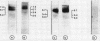Abstract
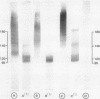
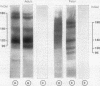
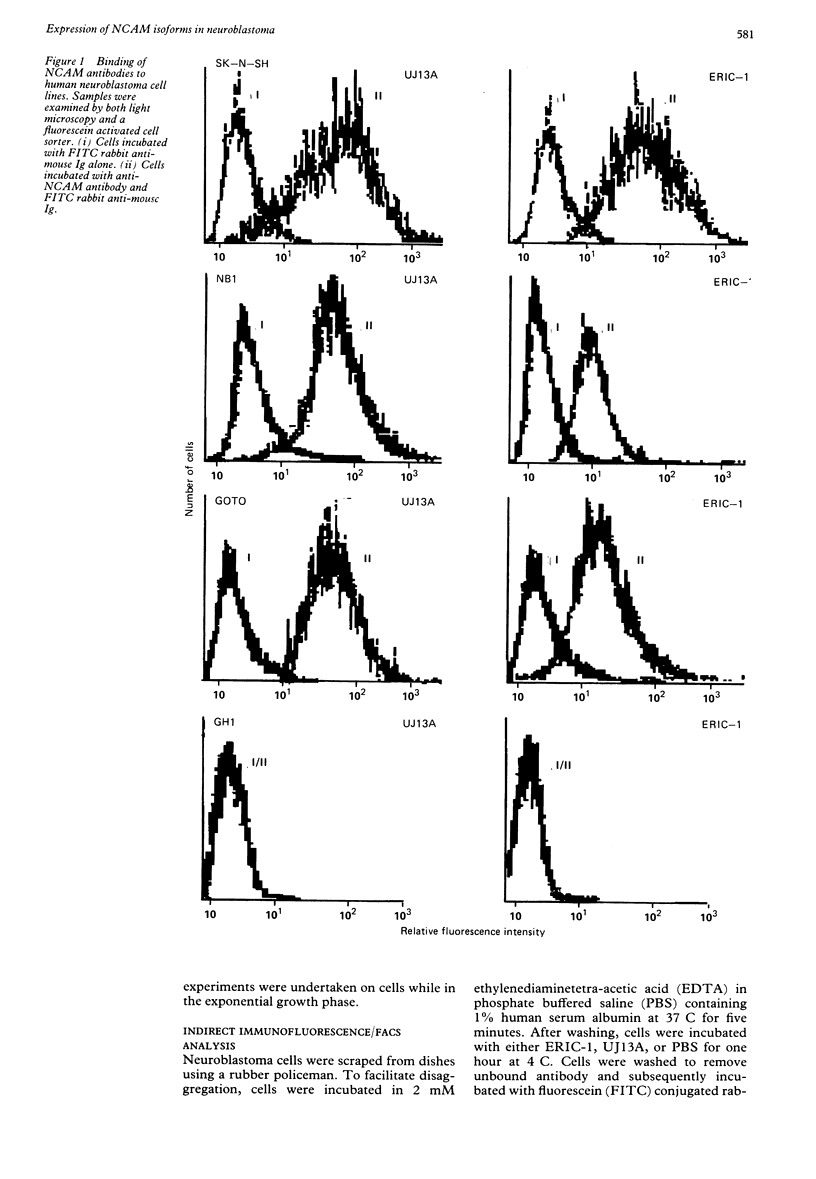
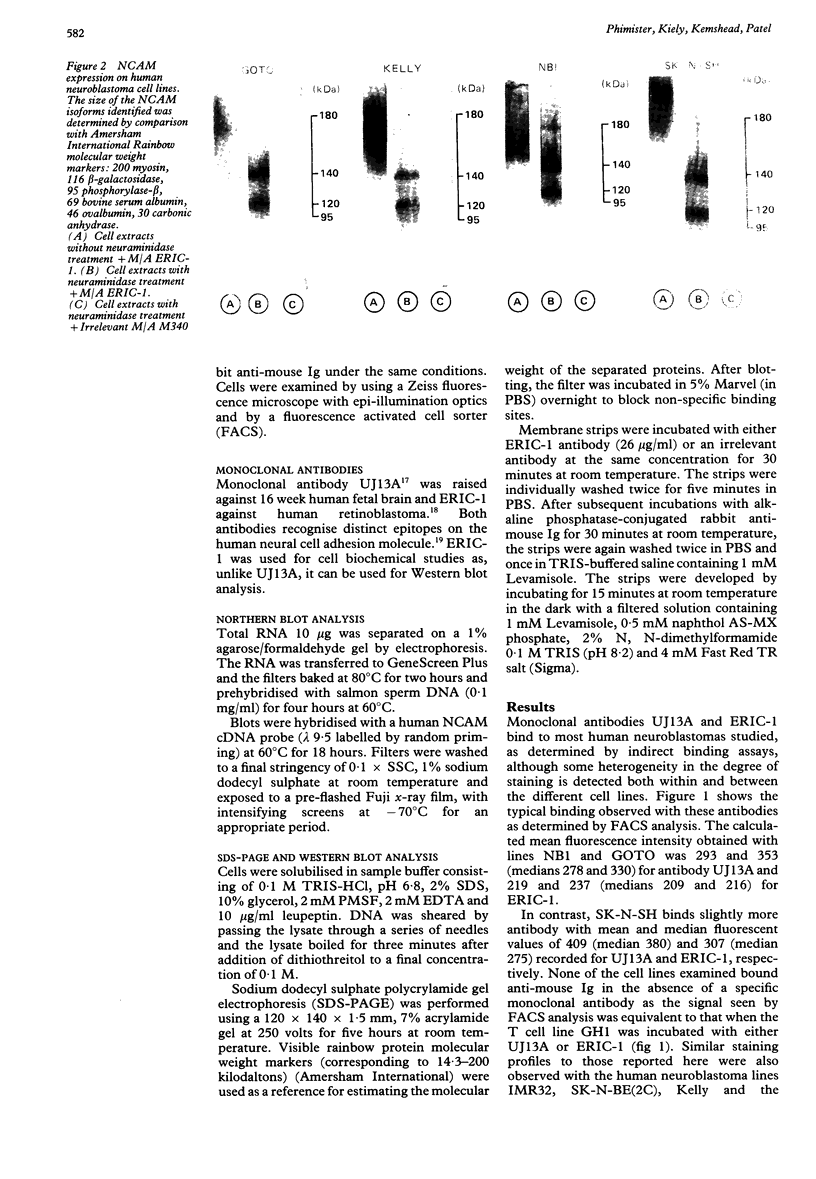
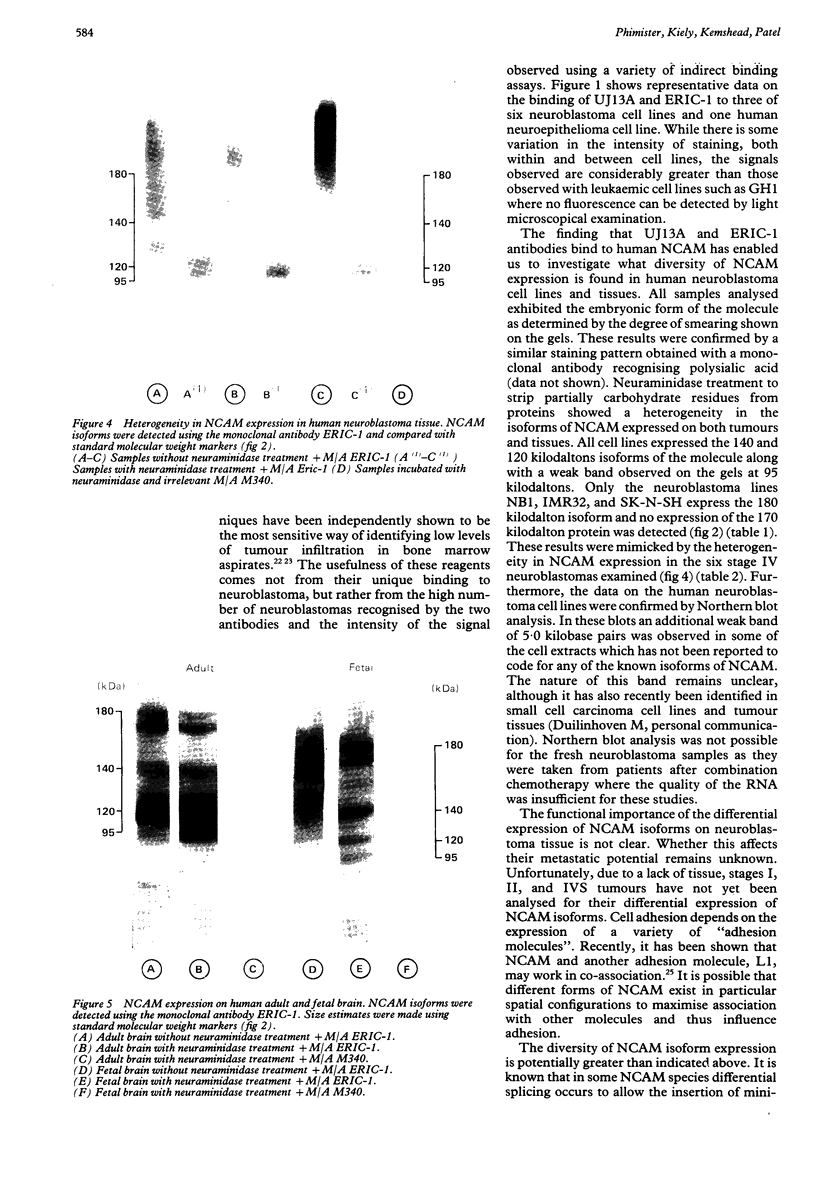
A comparative study on the expression of the neural cell adhesion molecule (NCAM) in human neuroblastoma cell lines and tissues was undertaken. NCAMs are a family of closely related cell surface glycoproteins involved in cell-cell interactions. Using antibodies that recognise distinct epitopes on NCAM, their presence was shown in neuroblastoma, but these studies do not yield any information on the specific NCAM isoforms associated with the tumour. Western and Northern blot analyses were therefore carried out to characterise the NCAM isoforms in this neuroectodermal tumour. Western blot studies using the monoclonal antibody ERIC-1 showed that all human neuroblastoma cell lines tested expressed the 140 and 120 kilodalton isoforms of NCAM in their desialo state. Some of the cell lines also expressed NCAM-180. The data are corroborated by Northern blotting where a transcript of 7.4 kilobase pairs was identified only in lines expressing NCAM-180; the 6.7 and 5.4 kilobase pair transcripts coding for 140 and 120 kilodalton isoforms, respectively, were present in all the cell lines tested. The NCAM isoforms identified in neuroblastoma were also different from those found in adult and fetal brain tissue, suggesting that aberrations are expressed in the molecule during tumorigenesis.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Biedler J. L., Helson L., Spengler B. A. Morphology and growth, tumorigenicity, and cytogenetics of human neuroblastoma cells in continuous culture. Cancer Res. 1973 Nov;33(11):2643–2652. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham B. A., Hemperly J. J., Murray B. A., Prediger E. A., Brackenbury R., Edelman G. M. Neural cell adhesion molecule: structure, immunoglobulin-like domains, cell surface modulation, and alternative RNA splicing. Science. 