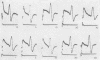
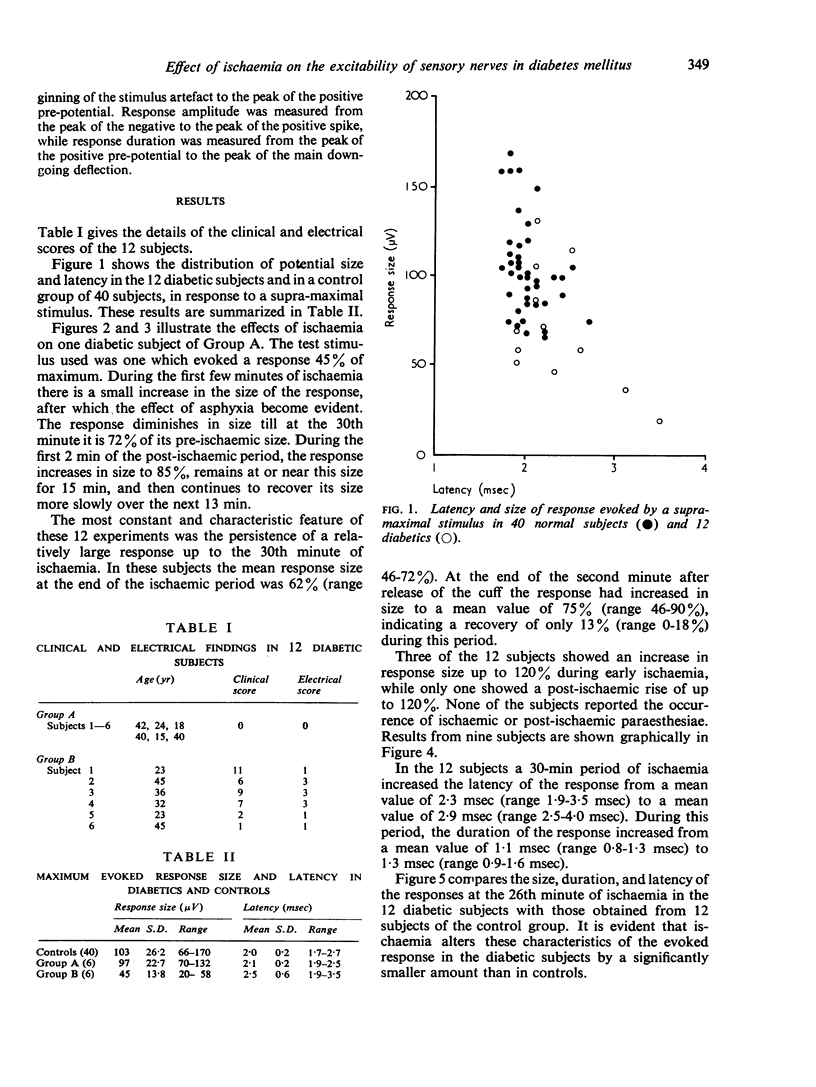
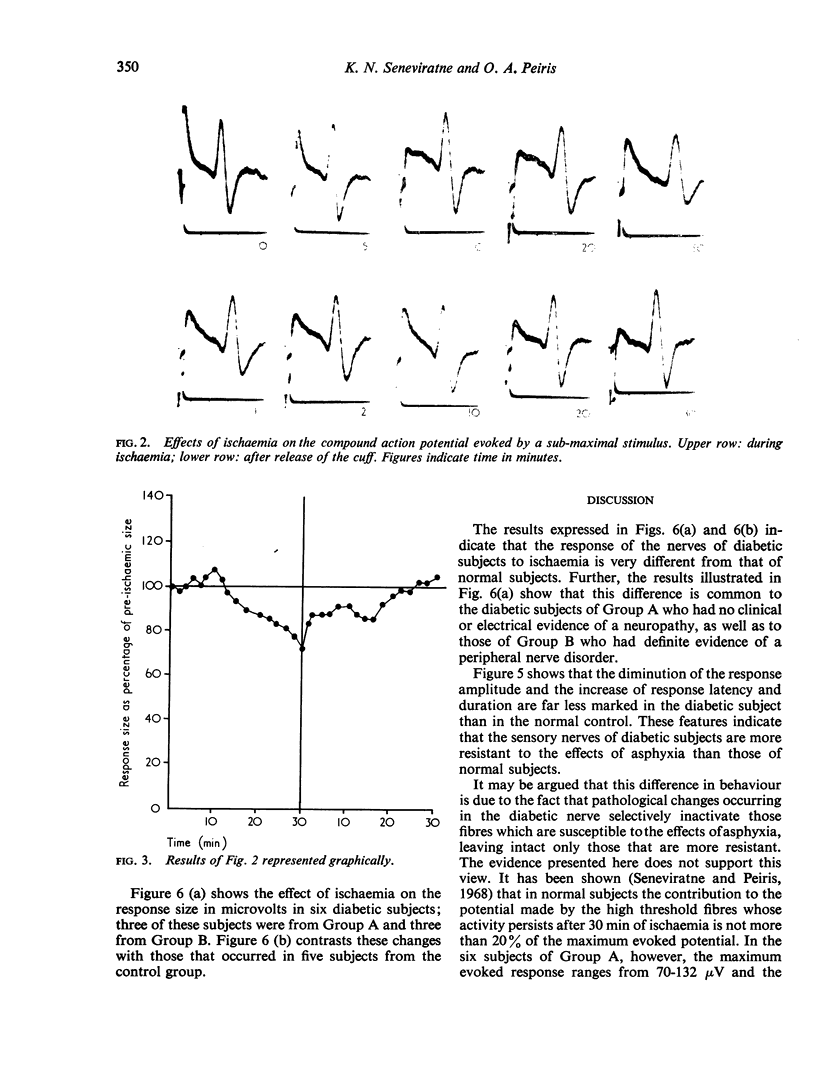
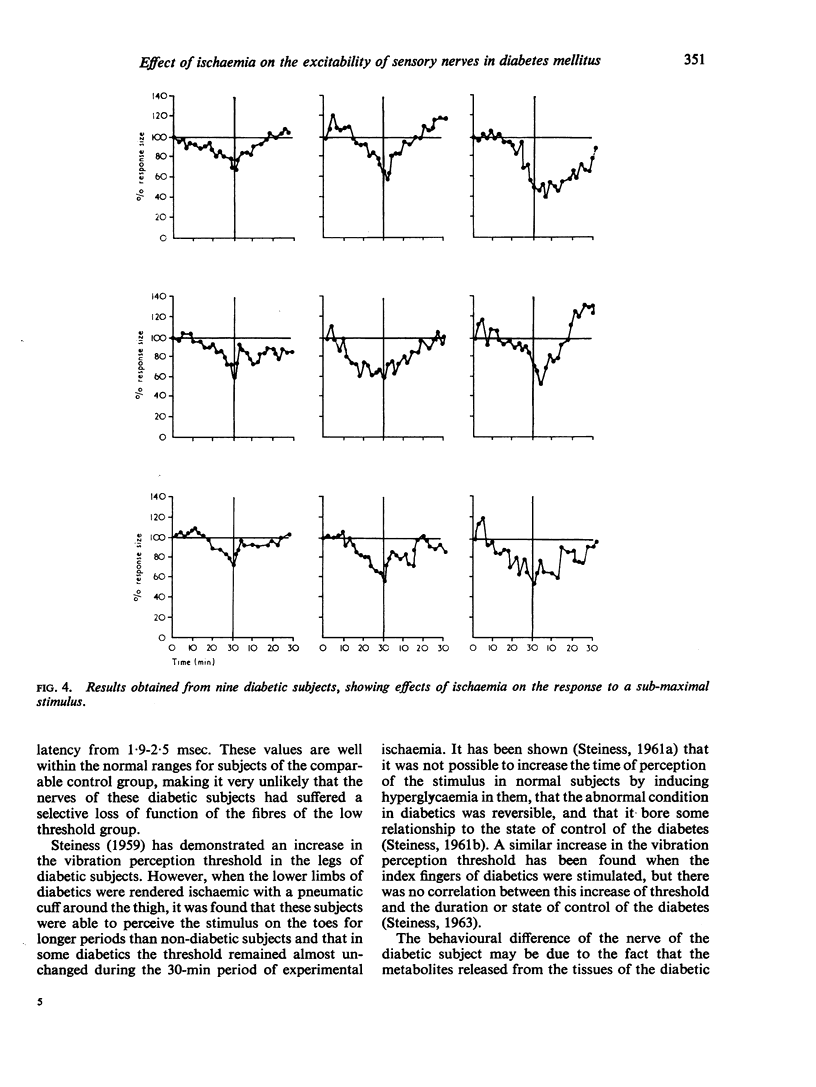
Full text
PDF
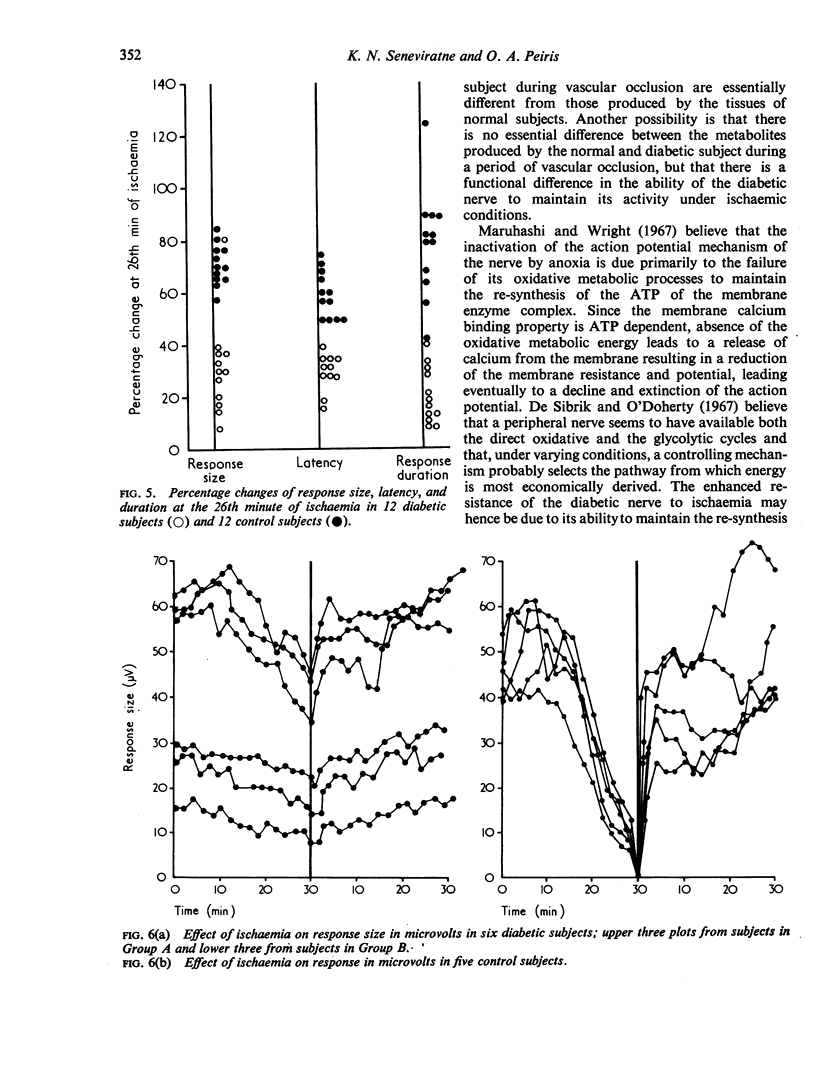

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- DOWNIE A. W., NEWELL D. J. Sensory nerve conduction in patients with diabetes mellitus and controls. Neurology. 1961 Oct;11:876–882. doi: 10.1212/wnl.11.10.876. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeSibrik I., O'Doherty D. Peripheral nerve glycolysis in Wallerian degeneration. Arch Neurol. 1967 Jun;16(6):628–634. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1967.00470240066009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GILLIATT R. W., WILLISON R. G. Peripheral nerve conduction in diabetic neuropathy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1962 Feb;25:11–18. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.25.1.11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HELLER I. H., HESSE S. Action of insulin on the respiration of rat sciatic nerve. Lancet. 1960 Aug 20;2(7147):406–407. