The authors of “The alternate AP-1 adaptor subunit Apm2 interacts with the Mil1 regulatory protein and confers differential cargo sorting” (Mol. Biol. Cell [2016] 27, 588–598; originally published in MBoC In Press as 10.1091/mbc.E15-09-0621) wish to make a correction to Figure 4G of the article. In the original HTML and PDF versions, the bottom (horizontal) label incorrectly read “apm2∆.” This label has been changed to “mil1∆” in the corrected figure below.
The HTML and PDF versions were corrected on the Molecular Biology of the Cell website on July 5, 2016. These corrections may not appear on copies of the article that reside on other websites.
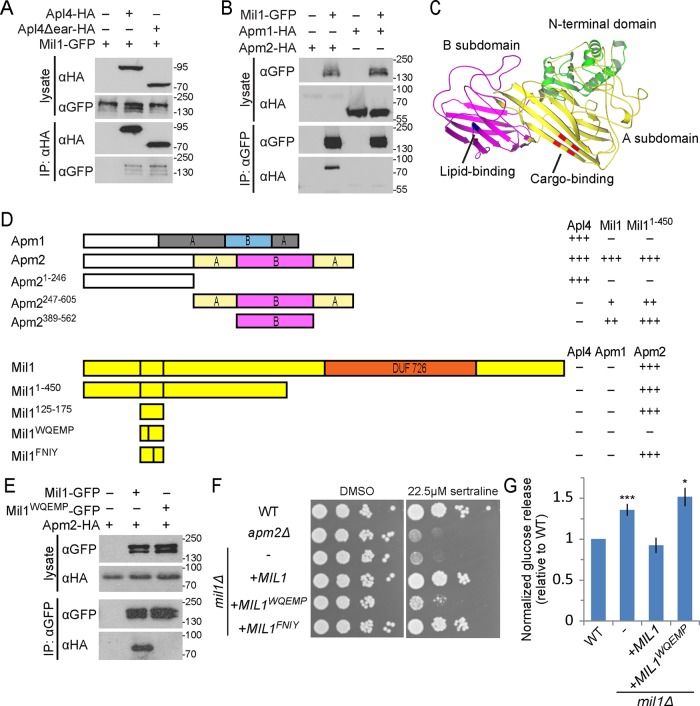
FIGURE 4:
Mil1 interacts with Apm2 through its WQEMP motif. (A) Mil1-GFP copurified with immunoprecipitated Apl4-3HA and with a truncated version lacking the γ appendage (Apl4Δear-HA) known to bind several AP-regulatory proteins. Loading of lysate relative to immunoprecipitate was 1:9. All proteins were genomically tagged. (B) Pull down of Mil1-GFP in strains coexpressing either Apm1-3HA or Apm2-3HA shows that Mil1 binds specifically to Apm2. All proteins were genomically tagged. (C) Phyre2 homology model of Apm2, colored to indicate the N-terminal AP-binding domain (green) and a C-terminal region composed of A (yellow) and B (magenta) subdomains. Key residues predicted to be involved in YxxΦ binding (red) or lipid binding (blue) based on alignment with regions of AP-1 and AP-2 μ subunits are indicated. (D) Yeast two-hybrid mapping of Apm2-Mil1–binding domains. Full-length or truncated Apm2 constructs were fused to the GAL4 DNA-binding domain (GBD), and full-length, truncated, or mutated Mil1 constructs were fused to the GAL4-activating domain (GAD). Qualitative interaction strengths are indicated. Mil1WQEMP represents the W143QEMP>AAEAA mutant, and Mil1FNIY represents the F152NIY>ANAA mutant. (E) Anti-GFP immunoprecipitation of plasmid-expressed wild-type Mil1-GFP or Mil1WQEMP-GFP from strains coexpressing genomically tagged Apm2-3HA. (F) Sertraline sensitivity was assessed by plating strains in a 10× dilution series on YPD containing 22.5 μM sertraline or DMSO as a control. (G) The mil1WQEMP mutant is unable to restore sorting of the Snc1 reporter GSS. Cell-surface GSS levels in the indicated strains were determined by quantifying invertase activity and normalizing to levels in wild-type cells. Unpaired t test compared with wild type, ***p < 0.0001 and *p < 0.05. Error bars represent SEM (n = 10).