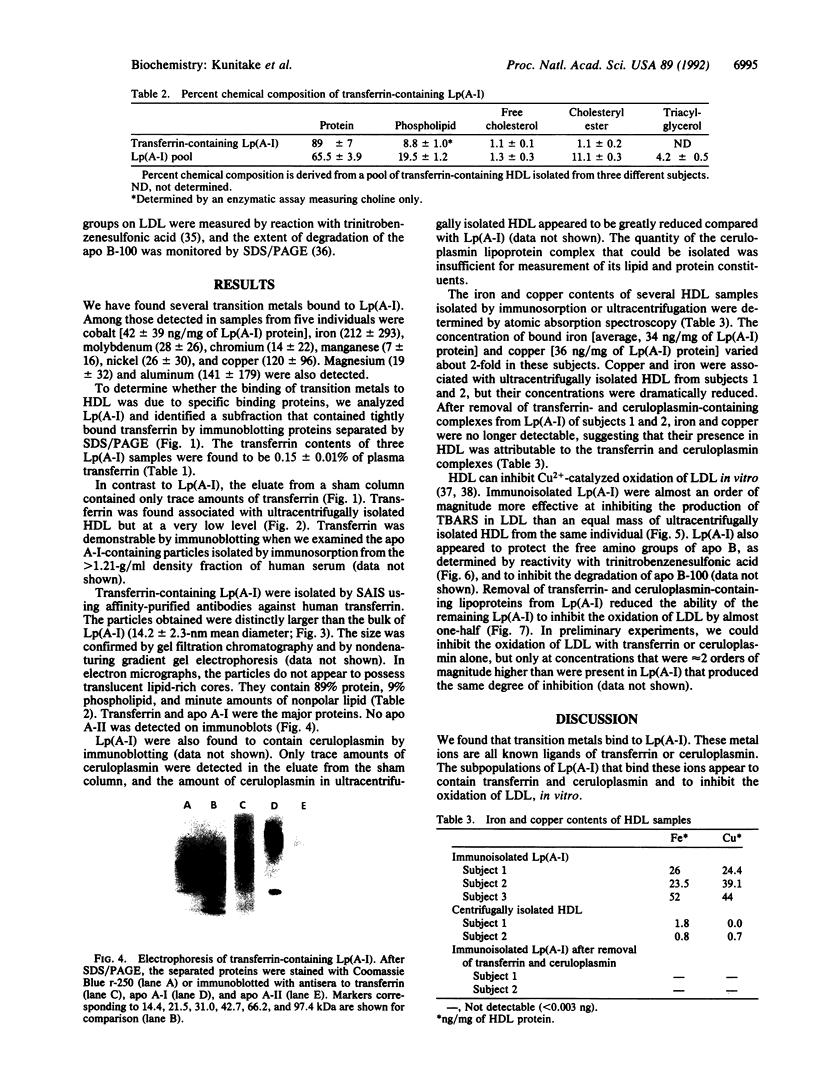
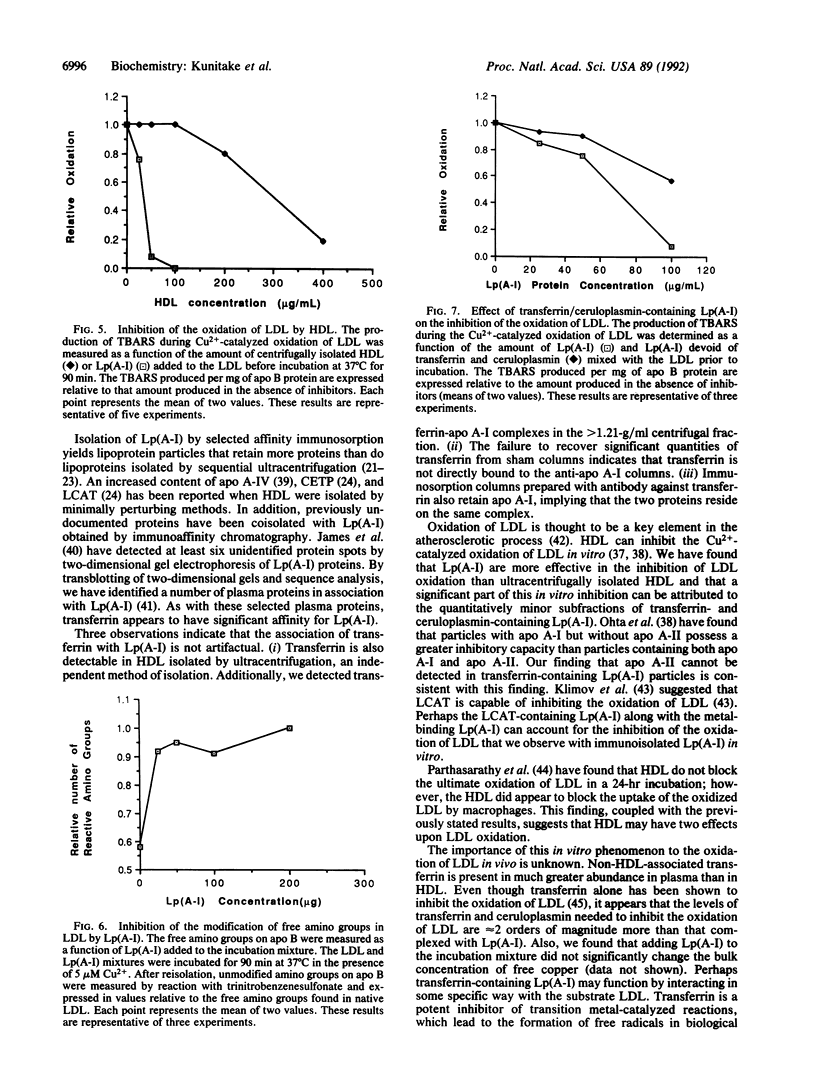
Abstract
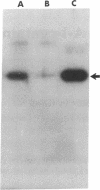
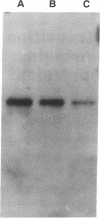
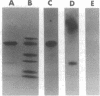
We have found transition metals tightly bound to apolipoprotein A-I-containing lipoproteins [Lp(A-I)] isolated by selected affinity immunosorption from human serum. Prominent among the metal ions detected were iron and copper. By immunoblotting the proteins of Lp(A-I), we detected both transferrin and ceruloplasmin. The transferrin-containing Lp(A-I) particles, isolated by selected affinity immunosorption against transferrin, were larger (mean diameter of 14.2 nm) and had a higher protein content than most high density lipoproteins (HDL). Ultracentrifugally isolated HDL were found to contain much less transferrin, whereas transferrin was found associated with apolipoprotein A-I from the greater than 1.21-g/ml ultracentrifugal fraction. This suggests that the complex is not recovered in the classic HDL density interval because of its very high density. HDL inhibit copper-catalyzed oxidation of low density lipoproteins (LDL) in vitro. We have found that immunoisolated Lp(A-I) are an order of magnitude more effective in inhibiting the oxidation of LDL than ultracentrifugally isolated HDL, on the basis of protein mass. When the Lp(A-I) particles containing transferrin and ceruloplasmin were removed from the bulk of Lp(A-I), inhibition of the in vitro oxidation of LDL was significantly decreased.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson D. W., Nichols A. V., Forte T. M., Lindgren F. T. Particle distribution of human serum high density lipoproteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Jul 22;493(1):55–68. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(77)90259-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blanche P. J., Gong E. L., Forte T. M., Nichols A. V. Characterization of human high-density lipoproteins by gradient gel electrophoresis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Sep 24;665(3):408–419. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(81)90253-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bucolo G., David H. Quantitative determination of serum triglycerides by the use of enzymes. Clin Chem. 1973 May;19(5):476–482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carson S. D. Plasma high density lipoproteins inhibit the activation of coagulation factor X by factor VIIa and tissue factor. FEBS Lett. 1981 Sep 14;132(1):37–40. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80422-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen G. C., Kane J. P., Hamilton R. L. Thermal behavior of cores of human serum triglyceride-rich lipoproteins: a study of induced circular dichroism of beta-carotene. Biochemistry. 1984 Mar 13;23(6):1119–1124. doi: 10.1021/bi00301a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen G. C., Zhu S., Hardman D. A., Schilling J. W., Lau K., Kane J. P. Structural domains of human apolipoprotein B-100. Differential accessibility to limited proteolysis of B-100 in low density and very low density lipoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 25;264(24):14369–14375. