Abstract
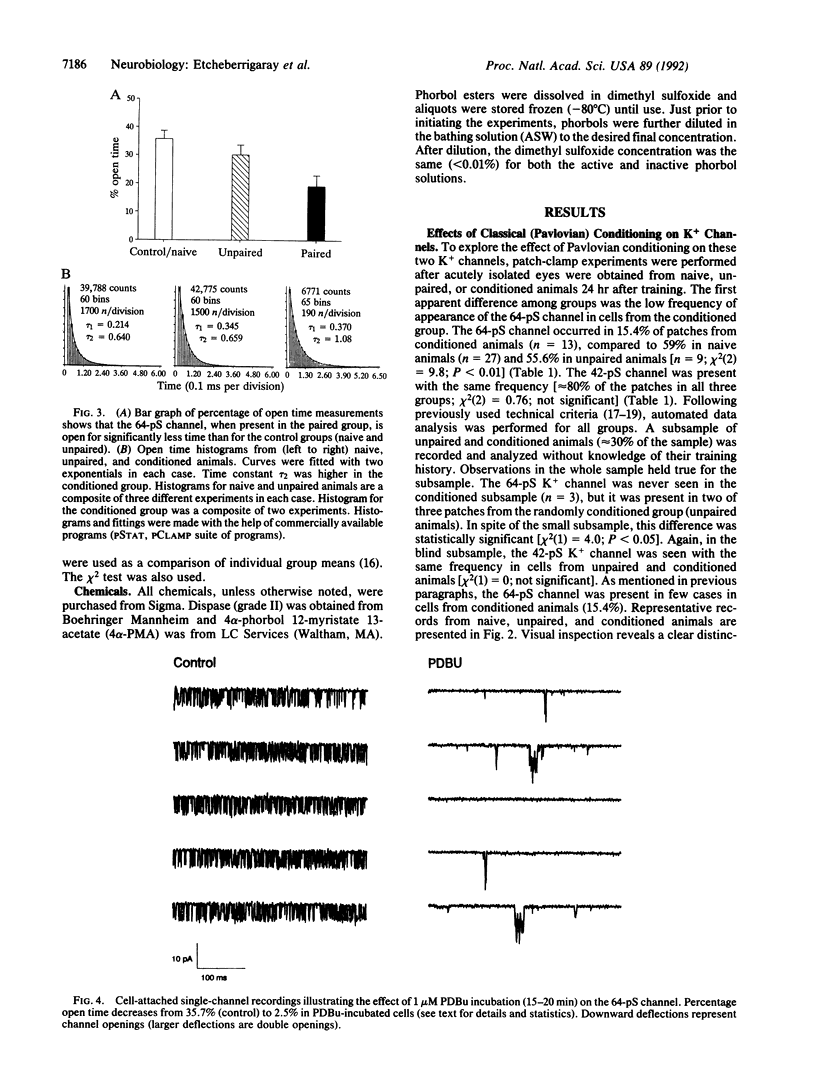
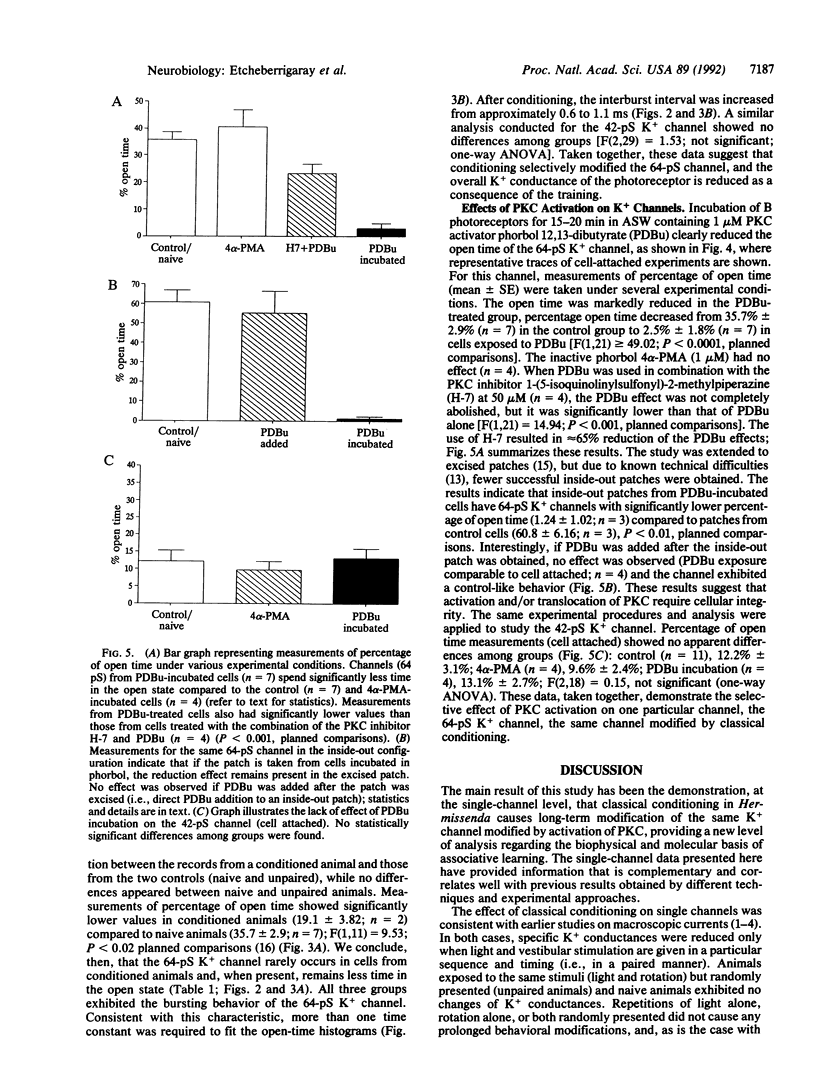
The patch-clamp technique was used to study the effects of classical conditioning and protein kinase C (PKC) activation on K+ channels of identified neurons in the snail Hermissenda crassicornis. Here we present evidence that classical conditioning and PKC activation similarly modify the same K+ channel. K+ channels were recorded in cells from animals with different training experience. The 64-pS K+ channel appeared with significantly lower frequency in the conditioned group compared to the frequencies in control animals (naive and unpaired). In addition, when present, the 64-pS channel exhibited a lower percentage of open time and an increased interval between opening bursts in cells from conditioned animals. The 42-pS K+ channel was observed with about the same frequency in all three groups, and its percentage of open time was invariant, regardless of the animal's experience. Incubation of the photoreceptor with the PKC activator phorbol 12,13-dibutyrate (PDBu) led to a profound decrease in the percentage of open time of the 64-pS K+ channel, from 35.7% in the control group to 2.5% in the PDBu-treated group. The inactive phorbol 4 alpha-phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate had no effect. The use of the PKC inhibitor H-7 significantly blocked the phorbol effect. Inside-out patches obtained from phorbol preincubated cells likewise showed the same effect of PDBu on K+ channels, but the effect was not observed when phorbol was added after the cell-free patches were obtained from nontreated cells. By contrast, the percentage of open time of the 42-pS K+ channel remained unchanged after phorbol treatment.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alkon D. L. Calcium-mediated reduction of ionic currents: a biophysical memory trace. Science. 1984 Nov 30;226(4678):1037–1045. doi: 10.1126/science.6093258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alkon D. L. Changes of membrane currents during learning. J Exp Biol. 1984 Sep;112:95–112. doi: 10.1242/jeb.112.1.95. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alkon D. L., Lederhendler I., Shoukimas J. J. Primary changes of membrane currents during retention of associative learning. Science. 1982 Feb 5;215(4533):693–695. doi: 10.1126/science.7058334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alkon D. L., Naito S., Kubota M., Chen C., Bank B., Smallwood J., Gallant P., Rasmussen H. Regulation of Hermissenda K+ channels by cytoplasmic and membrane-associated C-kinase. J Neurochem. 1988 Sep;51(3):903–917. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1988.tb01827.