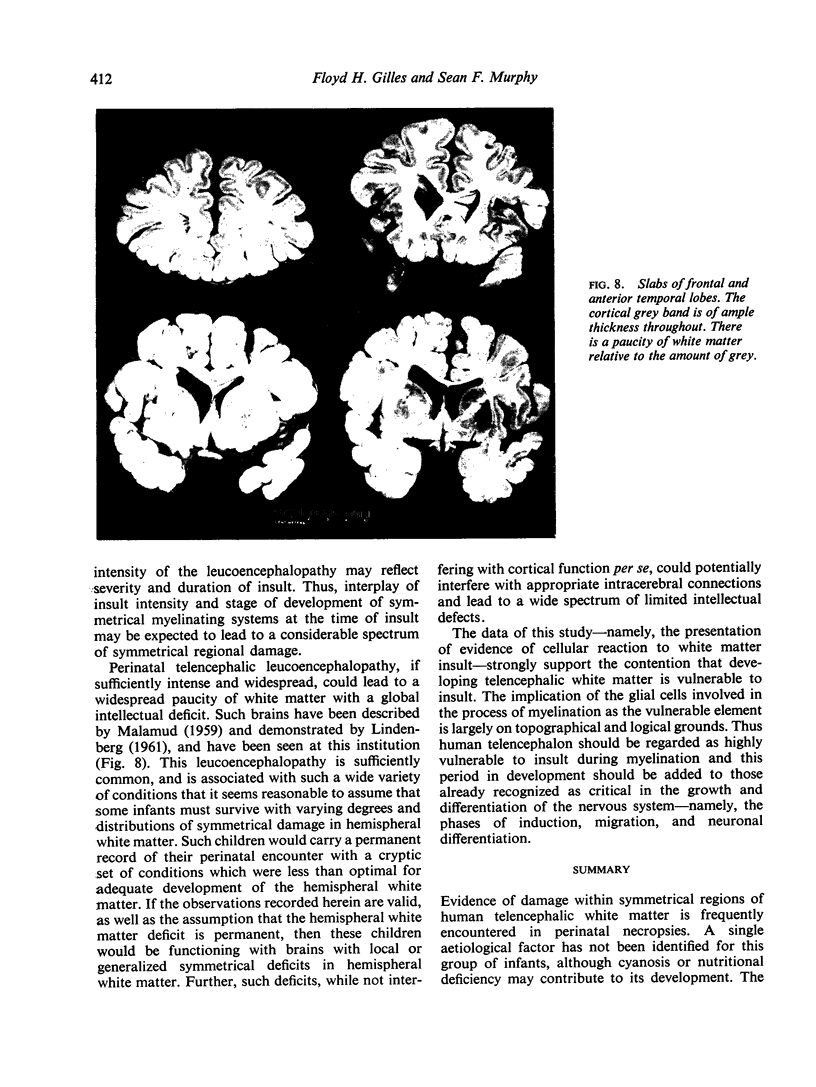
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- APGAR V., GIRDANY B. R., McINTOSH R., TAYLOR H. C., Jr Neonatal anoxia. I. A study of the relation of oxygenation at birth to intellectual development. Pediatrics. 1955 Jun;15(6):653–662. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BANKER B. Q., LARROCHE J. C. Periventricular leukomalacia of infancy. A form of neonatal anoxic encephalopathy. Arch Neurol. 1962 Nov;7:386–410. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1962.04210050022004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown R. E. Decreased brain weight in malnutrition and its implications. East Afr Med J. 1965 Nov;42(11):584–595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAMPBELL W. A. B., CHEESEMAN E. A., KILPATRICK A. W. The effects of neonatal asphyxia on physical and mental development. Arch Dis Child. 1950 Dec;25(124):351–359. doi: 10.1136/adc.25.124.351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison A. N., Dobbing J. Myelination as a vulnerable period in brain development. Br Med Bull. 1966 Jan;22(1):40–44. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a070434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobbing J., Widdowson E. M. The effect of undernutrition and subsequent rehabilitation on myelination of rat brain as measured by its composition. Brain. 1965 Jun;88(2):357–366. doi: 10.1093/brain/88.2.357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRAHAM F. K., CALDWELL B. M., ERNHART C. B., PENNOYER M. M., HARTMANN A. F. Anoxia as a significant perinatal experience: a critique. J Pediatr. 1957 May;50(5):556–569. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(57)80220-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRUENWALD P. CHRONIC FETAL DISTRESS AND PLACENTAL INSUFFICIENCY. Biol Neonat. 1963;5:215–265. doi: 10.1159/000239870. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HICKS S. P. Developmental brain metabolism; effects of cortisone, anoxia fluoroacetate, radiation, insulin, and other inhibitors on the embryo, newborn, and adult. AMA Arch Pathol. 1953 Apr;55(4):302–327. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JAMES L. S., ROWE R. D. The pattern of response of pulmonary and systemic arterial pressures in newborn and older infants to short periods of hypoxia. J Pediatr. 1957 Jul;51(1):5–11. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(57)80274-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JAMES L. S., WEISBROT I. M., PRINCE C. E., HOLADAY D. A., APGAR V. The acid-base status of human infants in relation to birth asphyxia and the onset of respiration. J Pediatr. 1958 Apr;52(4):379–394. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(58)80058-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MALAMUD N. Sequelae of perinatal trauma. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1959 Jan;18(1):141–155. doi: 10.1097/00005072-195901000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOTT J. C. The ability of young mammals to withstand total oxygen lack. Br Med Bull. 1961 May;17:144–148. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a069889. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mickel H. S., Gilles F. H. Changes in glial cells during myelinogenesis. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1968 Jan;27(1):146–147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NORMAN R. M., URICH H., MCMENEMEY W. H. Vascular mechanisms of birth injury. Brain. 1957 Mar;80(1):49–58. doi: 10.1093/brain/80.1.49. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RANCK J. B., Jr, WINDLE W. F. Brain damage in the monkey, macaca mulatta, by asphyxia neonatorum. Exp Neurol. 1959 Jun;1(2):130–154. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(59)90032-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young M. Responses of the systemic circulation of the new-born infant. Br Med Bull. 1966 Jan;22(1):70–72. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a070441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]