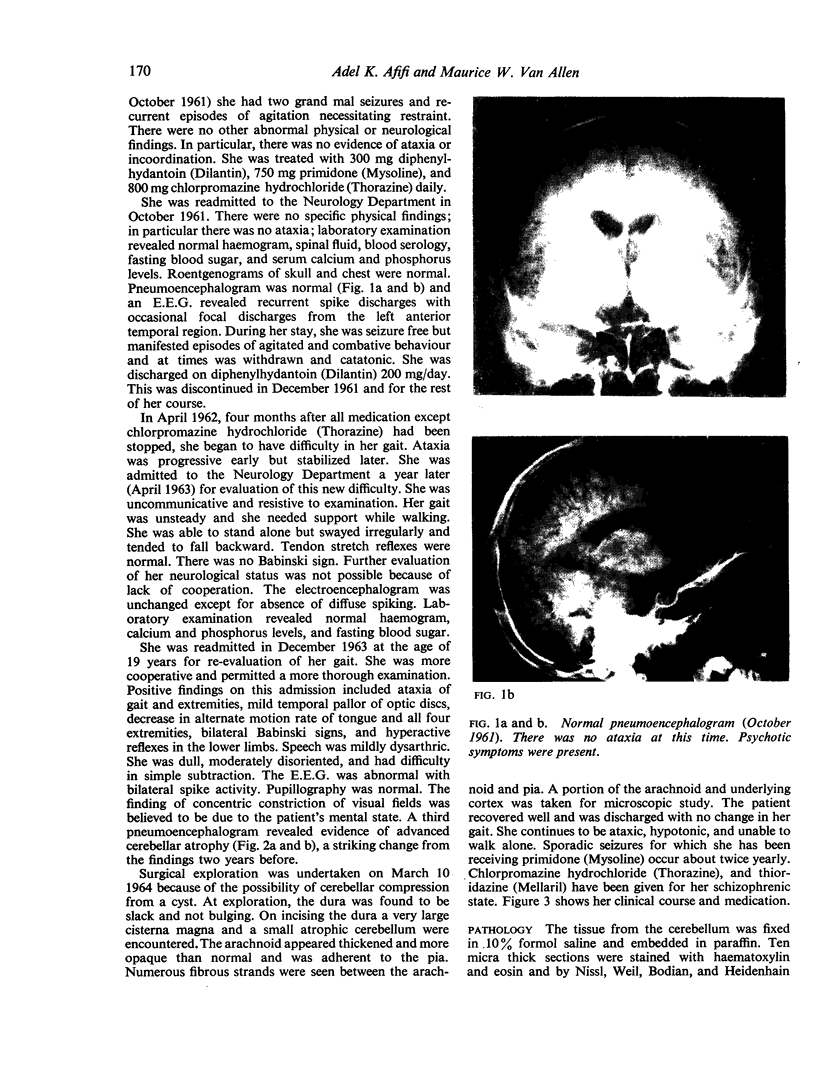
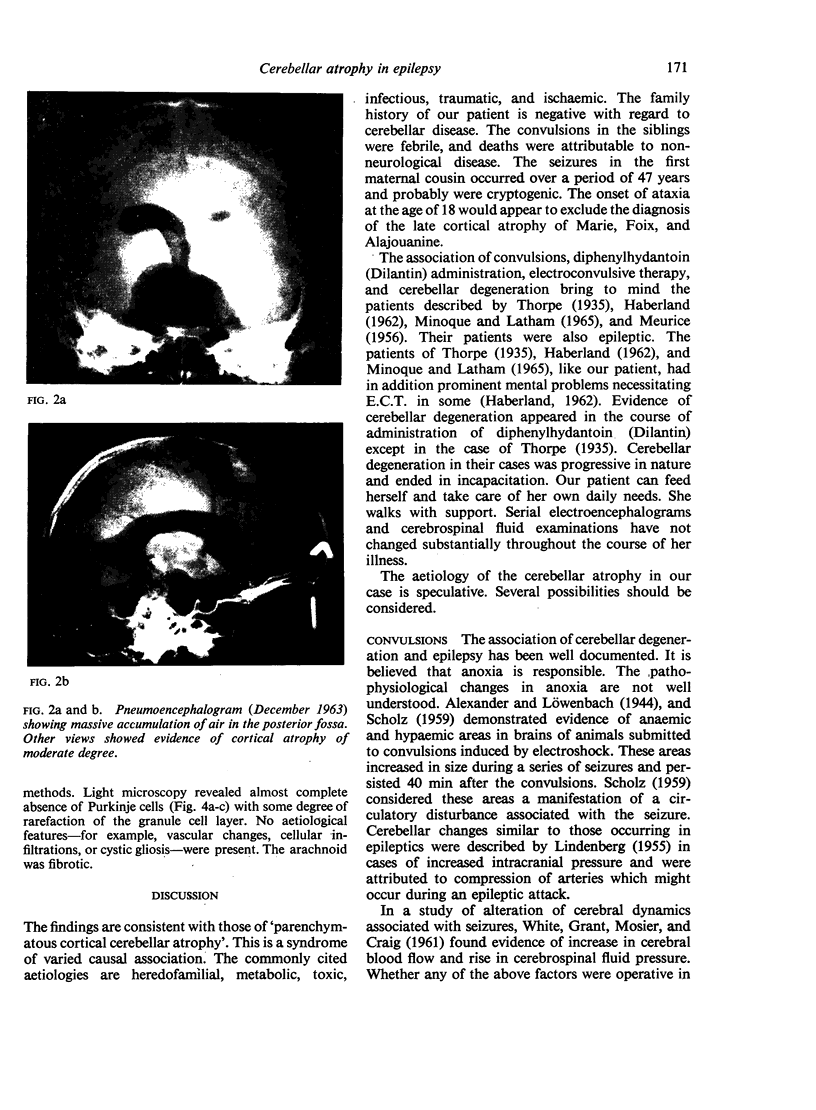
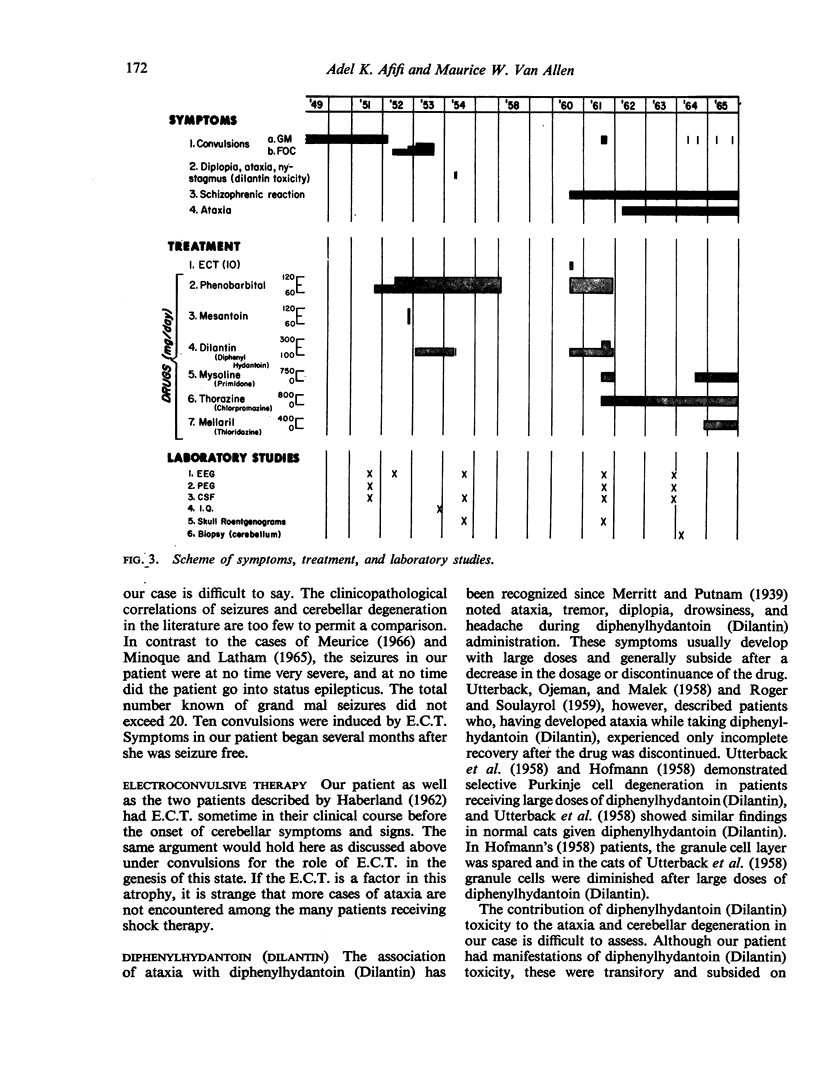
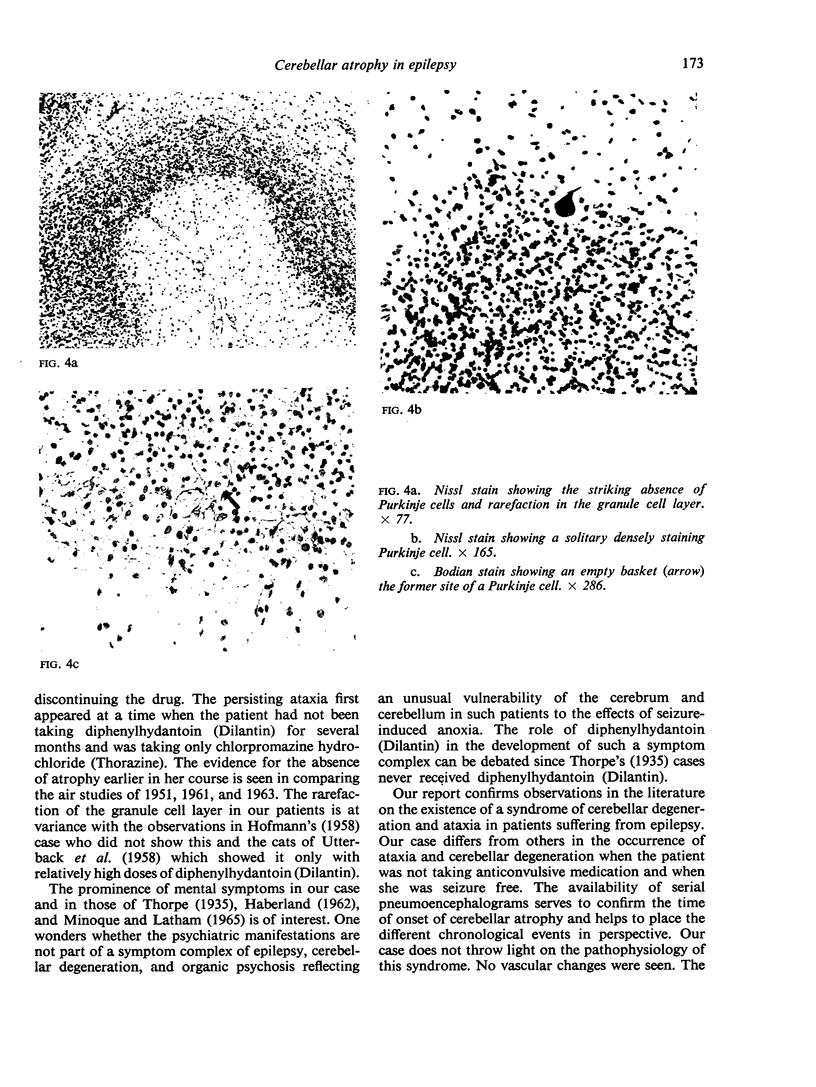
Full text
PDF

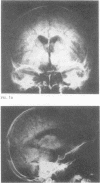
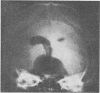
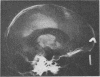
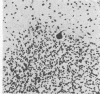
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- HABERLAND C. Cerebellar degeneration with clinical manifestation in chronic epileptic patients. Psychiatr Neurol (Basel) 1962;143:29–44. doi: 10.1159/000131114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOFMANN W. W. Cerebellar lesions after parenteral dilantin administration. Neurology. 1958 Mar;8(3):210–214. doi: 10.1212/wnl.8.3.210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LINDENBERG R. Compression of brain arteries as pathogenetic factor for tissue necroses and their areas of predilection. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1955 Jul;14(3):223–243. doi: 10.1097/00005072-195507000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MEURICE E. Documents anatomo-cliniques sur l'épilepsie. I. D'un syndrome cérébello-spasmodique progressif de longue durée dans l'épilepsie d'allure temporale. Acta Neurol Psychiatr Belg. 1956 Jun;56(6):396–401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MEYER A., BECK E., SHEPHERD M. Unusually severe lesions in the brain following status epilepticus. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1955 Feb;18(1):24–33. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.18.1.24. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROGER J., SOULAYROL R. [Apropos of neurological complications of the treatment of epilepsy by hydantoins]. Rev Neurol (Paris) 1959 Jun;100:783–785. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WHITE P. T., GRANT P., MOSIER J., CRAIG A. Changes in cerebral dynamics associated with seizures. Neurology. 1961 Apr;11(4):354–361. doi: 10.1212/wnl.11.4.354. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]