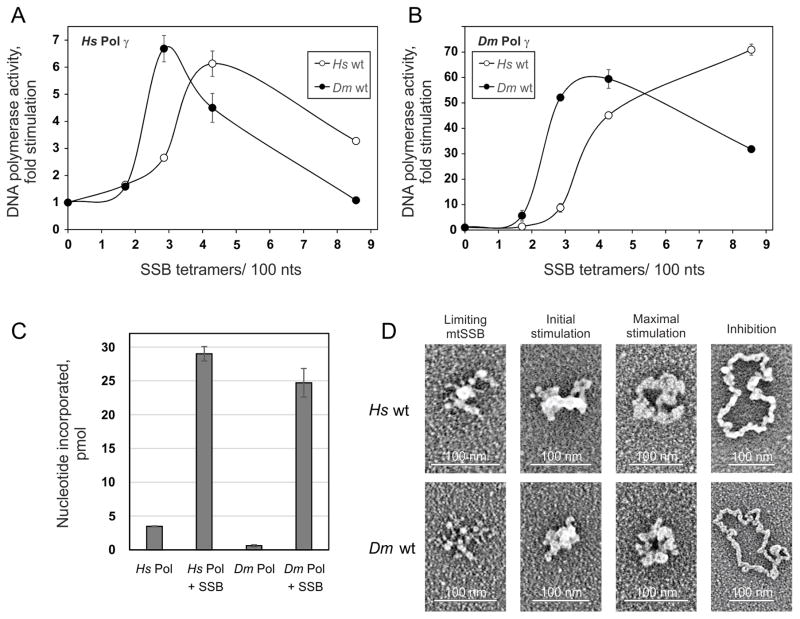
Figure 6.
Stimulation of DNA synthesis catalyzed by Pol γ correlates with specific ssDNA template organization by mtSSB. A and B, DNA polymerase assays were performed using 58.5 fmol of singly primed M13 DNA, 35 fmol of human Pol γ-α, 220 fmol of human Pol γ-β (A) or 40 fmol of D. melanogaster Pol γ (as Pol γ-α) (B), and 0, 6.4, 10.7, 16, or 32 pmol of either human (open circles) or D. melanogaster (closed circles) wild-type mtSSB. Assays were performed at 30 mM KCl and 4 mM MgCl2. The data were normalized to the amount of nucleotide incorporated by human Pol γ in the absence of mtSSB (arbitrarily set to 1 in each case). C, Comparison of nucleotide incorporation by human and D. melanogaster Pol γ in the absence or presence of their cognate mtSSBs at the concentrations resulting in maximal stimulation. D, electron microscopy of human (top) and D. melanogaster (bottom) wild-type mtSSB proteins bound to M13 DNA. The binding reaction was performed at 30 mM KCl and 4 mM MgCl2. The images are representative of template species formed at the following ratios of mtSSB tetramers per 100 nucleotides, which correspond to the indicated individual phases of the stimulation of human Pol γ activity: limiting mtSSB, 1.6 human and 1.2 D. melanogaster mtSSB; initial stimulation, 3.2 human and 1.8 D. melanogaster mtSSB; maximal stimulation, 3.8 human and 2.5 D. melanogaster mtSSB; inhibition, 6.4 human and 7 D. melanogaster mtSSB. Reproduced with permission from “G.L. Ciesielski, O. Bermek, F.A. Rosado-Ruiz, S.L. Hovde, O.J. Neitzke, J.D. Griffith, L.S. Kaguni: Mitochondrial single-stranded DNA-binding proteins stimulate the activity of DNA polymerase γ by organization of the template DNA. Journal of Biological Chemistry (2015) 290, 28697–28707”.