1987 May 15;236(4803):799–806. doi: 10.1126/science.3576199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Figarella-Branger D. F., Durbec P. L., Rougon G. N. Differential spectrum of expression of neural cell adhesion molecule isoforms and L1 adhesion molecules on human neuroectodermal tumors. Cancer Res. 1990 Oct 1;50(19):6364–6370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imashuku S., Inui A., Nakamura T., Tanaka J., Miyake S. Catecholamine metabolism in tissue culture cells of a neuroblastoma. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1973 May;36(5):931–936. doi: 10.1210/jcem-36-5-931. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadmon G., Kowitz A., Altevogt P., Schachner M. The neural cell adhesion molecule N-CAM enhances L1-dependent cell-cell interactions. J Cell Biol. 1990 Jan;110(1):193–208. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.1.193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemshead J. T., Goldman A., Fritschy J., Malpas J. S., Pritchard J. Use of panels of monoclonal antibodies in the differential diagnosis of neuroblastoma and lymphoblastic disorders. Lancet. 1983 Jan 1;1(8314-5):12–15. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)91559-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemshead J. T., Heath L., Gibson F. M., Katz F., Richmond F., Treleaven J., Ugelstad J. Magnetic microspheres and monoclonal antibodies for the depletion of neuroblastoma cells from bone marrow: experiences, improvements and observations. Br J Cancer. 1986 Nov;54(5):771–778. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1986.239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanier L. L., Testi R., Bindl J., Phillips J. H. Identity of Leu-19 (CD56) leukocyte differentiation antigen and neural cell adhesion molecule. J Exp Med. 1989 Jun 1;169(6):2233–2238. doi: 10.1084/jem.169.6.2233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipinski M., Hirsch M. R., Deagostini-Bazin H., Yamada O., Tursz T., Goridis C. Characterization of neural cell adhesion molecules (NCAM) expressed by Ewing and neuroblastoma cell lines. Int J Cancer. 1987 Jul 15;40(1):81–86. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910400115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minowada J., Onuma T., Moore G. E. Rosette-forming human lymphoid cell lines. I. Establishment and evidence for origin of thymus-derived lymphocytes. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1972 Sep;49(3):891–895. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nguyen C., Mattei M. G., Mattei J. F., Santoni M. J., Goridis C., Jordan B. R. Localization of the human NCAM gene to band q23 of chromosome 11: the third gene coding for a cell interaction molecule mapped to the distal portion of the long arm of chromosome 11. J Cell Biol. 1986 Mar;102(3):711–715. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.3.711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppedal B. R., Storm-Mathisen I., Kemshead J. T., Brandtzaeg P. Bone marrow examination in neuroblastoma patients: a morphologic, immunocytochemical, and immunohistochemical study. Hum Pathol. 1989 Aug;20(8):800–805. doi: 10.1016/0046-8177(89)90076-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel K., Moore S. E., Dickson G., Rossell R. J., Beverley P. C., Kemshead J. T., Walsh F. S. Neural cell adhesion molecule (NCAM) is the antigen recognized by monoclonal antibodies of similar specificity in small-cell lung carcinoma and neuroblastoma. Int J Cancer. 1989 Oct 15;44(4):573–578. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910440402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth J., Blaha I., Bitter-Suermann D., Heitz P. U. Blastemal cells of nephroblastomatosis complex share an onco-developmental antigen with embryonic kidney and Wilms' tumor. An immunohistochemical study on polysialic acid distribution. Am J Pathol. 1988 Dec;133(3):596–608. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth J., Zuber C., Wagner P., Blaha I., Bitter-Suermann D., Heitz P. U. Presence of the long chain form of polysialic acid of the neural cell adhesion molecule in Wilms' tumor. Identification of a cell adhesion molecule as an oncodevelopmental antigen and implications for tumor histogenesis. Am J Pathol. 1988 Nov;133(2):227–240. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth J., Zuber C., Wagner P., Taatjes D. J., Weisgerber C., Heitz P. U., Goridis C., Bitter-Suermann D. Reexpression of poly(sialic acid) units of the neural cell adhesion molecule in Wilms tumor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(9):2999–3003. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.9.2999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlesinger H. R., Gerson J. M., Moorhead P. S., Maguire H., Hummeler K. Establishment and characterization of human neuroblastoma cell lines. Cancer Res. 1976 Sep;36(9 PT1):3094–3100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwab M., Alitalo K., Klempnauer K. H., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M., Gilbert F., Brodeur G., Goldstein M., Trent J. Amplified DNA with limited homology to myc cellular oncogene is shared by human neuroblastoma cell lines and a neuroblastoma tumour. Nature. 1983 Sep 15;305(5931):245–248. doi: 10.1038/305245a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekiguchi M., Oota T., Sakakibara K., Inui N., Fujii G. Establishment and characterization of a human neuroblastoma cell line in tissue culture. Jpn J Exp Med. 1979 Feb;49(1):67–83. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tumilowicz J. J., Nichols W. W., Cholon J. J., Greene A. E. Definition of a continuous human cell line derived from neuroblastoma. Cancer Res. 1970 Aug;30(8):2110–2118. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walsh F. S., Dickson G. Generation of multiple N-CAM polypeptides from a single gene. Bioessays. 1989 Oct;11(4):83–88. doi: 10.1002/bies.950110402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yogeeswaran G., Grönberg A., Welsh R. M., Kiessling R. Interferon-induced increase in neuraminidase-releasable sialic acid and glycosphingolipid metabolism in mouse lymphoma and L1210 leukemic cell lines: correlation with susceptibility to natural killer cell-mediated lysis. Int J Cancer. 1983 Apr 15;31(4):501–507. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910310417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]