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y. D., Kraemer F. B., Reaven G. M. Identification of specific high density lipoprotein-binding sites in rat testis and regulation of binding by human chorionic gonadotropin. J Biol Chem. 1980 Oct 10;255(19):9162–9167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung M. C., Albers J. J. Characterization of lipoprotein particles isolated by immunoaffinity chromatography. Particles containing A-I and A-II and particles containing A-I but no A-II. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 10;259(19):12201–12209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung M. C., Wolf A. C., Lum K. D., Tollefson J. H., Albers J. J. Distribution and localization of lecithin:cholesterol acyltransferase and cholesteryl ester transfer activity in A-I-containing lipoproteins. J Lipid Res. 1986 Nov;27(11):1135–1144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung B. H., Segrest J. P., Cone J. T., Pfau J., Geer J. C., Duncan L. A. High resolution plasma lipoprotein cholesterol profiles by a rapid, high volume semi-automated method. J Lipid Res. 1981 Aug;22(6):1003–1014. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curry M. D., Alaupovic P., Suenram C. A. Determination of apolipoprotein A and its constitutive A-I and A-II polypeptides by separate electroimmunoassays. Clin Chem. 1976 Mar;22(3):315–322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fainaru M., Havel R. J., Felker T. E. Radioimmunoassay of apolipoprotein A-I of rat serum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Sep 28;446(1):56–68. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(76)90097-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fielding C. J., Fielding P. E. Cholesterol transport between cells and body fluids. Role of plasma lipoproteins and the plasma cholesterol esterification system. Med Clin North Am. 1982 Mar;66(2):363–373. doi: 10.1016/s0025-7125(16)31425-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAVEL R. J., EDER H. A., BRAGDON J. H. The distribution and chemical composition of ultracentrifugally separated lipoproteins in human serum. J Clin Invest. 1955 Sep;34(9):1345–1353. doi: 10.1172/JCI103182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habeeb A. F. Determination of free amino groups in proteins by trinitrobenzenesulfonic acid. Anal Biochem. 1966 Mar;14(3):328–336. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(66)90275-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang H., Kauan J. W., Guilbault G. G. Fluorometric enzymatic determination of total cholesterol in serum. Clin Chem. 1975 Oct;21(11):1605–1608. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivanova E. M., Nikiforova A. A., Alksnis E. G. Poluchenie proteoliposom--iskusstvennogo substrata dlia izmereniia skorosti letsitin-kholesterin-atsiltransferaznoi reaktsii v tsel'noi plazme krovi. Vopr Med Khim. 1985 Nov-Dec;31(6):123–126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James R. W., Hochstrasser D., Tissot J. D., Funk M., Appel R., Barja F., Pellegrini C., Muller A. F., Pometta D. Protein heterogeneity of lipoprotein particles containing apolipoprotein A-I without apolipoprotein A-II and apolipoprotein A-I with apolipoprotein A-II isolated from human plasma. J Lipid Res. 1988 Dec;29(12):1557–1571. