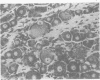
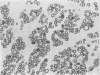
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARNES J. M., DENZ F. A. Experimental demyelination with organo-phosphorus compounds. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1953 Apr;65(2):597–605. doi: 10.1002/path.1700650230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARON R. L., BENNETT D. R., CASIDA J. E. Neurotoxic syndrome produced in chickens by a cyclic phosphate metabolite of tri-o-cresyl phosphate--a clinical and pathological study. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1962 Jun;18:465–474. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1962.tb01168.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAVANAGH J. B., DAVIES D. R., HOLLAND P., LANCASTER M. Comparison of the functional effects of dyflos, tri-o-cresyl phosphate and tri-p-ethylphenyl phosphate in chickens. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1961 Aug;17:21–27. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1961.tb01100.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAVANAGH J. B., PATANGIA G. N. CHANGES IN THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM IN THE CAT AS THE RESULT OF TRI-O-CRESYL PHOSPHATE POISONING. Brain. 1965 Mar;88:165–180. doi: 10.1093/brain/88.1.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAVANAGH J. B. The toxic effects of triortho-cresyl phosphate on the nervous system; an experimental study in hens. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1954 Aug;17(3):163–172. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.17.3.163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIEZEL P. B., QUADBECK G. [Nerve injury caused by p-bromophenylacetylurea]. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Exp Pathol Pharmakol. 1960;238:534–541. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EVERETT G. M., RICHARDS R. K. Pharmacological studies of phenacetylurea (phenurone) an anticonvulsant drug. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1952 Nov;106(3):303–313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FENTON J. C. The nature of the paralysis in chickens following organo-phosphorus poisoning. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1955 Jan-Apr;69(1-2):181–189. doi: 10.1002/path.1700690124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GLASSON B., LERCH P., BENAKIS A. [Distribution and elimination of labeled pheneturide]. Therapie. 1960;15:368–376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAJNO G., KARNOVSKY M. L. A biochemical and morphologic study of myelination and demyelination. III. Effect of an organo-phosphorus compound (Mipafox) on the biosynthesis of lipid by nervous tissue of rats and hens. J Neurochem. 1961 Oct;8:1–16. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1961.tb13521.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SWINYARD E. A., BROWN W. C., GOODMAN L. S. Comparative assays of antiepileptic drugs in mice and rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1952 Nov;106(3):319–330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEAVER L. C., SWINYARD E. A., GOODMAN L. S. Effects of liver injury and nephrectomy on the anticonvulsant activity of phenacemide. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1952 Aug-Sep;80(4):744–746. doi: 10.3181/00379727-80-19749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]