Figure S3.
Sub-cellular Fractionation of Embryos, Related to Figure 2
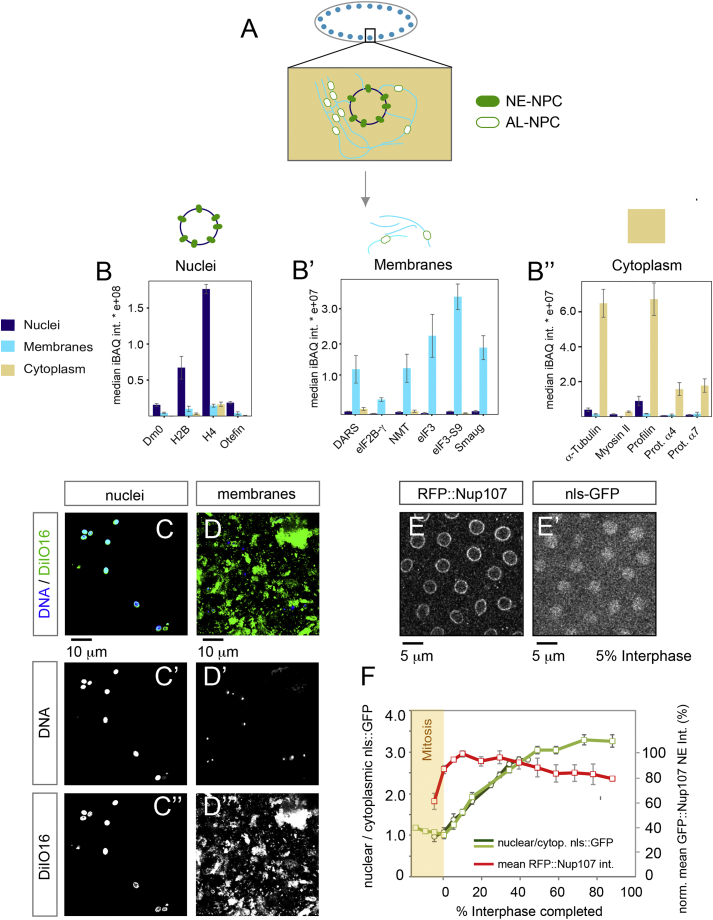
(A) Biochemical fractionation of syncytial blastoderm Drosophila embryos.
(B–D) Quality controls of fractionation. (B–B″) Median intensity based absolute quantification (iBAQ) scores of selected control proteins representative for either nuclei, membranes or cytoplasm, measured in the three respective fractions (n = 3 biological replicates). (C and D) Immunofluorescence of nuclear and membrane fractions, stained for DNA and with the membrane dye DiIO16, respectively. Nuclear integrity is preserved in the nuclear fraction (C and C′), where DNA is enclosed by DiIO16 labeled NE. No further membranes are attached to nuclei (C″). No nuclei are in the membrane fraction (D and D′).
(E and F) Nuclear import of nls-GFP is delayed compared to NPC scaffold accumulation at the NE. Early interphase stills from a time lapse movie recording RFP::Nup107 (E) and nls-GFP (E′). (F) Mean fluorescence intensities of nuclear/cytoplasmic nls-GFP and of RFP::Nup107 at the NE were quantified in regions of interest (ROIs) on images as in (E and E′). Mean Intensities ± STDV (n = 23 nuclei in 2 embryos) are plotted as function of % interphase progression.