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alkon D. L., Sakakibara M., Forman R., Harrigan J., Lederhendler I., Farley J. Reduction of two voltage-dependent K+ currents mediates retention of a learned association. Behav Neural Biol. 1985 Sep;44(2):278–300. doi: 10.1016/s0163-1047(85)90296-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baraban J. M., Snyder S. H., Alger B. E. Protein kinase C regulates ionic conductance in hippocampal pyramidal neurons: electrophysiological effects of phorbol esters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(8):2538–2542. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.8.2538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collin C., Ikeno H., Harrigan J. F., Lederhendler I., Alkon D. L. Sequential modification of membrane currents with classical conditioning. Biophys J. 1988 Nov;54(5):955–960. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(88)83031-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulter D. A., Lo Turco J. J., Kubota M., Disterhoft J. F., Moore J. W., Alkon D. L. Classical conditioning reduces amplitude and duration of calcium-dependent afterhyperpolarization in rabbit hippocampal pyramidal cells. J Neurophysiol. 1989 May;61(5):971–981. doi: 10.1152/jn.1989.61.5.971. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doerner D., Abdel-Latif M., Rogers T. B., Alger B. E. Protein kinase C-dependent and -independent effects of phorbol esters on hippocampal calcium channel current. J Neurosci. 1990 May;10(5):1699–1706. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.10-05-01699.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doerner D., Pitler T. A., Alger B. E. Protein kinase C activators block specific calcium and potassium current components in isolated hippocampal neurons. J Neurosci. 1988 Nov;8(11):4069–4078. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.08-11-04069.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etcheberrigaray R., Huddie P. L., Alkon D. L. Gigaohm single-channel recording from isolated Hermissenda crassicornis type B photoreceptors. J Exp Biol. 1991 Mar;156:619–623. doi: 10.1242/jeb.156.1.619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farley J., Auerbach S. Protein kinase C activation induces conductance changes in Hermissenda photoreceptors like those seen in associative learning. Nature. 1986 Jan 16;319(6050):220–223. doi: 10.1038/319220a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franciolini F. Calcium and voltage dependence of single Ca2+-activated K+ channels from cultured hippocampal neurons of rat. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Sep 1;943(3):419–427. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(88)90373-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grega D. S., Werz M. A., Macdonald R. L. Forskolin and phorbol esters reduce the same potassium conductance of mouse neurons in culture. Science. 