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kane J. P., Hardman D. A., Dimpfl J. C., Levy J. A. Apolipoprotein is responsible for neutralization of xenotropic type C virus by mouse serum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5957–5961. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klimov A. N., Kozhemiakin L. A., Pleskov V. M., Andreeva L. I. Antioksidantnyi éffekt lipoproteidov vysokoi plotnosti pri perekisnom okislenii lipoproteidov nizkoi plotnosti. Biull Eksp Biol Med. 1987 May;103(5):550–552. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostner G. M., Patsch J. R., Sailer S., Braunsteiner H., Holasek A. Polypeptide distribution of the main lipoprotein density classes separated from human plasma by rate zonal ultracentrifugation. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jun 15;45(2):611–621. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03587.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunitake S. T., Chen G. C., Kung S. F., Schilling J. W., Hardman D. A., Kane J. P. Pre-beta high density lipoprotein. Unique disposition of apolipoprotein A-I increases susceptibility to proteolysis. Arteriosclerosis. 1990 Jan-Feb;10(1):25–30. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.10.1.25. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunitake S. T., Kane J. P. Factors affecting the integrity of high density lipoproteins in the ultracentrifuge. J Lipid Res. 1982 Aug;23(6):936–940. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagrost L., Gambert P., Boquillon M., Lallemant C. Evidence for high density lipoproteins as the major apolipoprotein A-IV-containing fraction in normal human serum. J Lipid Res. 1989 Oct;30(10):1525–1534. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahley R. W., Holcombe K. S. Alterations of the plasma lipoproteins and apoproteins following cholesterol feeding in the rat. J Lipid Res. 1977 May;18(3):314–324. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makino T., Takahara K. Direct determination of plasma copper and zinc in infants by atomic absorption with discrete nebulization. Clin Chem. 1981 Aug;27(8):1445–1447. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcel Y. L., Weech P. K., Nguyen T. D., Milne R. W., McConathy W. J. Apolipoproteins as the basis for heterogeneity in high-density lipoprotein2 and high-density lipoprotein3. Studies by isoelectric focusing on agarose films. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Sep 17;143(3):467–476. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08394.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNamara B. C., Booth R., Stansfield D. A. Evidence for an essential role for high-density lipoprotein in progesterone synthesis by rat corpus luteum. FEBS Lett. 1981 Nov 2;134(1):79–82. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80555-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McVicar J. P., Kunitake S. T., Hamilton R. L., Kane J. P. Characteristics of human lipoproteins isolated by selected-affinity immunosorption of apolipoprotein A-I. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(5):1356–1360. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.5.1356. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohashi M., Carr B. R., Simpson E. R. Binding of high density lipoprotein to human fetal adrenal membrane fractions. Endocrinology. 1981 Sep;109(3):783–788. doi: 10.1210/endo-109-3-783. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohta T., Takata K., Horiuchi S., Morino Y., Matsuda I. Protective effect of lipoproteins containing apoprotein A-I on Cu2+-catalyzed oxidation of human low density lipoprotein. FEBS Lett. 1989 Nov 6;257(2):435–438. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81590-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ormerod W. E., Venkatesan S. Similarities of lipid metabolism in mammalian and protozoan cells: an evolutionary hypothesis for the prevalence of atheroma. Microbiol Rev. 1982 Sep;46(3):296–307. doi: 10.1128/mr.46.3.296-307.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parthasarathy S., Barnett J., Fong L. G. High-density lipoprotein inhibits the oxidative modification of low-density lipoprotein. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 May 22;1044(2):275–283. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(90)90314-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudel L. L., Lee J. A., Morris M. D., Felts J. M. Characterization of plasma lipoproteins separated and purified by agarose-column chromatography. Biochem J. 1974 Apr;139(1):89–95. doi: 10.1042/bj1390089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinberg D., Parthasarathy S., Carew T. E., Khoo J. C., Witztum J. L. Beyond cholesterol. Modifications of low-density lipoprotein that increase its atherogenicity. N Engl J Med. 1989 Apr 6;320(14):915–924. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198904063201407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart C. P., Hendry E. B. The phospholipins of blood. Biochem J. 1935 Jul;29(7):1683–1689. doi: 10.1042/bj0291683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tauber J. P., Cheng J., Massoglia S., Gospodarowicz D. High density lipoproteins and the growth of vascular endothelial cells in serum-free medium. In Vitro. 1981 Jun;17(6):519–530. doi: 10.1007/BF02633513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulevitch R. J., Johnston A. R., Weinstein D. B. New function for high density lipoproteins. Isolation and characterization of a bacterial lipopolysaccharide-high density lipoprotein complex formed in rabbit plasma. J Clin Invest. 1981 Mar;67(3):827–837. doi: 10.1172/JCI110100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Utermann G. Disc-electrophoretic patterns of human serum high density lipoproteins. Clin Chim Acta. 1972 Feb;36(2):521–529. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(72)90029-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yagi K. A simple fluorometric assay for lipoperoxide in blood plasma. Biochem Med. 1976 Apr;15(2):212–216. doi: 10.1016/0006-2944(76)90049-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]