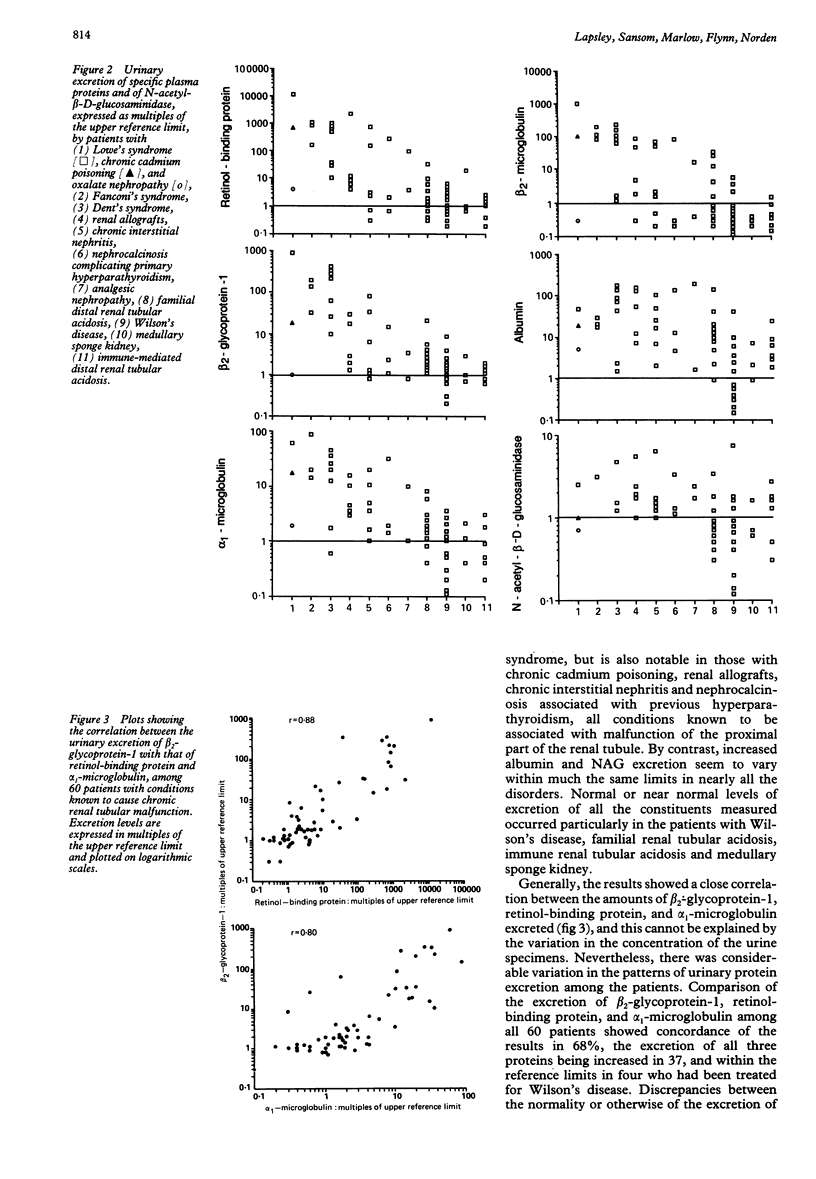
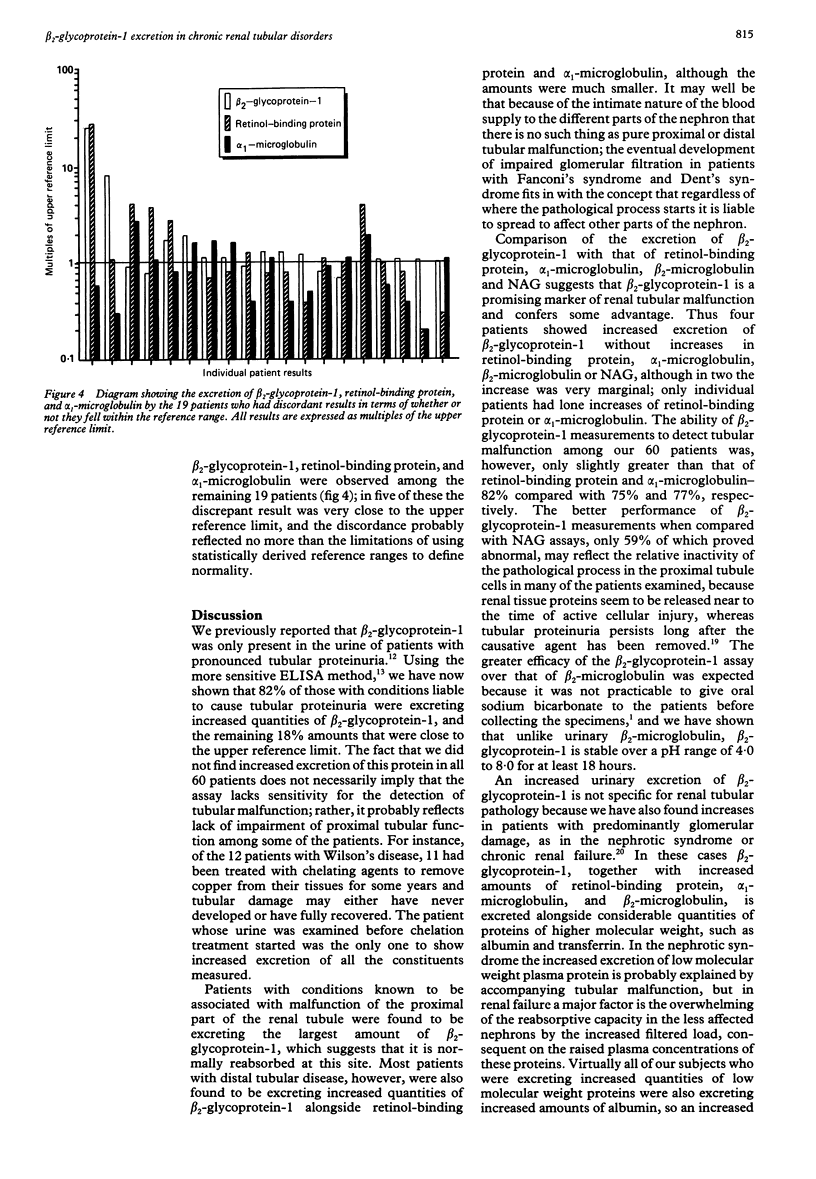
Abstract
Urinary beta 2-glycoprotein-1 was measured in 60 patients with conditions recognised as causing renal tubular impairment and compared with established markers of early tubular malfunction. Increased beta 2-glycoprotein-1 excretion was found in 49 (82%) of the subjects; raised excretion of alpha 1-microglobulin, retinol-binding protein, and beta 2-microglobulin was found in 46 (77%), 45 (75%), and 31 (52%), respectively, and increased urinary N-acetyl-beta-D-glucosaminidase activity in 32 of 54 of the subjects (59%). The increase was particularly pronounced in those with proximal tubule malfunction, although considerable variation occurred. beta 2-glycoprotein-1 was shown to be stable in urine over the physiological pH range, and it is concluded that its measurement provides a means of detecting chronic malfunction of the renal tubules that is marginally more sensitive than assays of alpha 1-microglobulin or retinol-binding protein, and more reliable than assays of beta 2-microglobulin or N-acetyl-beta-D-glucosaminidase.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bernard A. M., Lauwerys R. R. Retinol binding protein in urine: a more practical index than urinary beta 2-microglobulin for the routine screening of renal tubular function. Clin Chem. 1981 Oct;27(10):1781–1782. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernard A. M., Vyskocil A. A., Mahieu P., Lauwerys R. R. Assessment of urinary retinol-binding protein as an index of proximal tubular injury. Clin Chem. 1987 Jun;33(6):775–779. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernard A., Vyskocyl A., Mahieu P., Lauwerys R. Effect of renal insufficiency on the concentration of free retinol-binding protein in urine and serum. Clin Chim Acta. 1988 Jan 15;171(1):85–93. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(88)90293-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumsohn A., Morris B. W., Griffiths H., Ramsey C. F. Stability of beta 2-microglobulin and retinol binding protein at different values of pH and temperature in normal and pathological urine. Clin Chim Acta. 1991 Jan 15;195(3):133–137. