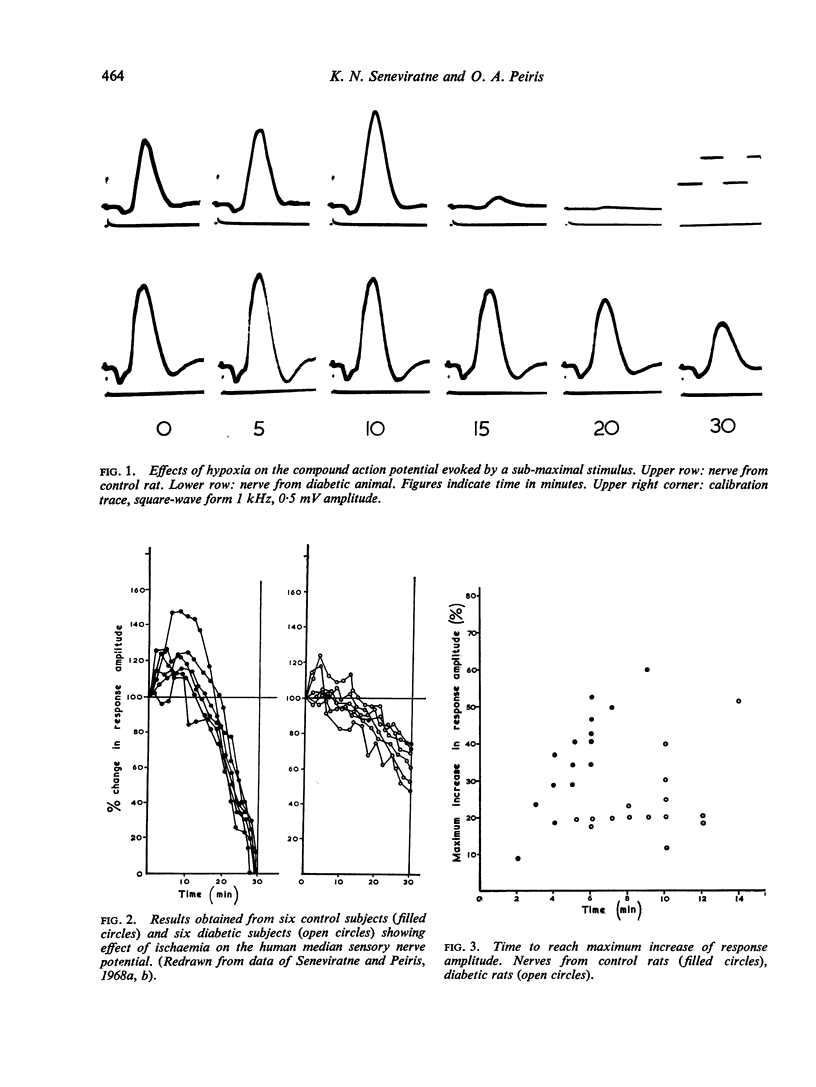
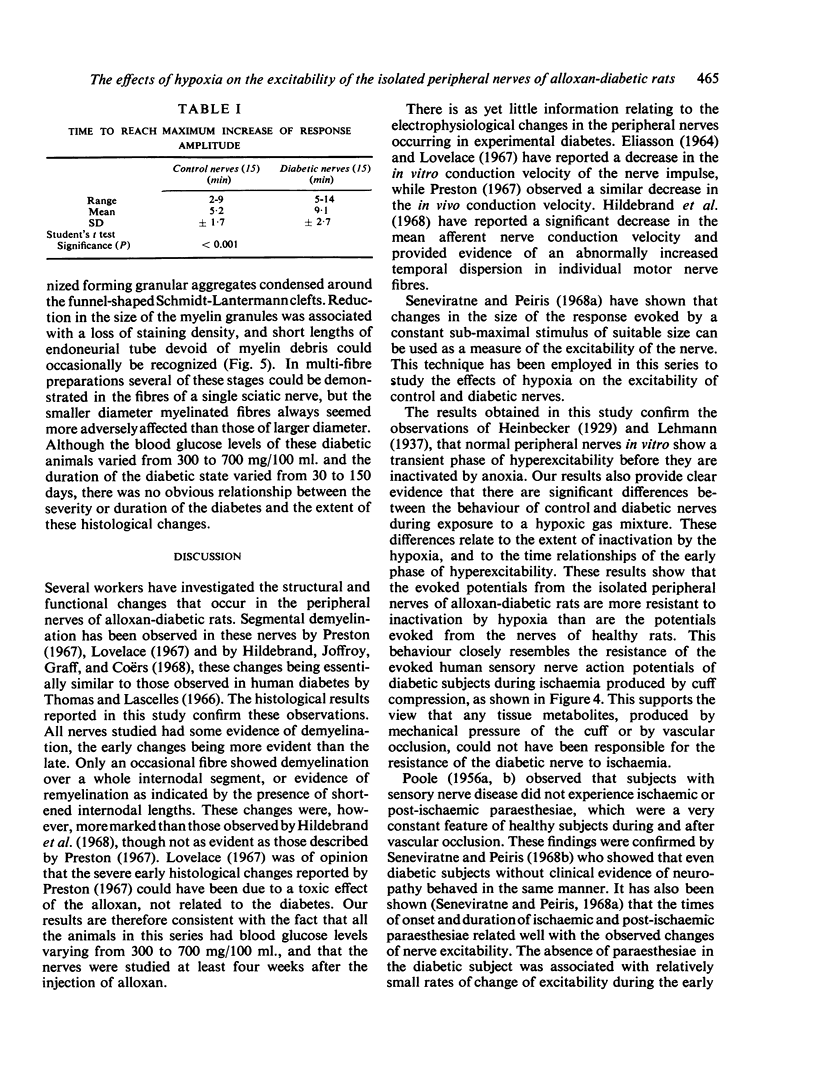
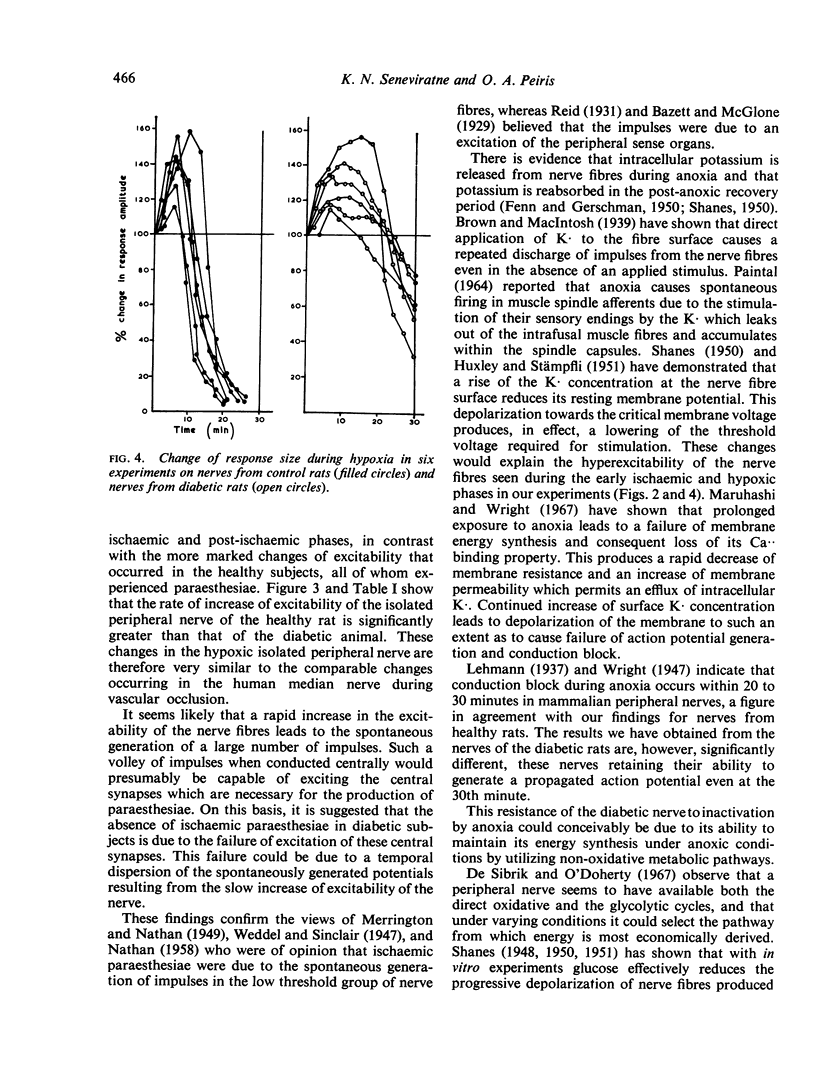
Full text
PDF

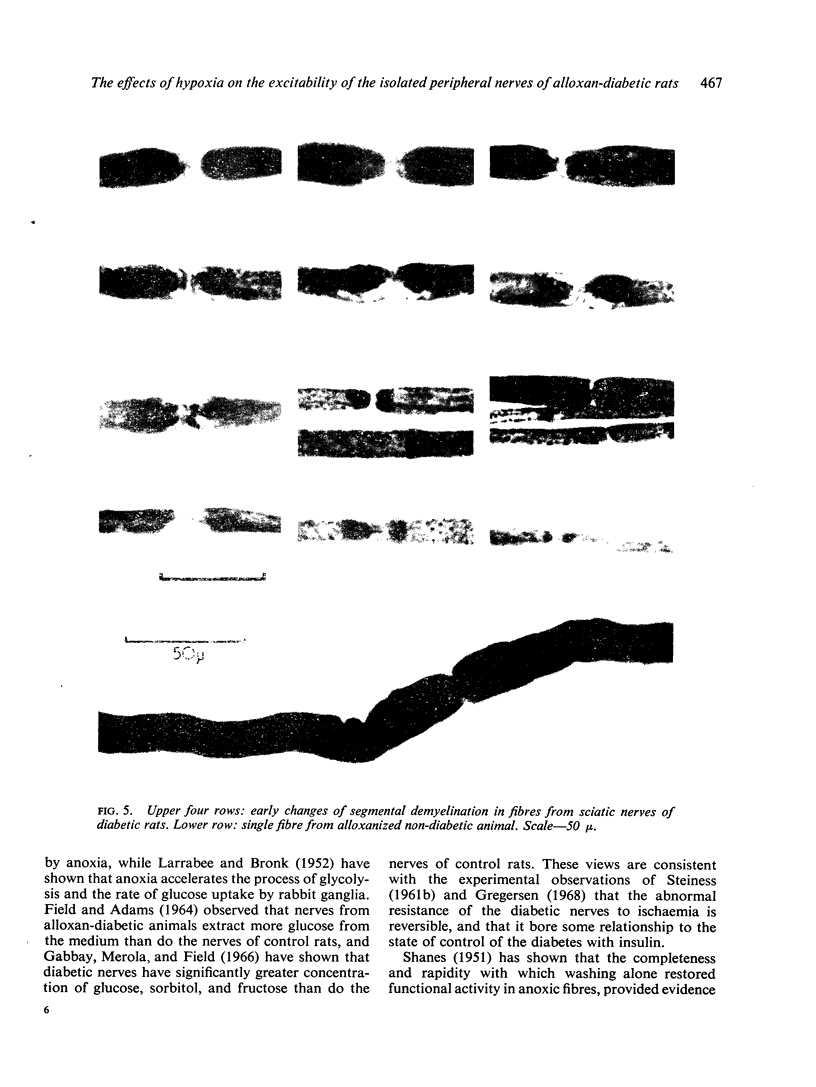


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bischoff A. Diabetic neuropathy. Morbid anatomy, patho-physiology and pathogenesis based on electron-microscopic findings. Ger Med Mon. 1968 May;13(5):214–passim. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAUSEY G., PALMER E. The epineural sheath of a nerve as a barrier to the diffusion of phosphate ions. J Anat. 1953 Jan;87(1):30–36. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRESCITELLI F. Nerve sheath as a barrier to the action of certain substances. Am J Physiol. 1951 Aug;166(2):229–240. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1951.166.2.229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castaigne P., Cathala H. P., Dry J., Mastropaolo C. Les réponses der nerfs et des muscles à des stimulations électriques AU COURS D'une epreuve de garrot ischémique chez l'homme normal et chez le diabétique. Rev Neurol (Paris) 1966 Jul;115(1):61–66. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAINTY J., KRNJEVIC K. The rate of exchange of 24Na in cat nerves. J Physiol. 1955 Jun 28;128(3):489–503. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1955.sp005320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeSibrik I., O'Doherty D. Peripheral nerve glycolysis in Wallerian degeneration. Arch Neurol. 1967 Jun;16(6):628–634. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1967.00470240066009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELIASSON S. G. NERVE CONDUCTION CHANGES IN EXPERIMENTAL DIABETES. J Clin Invest. 1964 Dec;43:2353–2358. doi: 10.1172/JCI105109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FENG T. P., LIU Y. M. The connective tissue sheath of the nerve as effective diffusion barrier. J Cell Physiol. 