Abstract
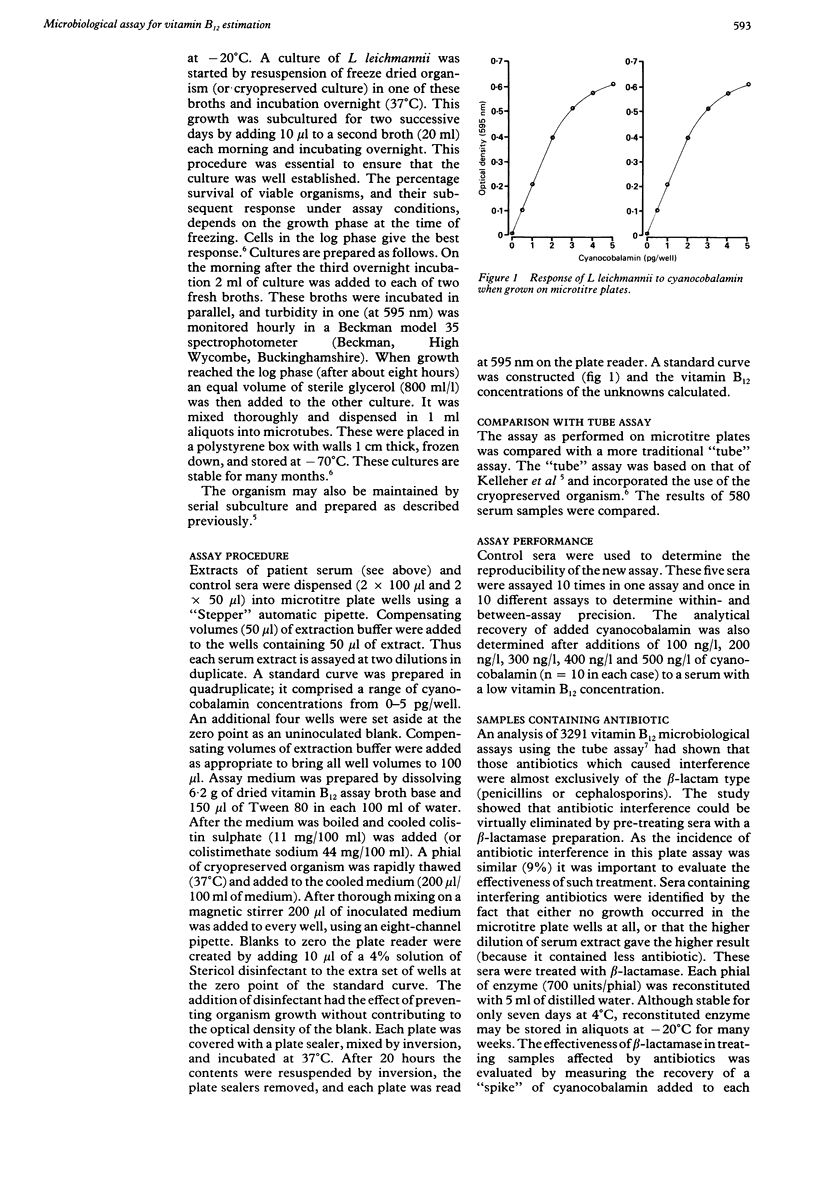
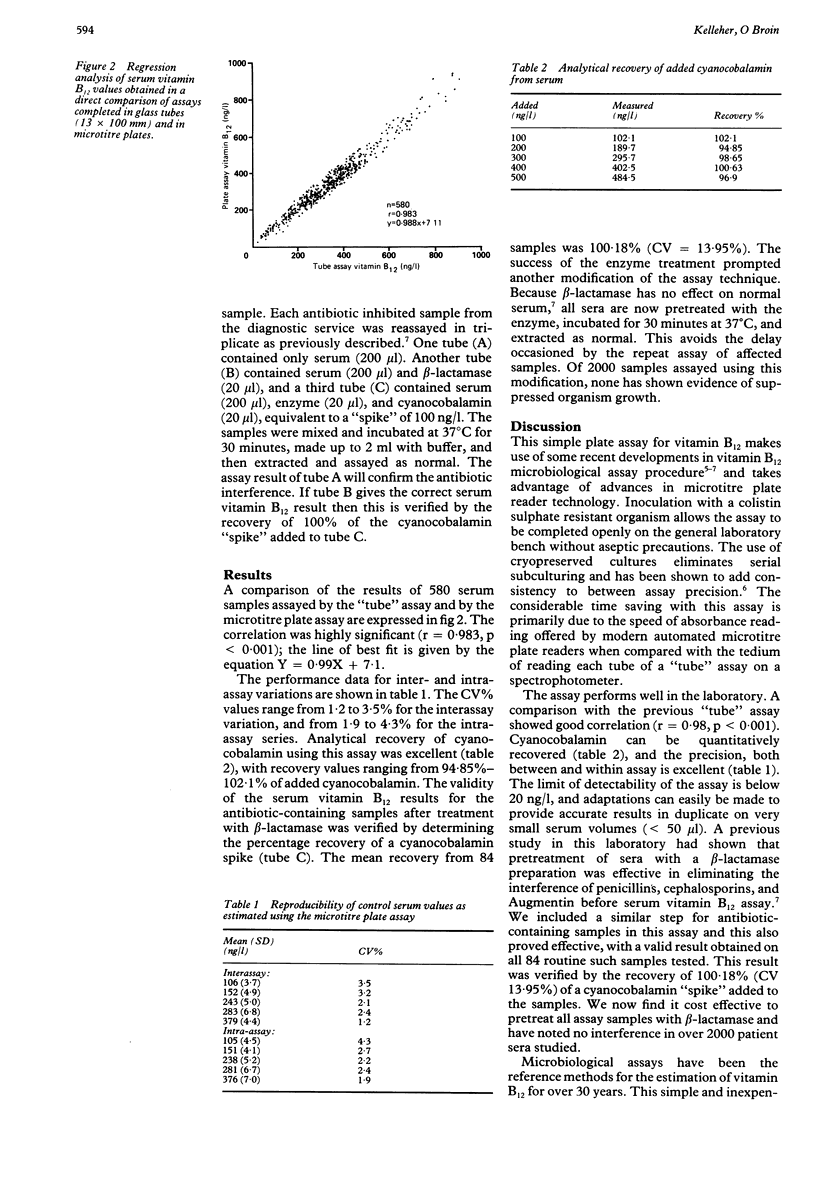
A simplified microbiological assay for vitamin B12 estimation, completed on microtitre plates using a colistin sulphate resistant strain of Lactobacillus leichmannii (NCIB 12519), and cryopreserved cultures is described. The new assay correlated well with a more conventional "tube" assay and was not influenced by the presence of antibiotics in serum. Evaluation of assay performance showed excellent interassay and intra-assay precision with quantitative recovery of added cyanocobalamin over a wide range of additions (94.9%-102.1%). The advantages of short incubation time, easy reading, and minimal reagent costs make this assay an attractive option in the routine clinical laboratory and in research.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANDERSON B. B. INVESTIGATIONS INTO THE EUGLENA METHOD FOR THE ASSAY OF THE VITAMIN B12 IN SERUM. J Clin Pathol. 1964 Jan;17:14–26. doi: 10.1136/jcp.17.1.14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelleher B. P., Scott J. M., O'Broin S. D. Use of beta-lactamase to hydrolyse interfering antibiotics in vitamin B12 microbiological assay using Lactobacillus leichmannii. Clin Lab Haematol. 1990;12(1):87–95. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2257.1990.tb01114.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindenbaum J. Status of laboratory testing in the diagnosis of megaloblastic anemia. Blood. 1983 Apr;61(4):624–627. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mollin D. L., Anderson B. B., Burman J. F. The serum vitamin B12 level: its assay and significance. Clin Haematol. 1976 Oct;5(3):521–546. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPRAY G. H. An improved method for the rapid estimation of vitamin B12 in serum. Clin Sci. 1955 Nov;14(4):661–667. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Temperley I. J., Collery D. The significance of the serum vitamin B 12 estimation in clinical practice. Ir J Med Sci. 1965 Jul-Oct;6(475):317–325. doi: 10.1007/BF02942199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



