Abstract
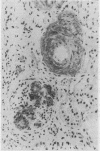
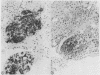
The amyloid deposits in 21 renal biopsy specimens were subjected to a detailed immunohistochemical analysis using a panel of antibodies against recognised constituents of tissue amyloid. This was a retrospective study of material originally submitted during the investigation of various renal abnormalities and studied by a routine protocol including histochemistry, electron microscopy, and immunofluorescence. The presence of an amyloid was confirmed in all 21 cases. Seventeen cases contained P component and either amyloid A (AA) (11 cases) or an immunoglobulin light chain associated amyloid (six cases). Four cases contained amyloid material with unusual immunohistochemical findings; one case had AA and P-component (PC) in the interstitium, one case had lambda light chain and beta-2 microglobulin, one case had kappa light chain and Clq, and one case had lambda light chains only. It was possible, therefore, to identify precisely the amyloid constituents and thereby "type" the amyloid by immunohistochemical means. The availability of the antibodies used and their application using these techniques could simplify the confirmation of clinically suspected amyloidosis.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alpers C. E., Hopper J., Jr, Biava C. G. Light-chain glomerulopathy with amyloid-like deposits. Hum Pathol. 1984 May;15(5):444–448. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(84)80078-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chastonay P., Hurlimann J. Characterization of different amyloids with immunological techniques. Pathol Res Pract. 1986 Dec;181(6):657–663. doi: 10.1016/S0344-0338(86)80040-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen A. S., Shirahama T., Sipe J. D., Skinner M. Amyloid proteins, precursors, mediator, and enhancer. Lab Invest. 1983 Jan;48(1):1–4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donini U., Casanova S., Dal Bosco F., Linke R. P. Immunohistochemical typing of amyloid on hydroxyethyl-methacrylate-embedded renal biopsies. Appl Pathol. 1984;2(6):299–307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujihara S., Balow J. E., Costa J. C., Glenner G. G. Identification and classification of amyloid in formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissue sections by the unlabeled immunoperoxidase method. Lab Invest. 1980 Oct;43(4):358–365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujihara S., Glenner G. G. Primary localized amyloidosis of the genitourinary tract: immunohistochemical study on eleven cases. Lab Invest. 1981 Jan;44(1):55–60. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishii T., Haga S. Immuno-electron-microscopic localization of complements in amyloid fibrils of senile plaques. Acta Neuropathol. 1984;63(4):296–300. doi: 10.1007/BF00687336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz A., Weicker-Thorne J., Painter R. H. The relationship of a serum protein, C1t, to a common nonfibrillar constituent of amyloid (P component) as revealed by immunohistochemical studies. Am J Pathol. 1977 Sep;88(3):679–698. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirkpatrick C. J., Curry A., Galle J., Melzner I. Systemic kappa light chain deposition and amyloidosis in multiple myeloma: novel morphological observations. Histopathology. 1986 Oct;10(10):1065–1076. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1986.tb02543.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linder J., Silberman H. R., Croker B. P. Amyloidosis complicating hairy cell leukemia. Am J Clin Pathol. 1982 Dec;78(6):864–867. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/78.6.864. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linke R. P., Hampl H., Bartel-Schwarze S., Eulitz M. Beta 2-microglobulin, different fragments and polymers thereof in synovial amyloid in long-term hemodialysis. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler. 1987 Feb;368(2):137–144. doi: 10.1515/bchm3.1987.368.1.137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linke R. P. Monoclonal antibodies against amyloid fibril protein AA. Production, specificity, and use for immunohistochemical localization and classification of AA-type amyloidosis. J Histochem Cytochem. 1984 Mar;32(3):322–328. doi: 10.1177/32.3.6363521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Löfberg H., Grubb A., Thysell H., Nilsson E., Kjellander B., Möller C., Gruic V., Ljungquist A., Sternby N. H. The prevalence of renal amyloidosis of the AA-type in a series of 1,158 consecutive autopsies. Acta Pathol Microbiol Immunol Scand A. 1987 Sep;95(5):297–302. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1987.tb00044_95a.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClure J., Bartley C. J., Ackrill P. Carpal tunnel syndrome caused by amyloid containing beta 2 microglobulin: a new amyloid and a complication of long term haemodialysis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1986 Dec;45(12):1007–1011. doi: 10.1136/ard.45.12.1007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muñoz-Gómez J., Gómez-Pérez R., Solé-Arques M., Llopart-Buisán E. Synovial fluid examination for the diagnosis of synovial amyloidosis in patients with chronic renal failure undergoing haemodialysis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1987 Apr;46(4):324–326. doi: 10.1136/ard.46.4.324. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noel L. H., Droz D., Ganeval D. Immunohistochemical characterization of renal amyloidosis. Am J Clin Pathol. 1987 Jun;87(6):756–761. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/87.6.756. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAUL W. E., COHEN A. S. ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC STUDIES OF AMYLOID FIBRILS WITH FERRITINCONJUGATED ANTIBODY. Am J Pathol. 1963 Oct;43:721–738. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powers J. M., Schlaepfer W. W., Willingham M. C., Hall B. J. An immunoperoxidase study of senile cerebral amyloidosis with pathogenetic considerations. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1981 Nov;40(6):592–612. doi: 10.1097/00005072-198111000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pras M., Schubert M., Zucker-Franklin D., Rimon A., Franklin E. C. The characterization of soluble amyloid prepared in water. J Clin Invest. 1968 Apr;47(4):924–933. doi: 10.1172/JCI105784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts G. W., Lofthouse R., Allsop D., Landon M., Kidd M., Prusiner S. B., Crow T. J. CNS amyloid proteins in neurodegenerative diseases. Neurology. 1988 Oct;38(10):1534–1540. doi: 10.1212/wnl.38.10.1534. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright J. R., Calkins E., Humphrey R. L. Potassium permanganate reaction in amyloidosis. A histologic method to assist in differentiating forms of this disease. Lab Invest. 1977 Mar;36(3):274–281. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]