1949 Aug;34(1):1–16. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1030340102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FENN W. O., GERSCHMAN R. The loss of potassium from frog nerves in anoxia and other conditions. J Gen Physiol. 1950 Jan 20;33(3):195–203. doi: 10.1085/jgp.33.3.195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FIELD R. A., ADAMS L. C. INSULIN RESPONSE OF PERIPHERAL NERVE. I. EFFECTS ON GLUCOSE METABOLISM AND PERMEABILITY. Medicine (Baltimore) 1964 May;43:275–279. doi: 10.1097/00005792-196405000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GAMBLE H. J. COMPARATIVE ELECTRON-MICROSCOPIC OBSERVATIONS ON THE CONNECTIVE TISSUES OF A PERIPHERAL NERVE AND A SPINAL NERVE ROOT IN THE RAT. J Anat. 1964 Jan;98:17–26. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabbay K. H., Merola L. O., Field R. A. Sorbitol pathway: presence in nerve and cord with substrate accumulation in diabetes. Science. 1966 Jan 14;151(3707):209–210. doi: 10.1126/science.151.3707.209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregersen G. A study of the peripheral nerves in diabetic subjects during ischaemia. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1968 Apr;31(2):175–181. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.31.2.175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUXLEY A. F., STAMPFLI R. Effect of potassium and sodium on resting and action potentials of single myelinated nerve fibers. J Physiol. 1951 Feb;112(3-4):496–508. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1951.sp004546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haftek J., Thomas P. K. Electron-microscope observations on the effects of localized crush injuries on the connective tissues of peripheral nerve. J Anat. 1968 Sep;103(Pt 2):233–243. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hildebrand J., Joffroy A., Graff G., Coërs C. Neuromuscular changes with alloxan hyperglycemia. Electrophysiological, biochemical, and histological study in rats. Arch Neurol. 1968 Jun;18(6):633–641. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1968.00470360055005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KLEBANOFF S. J., GREENBAUM A. L. The effect of pH on the diabetogenic action of alloxan. J Endocrinol. 1954 Nov;11(4):314–322. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0110314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRNJEVIC K. The connective tissue of the frog sciatic nerve. Q J Exp Physiol Cogn Med Sci. 1954;39(1):55–72. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1954.sp001048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LARRABEE M. G., BRONK D. W. [Metabolic requirements of sympathetic neurons]. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1952;17:245–266. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1952.017.01.023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruhashi J., Wright E. B. Effect of oxygen lack on the single isolated mammalian (rat) nerve fiber. J Neurophysiol. 1967 May;30(3):434–452. doi: 10.1152/jn.1967.30.3.434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NATHAN P. W. Ischaemic and post-ischaemic numbness and paraesthesiae. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1958 Feb;21(1):12–23. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.21.1.12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAINTAL A. S. EFFECTS OF DRUGS ON VERTEBRATE MECHANORECEPTORS. Pharmacol Rev. 1964 Dec;16:341–380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POOLE E. W. Ischaemic and post-ischaemic paraesthesiae; normal responses in the upper limb with special reference to the effect of age. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1956 May;19(2):148–154. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.19.2.148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston G. M. Peripheral neuropathy in the alloxan-diabetic rat. J Physiol. 1967 Apr;189(2):49P–50P. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RASHBASS C., RUSHTON W. A. H. The relation of structure to the spread of excitation in the frog's sciatic trunk. J Physiol. 1949 Dec 15;110(1-2):110–135. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1949.sp004426. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEINESS I. Vibratory perception in diabetics during arrested blood flow to the limb. Acta Med Scand. 1959 Mar 4;163(3):195–205. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1959.tb10400.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seneviratne K. N., Peiris O. A. The effect of ischaemia on the excitability of human sensory nerve. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1968 Aug;31(4):338–347. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.31.4.338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMAS P. K. The connective tissue of peripheral nerve: an electron microscope study. J Anat. 1963 Jan;97:35–44. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMAS P. K., YOUNG J. Z. Internode lengths in the nerves of fishes. J Anat. 1949 Oct;83(4):336-50, pl. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WRIGHT E. B., OOYAMA H. Role of cations, potassium, calcium, and sodium during excitation of frog single nerve fiber. J Neurophysiol. 1962 Jan;25:94–109. doi: 10.1152/jn.1962.25.1.94. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]