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(91)90133-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davey P. G., Gosling P. beta 2-Microglobulin instability in pathological urine. Clin Chem. 1982 Jun;28(6):1330–1333. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donaldson M. D., Chambers R. E., Woolridge M. W., Whicher J. T. Stability of alpha 1-microglobulin, beta 2-microglobulin and retinol binding protein in urine. Clin Chim Acta. 1989 Jan 13;179(1):73–77. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(89)90024-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evrin P. E., Wibell L. The serum levels and urinary excretion of 2 -microglobulin in apparently healthy subjects. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1972 Feb;29(1):69–74. doi: 10.3109/00365517209081057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flynn F. V. Assessment of renal function: selected developments. Clin Biochem. 1990 Feb;23(1):49–54. doi: 10.1016/0009-9120(90)90435-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lozier J., Takahashi N., Putnam F. W. Complete amino acid sequence of human plasma beta 2-glycoprotein I. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(12):3640–3644. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.12.3640. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mutti A. Detection of renal diseases in humans: developing markers and methods. Toxicol Lett. 1989 Mar;46(1-3):177–191. doi: 10.1016/0378-4274(89)90126-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakaya Y., Schaefer E. J., Brewer H. B., Jr Activation of human post heparin lipoprotein lipase by apolipoprotein H (beta 2-glycoprotein I). Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Aug 14;95(3):1168–1172. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)91595-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norden A. G., Flynn F. V. Degradation of beta 2-microglobulin in infected urine by leukocyte elastase-like activity. Clin Chim Acta. 1983 Oct 31;134(1-2):167–176. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(83)90194-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norden A. G., Fulcher L. M., Lapsley M., Flynn F. V. Excretion of beta 2-glycoprotein I (apolipoprotein H) in renal tubular disease. Clin Chem. 1991 Jan;37(1):74–77. