Abstract
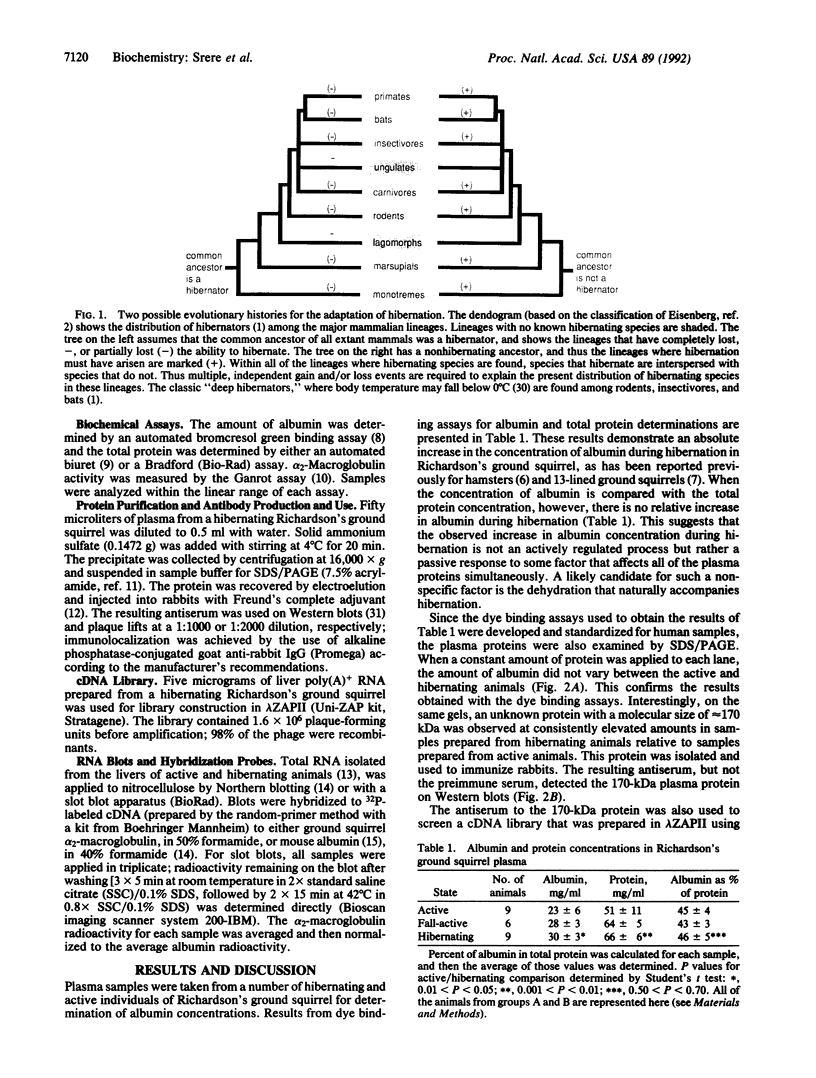
Mammalian hibernators experience dramatic reductions in body temperature, metabolic rate, respiratory rate, and heart rate during hibernation. These changes are precisely controlled and reversible with only internally driven mechanisms, suggesting specific biochemical regulation. We present a model that integrates our observations of differential liver gene expression during preparation for, and maintenance of, the hibernating state, with the known phylogenetic interspersion of hibernating species in several major mammalian lineages. This model predicts a major role for the differential expression of existing mammalian genes in the biochemical regulation of hibernation.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abbotts B., Wang L. C., Glass J. D. Absence of evidence for a hibernation "trigger" in blood dialyzate of Richardson's ground squirrel. Cryobiology. 1979 Apr;16(2):179–183. doi: 10.1016/0011-2240(79)90029-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnes B. M. Freeze avoidance in a mammal: body temperatures below 0 degree C in an Arctic hibernator. Science. 1989 Jun 30;244(4912):1593–1595. doi: 10.1126/science.2740905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corcoran R. M., Durnan S. M. Albumin determination by a modified bromcresol green method. Clin Chem. 1977;23(4):765–766. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawe A. R., Spurrier W. A. Hibernation induced in ground squirrels by blood transfusion. Science. 1969 Jan 17;163(3864):298–299. doi: 10.1126/science.163.3864.298. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doumas B. T., Bayse D. D., Carter R. J., Peters T., Jr, Schaffer R. A candidate reference method for determination of total protein in serum. I. Development and validation. Clin Chem. 1981 Oct;27(10):1642–1650. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fang X. M., Wu C. Y., Brennan M. D. Complexity in evolved regulatory variation for alcohol dehydrogenase genes in Hawaiian Drosophila. J Mol Evol. 1991 Mar;32(3):220–226. doi: 10.1007/BF02342744. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galster W. A., Morrison P. Seasonal changes in serum lipids and proteins in the 13-lined ground squirrel. Comp Biochem Physiol. 1966 Jul;18(3):489–501. doi: 10.1016/0010-406x(66)90233-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganrot P. O. Determination of alpha-2-macroglobulin as trypsin-protein esterase. Clin Chim Acta. 1966 Oct;14(4):493–501. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(66)90037-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gehring M. R., Shiels B. R., Northemann W., de Bruijn M. H., Kan C. C., Chain A. C., Noonan D. J., Fey G. H. Sequence of rat liver alpha 2-macroglobulin and acute phase control of its messenger RNA. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 5;262(1):446–454. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammer M. F., Schilling J. W., Prager E. M., Wilson A. C. Recruitment of lysozyme as a major enzyme in the mouse gut: duplication, divergence, and regulatory evolution. J Mol Evol. 1987;24(3):272–279. doi: 10.1007/BF02111240. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kan C. C., Solomon E., Belt K. T., Chain A. C., Hiorns L. R., Fey G. Nucleotide sequence of cDNA encoding human alpha 2-macroglobulin and assignment of the chromosomal locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(8):2282–2286. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.8.2282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kioussis D., Eiferman F., van de Rijn P., Gorin M. B., Ingram R. S., Tilghman S. M. The evolution of alpha-fetoprotein and albumin. II. The structures of the alpha-fetoprotein and albumin genes in the mouse. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 25;256(4):1960–1967. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
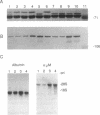
- Kondo N., Kondo J. Identification of novel blood proteins specific for mammalian hibernation. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 5;267(1):473–478. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurlandzka A., Rosenzweig R. F., Adams J. Identification of adaptive changes in an evolving population of Escherichia coli: the role of changes with regulatory and highly pleiotropic effects. Mol Biol Evol. 1991 May;8(3):261–281. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040650. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meijers J. C., Tijburg P. N., Bouma B. N. Inhibition of human blood coagulation factor Xa by alpha 2-macroglobulin. Biochemistry. 1987 Sep 8;26(18):5932–5937. doi: 10.1021/bi00392a053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Northemann W., Heisig M., Kunz D., Heinrich P. C. Molecular cloning of cDNA sequences for rat alpha 2-macroglobulin and measurement of its transcription during experimental inflammation. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 25;260(10):6200–6205. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson W. R., Lipman D. J. Improved tools for biological sequence comparison. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2444–2448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SOUTH F. E., 2nd, JEFFAY H. Alterations in serum proteins of hibernating hamsters. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1958 Aug-Sep;98(4):885–887. doi: 10.3181/00379727-98-24217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber G., Tsykin A., Aldred A. R., Thomas T., Fung W. P., Dickson P. W., Cole T., Birch H., De Jong F. A., Milland J. The acute phase response in the rodent. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1989;557:61–86. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1989.tb24000.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson K. W., Irwin D. M., Wilson A. C. Stomach lysozyme gene of the langur monkey: tests for convergence and positive selection. J Mol Evol. 1991 Nov;33(5):418–425. doi: 10.1007/BF02103133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang L. C., Belke D., Jourdan M. L., Lee T. F., Westly J., Nurnberger F. The "hibernation induction trigger": specificity and validity of bioassay using the 13-lined ground squirrel. Cryobiology. 1988 Aug;25(4):355–362. doi: 10.1016/0011-2240(88)90043-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson A. C., Carlson S. S., White T. J. Biochemical evolution. Annu Rev Biochem. 1977;46:573–639. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.46.070177.003041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]