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(60)92844-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAWRENCE D. G., LOCKE S. Motor nerve conduction velocity in diabetes. Arch Neurol. 1961 Nov;5:483–489. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1961.00450170021003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Locke S. Axons, Schwann cells, and diabetic neuropathy. Bull N Y Acad Med. 1967 Sep;43(9):784–791. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MULDER D. W., LAMBERT E. H., BASTRON J. A., SPRAGUE R. G. The neuropathies associated with diabetes mellitus. A clinical and electromyographic study of 103 unselected diabetic patients. Neurology. 1961 Apr;11(4):275–284. doi: 10.1212/wnl.11.4.275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruhashi J., Wright E. B. Effect of oxygen lack on the single isolated mammalian (rat) nerve fiber. J Neurophysiol. 1967 May;30(3):434–452. doi: 10.1152/jn.1967.30.3.434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POOLE E. W. Ischaemic and post-ischaemic paraesthesiae; normal responses in the upper limb with special reference to the effect of age. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1956 May;19(2):148–154. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.19.2.148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEINESS I. Vibratory perception in diabetics during arrested blood flow to the limb. Acta Med Scand. 1959 Mar 4;163(3):195–205. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1959.tb10400.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seneviratne K. N., Peiris O. A. The effect of ischaemia on the excitability of human sensory nerve. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1968 Aug;31(4):338–347. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.31.4.338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMAS P. K., SEARS T. A., GILLIATT R. W. The range of conduction velocity in normal motor nerve fibers to the small muscles of the hand and foot. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1959 Aug;22:175–181. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.22.3.175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]