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polz E., Kostner G. M. The binding of beta 2-glycoprotein-I to human serum lipoproteins: distribution among density fractions. FEBS Lett. 1979 Jun 1;102(1):183–186. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80955-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sansom P. A., Marlow C. T., Lapsley M., Flynn F. V. A sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for beta 2-glycoprotein I. Ann Clin Biochem. 1991 May;28(Pt 3):283–289. doi: 10.1177/000456329102800315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schardijn G. H., Statius van Eps L. W. Beta 2-microglobulin: its significance in the evaluation of renal function. Kidney Int. 1987 Nov;32(5):635–641. doi: 10.1038/ki.1987.255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schousboe I., Rasmussen M. S. The effect of beta 2-glycoprotein I on the dextran sulfate and sulfatide activation of the contact system (Hageman factor system) in the blood coagulation. Int J Biochem. 1988;20(8):787–792. doi: 10.1016/0020-711x(88)90065-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Topping M. D., Forster H. W., Dolman C., Luczynska C. M., Bernard A. M. Measurement of urinary retinol-binding protein by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay, and its application to detection of tubular proteinuria. Clin Chem. 1986 Oct;32(10):1863–1866. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waller K. V., Ward K. M., Mahan J. D., Wismatt D. K. Current concepts in proteinuria. Clin Chem. 1989 May;35(5):755–765. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu H., Yanagisawa Y., Forbes M. A., Cooper E. H., Crockson R. A., MacLennan I. C. Alpha-1-microglobulin: an indicator protein for renal tubular function. J Clin Pathol. 1983 Mar;36(3):253–259. doi: 10.1136/jcp.36.3.253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuen C. T., Kind P. R., Price R. G., Praill P. F., Richardson A. C. Colorimetric assay for N-acetyl-beta-D-glucosaminidase (NAG) in pathological urine using the omega-nitrostyryl substrate: the development of a kit and the comparison of manual procedure with the automated fluorimetric method. Ann Clin Biochem. 1984 Jul;21(Pt 4):295–300. doi: 10.1177/000456328402100411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


