Abstract
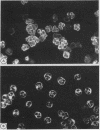
To differentiate between perinuclear immunofluorescence staining of antinuclear antibody (ANA) and the perinuclear form of anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody (P-ANCA), the pattern after formaldehyde vapour fixation of normal human neutrophils was compared with that of standard ethanol fixation. Fifteen out of 17 myeloperoxidase antibody positive sera showed cytoplasmic staining on formaldehyde vapour fixed cells; 30 of the 32 ANA positive samples became negative or gave weak nuclear staining on the same substrate. Formaldehyde vapour fixation is a simple, useful technique for differentiating between ANA and P-ANCA.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Falk R. J., Jennette J. C. Anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibodies with specificity for myeloperoxidase in patients with systemic vasculitis and idiopathic necrotizing and crescentic glomerulonephritis. N Engl J Med. 1988 Jun 23;318(25):1651–1657. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198806233182504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiik A. Delineation of a standard procedure for indirect immunofluorescence detection of ANCA. APMIS Suppl. 1989;6:12–13. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiik A. Granulocyte-specific antinuclear antibodies. Possible significance for the pathogenesis, clinical features and diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis. Allergy. 1980 Jun;35(4):263–289. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.1980.tb01768.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Woude F. J., Daha M. R., van Es L. A. The current status of neutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies. Clin Exp Immunol. 1989 Nov;78(2):143–148. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]