1987 Jan 16;235(4786):345–348. doi: 10.1126/science.2432663. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamill O. P., Marty A., Neher E., Sakmann B., Sigworth F. J. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflugers Arch. 1981 Aug;391(2):85–100. doi: 10.1007/BF00656997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansson A., Serhan C. N., Haeggström J., Ingelman-Sundberg M., Samuelsson B. Activation of protein kinase C by lipoxin A and other eicosanoids. Intracellular action of oxygenation products of arachidonic acid. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Feb 13;134(3):1215–1222. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90380-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lederhendler I. I., Alkon D. L. The interstimulus interval and classical conditioning in the marine snail Hermissenda crassicornis. Behav Brain Res. 1989 Oct 1;35(1):75–80. doi: 10.1016/s0166-4328(89)80010-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lederhendler I. I., Gart S., Alkon D. L. Classical conditioning of Hermissenda: origin of a new response. J Neurosci. 1986 May;6(5):1325–1331. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.06-05-01325.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotan I., Dascal N., Naor Z., Boton R. Modulation of vertebrate brain Na+ and K+ channels by subtypes of protein kinase C. FEBS Lett. 1990 Jul 2;267(1):25–28. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80279-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matzel L. D., Lederhendler I. I., Alkon D. L. Regulation of short-term associative memory by calcium-dependent protein kinase. J Neurosci. 1990 Jul;10(7):2300–2307. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.10-07-02300.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matzel L. D., Schreurs B. G., Alkon D. L. Pavlovian conditioning of distinct components of Hermissenda's responses to rotation. Behav Neural Biol. 1990 Sep;54(2):131–145. doi: 10.1016/0163-1047(90)91324-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran O., Dascal N., Lotan I. Modulation of a Shaker potassium A-channel by protein kinase C activation. FEBS Lett. 1991 Feb 25;279(2):256–260. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80162-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez-Andres J. V., Alkon D. L. Voltage-clamp analysis of the effects of classical conditioning on the hippocampus. J Neurophysiol. 1991 Apr;65(4):796–807. doi: 10.1152/jn.1991.65.4.796. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werz M. A., Macdonald R. L. Dual actions of phorbol esters to decrease calcium and potassium conductances of mouse neurons. Neurosci Lett. 1987 Jul 9;78(1):101–106. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(87)90569-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]