Abstract
The Deepwater Horizon accident has brought oil contamination of deep-sea environments to worldwide attention. The risk for new deep-sea spills is not expected to decrease in the future, as political pressure mounts to access deep-water fossil reserves, and poorly tested technologies are used to access oil. This also applies to the response to oil-contamination events, with bioremediation the only (bio)technology presently available to combat deep-sea spills. Many questions about the fate of petroleum-hydrocarbons within deep-sea environments remain unanswered, as well as the main constraints limiting bioremediation under increased hydrostatic pressures and low temperatures. The microbial pathways fueling oil bioassimilation are unclear, and the mild upregulation observed for beta-oxidation-related genes in both water and sediments contrasts with the high amount of alkanes present in the spilled oil. The fate of solid alkanes (tar), hydrocarbon degradation rates and the reason why the most predominant hydrocarbonoclastic genera were not enriched at deep-sea despite being present at hydrocarbon seeps at the Gulf of Mexico have been largely overlooked. This mini-review aims at highlighting the missing information in the field, proposing a holistic approach where in situ and ex situ studies are integrated to reveal the principal mechanisms accounting for deep-sea oil bioremediation.
Keywords: marine snow, dispersants, beta-oxidation, HMW, PAH, Alcanivorax, Thalassolituus, burn residue
Deep-Sea Oil Contamination
Contamination of deep-sea environments with petroleum following accidental spills represents a relatively emerging topic, which received worldwide attention after the Deepwater Horizon (DWH) accident at the Gulf of Mexico in April 2010 (Joint Analysis Group [JAG], 2010) when more than 500’000 tons of crude oil (+24% including gas; Reddy et al., 2012) were discharged at ∼1500 m below surface level (bsl; U.S. Geological Survey, 2010). As political reasons will keep pushing for deep-sea oil extraction, use of poorly tested technologies is not expected to decrease the risk of future accidents (Jernelov, 2010; Thibodeaux et al., 2011).
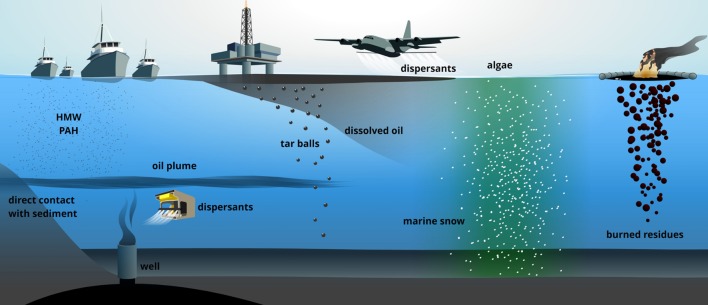
Spilled oil reaches the deep sea through numerous ways. Surface-water spills form thin layers which partially dissolve, emulsify and diffuse through the water column (Tkalich et al., 2003), or sink due to the formation of heavier particles (tar) (Parinos et al., 2013). Dispersants enhance oil solubility in water. Extensive injections of the dispersant COREXIT at deep sea (about 3 × 106 L) during the DWH contributed to the formation of a large oil plume at 1000–1300 m bsl (Camilli et al., 2010) preventing petroleum-hydrocarbons from reaching the surface (Kujawinski et al., 2011). Direct contact of the plume with the continental slope was partially responsible for contamination of deep-sea sediments (Romero et al., 2015). Another vector for sinking oil is the “so-called” marine snow. Oil contamination enhances phytoplankton production of exopolysaccharides (EPSs, Patton et al., 1981), whose amphiphilic nature favors hydrophobic-hydrophobic interactions with oil to form particles including microbial biomass that sink downward (Passow et al., 2012). This phenomenon represented the main cause for oil transfer to the seafloor during the DWH (Federal Interagency Solution Group, 2010; Ziervogel et al., 2014; Romero et al., 2015). In situ oil burning, one of the most widely applied strategies for oil-pollution control, is known to cause seafloor contamination (Wang et al., 1999; Federal Interagency Solution Group, 2010). Following mechanical oil recovery through skimming, the unrecoverable oil fraction on the surface is gathered within small areas for controlled burning, which generates denser mixtures of the less volatile fraction of the oil (resins, asphaltenes; Buist et al., 1997; Jézéquel et al., 2014). Finally, geochemical data on the increased heavy-molecular-weight polyaromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) fraction in DWH deep-sea sediments indicated that diesel exhaust from the 6000 vessels conducting safety operations cannot be excluded as contamination factor (Romero et al., 2015; Figure 1).
FIGURE 1.
The many ways through which accidentally-spilled petroleum-hydrocarbons reach the seafloor and deep-sea. HMW PAH, high molecular weight polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons.
There has been little to no effort in assessing the magnitude of deep-sea oil contamination worldwide. Between 3200 and 8000 km2 of deep seafloor were impacted with up to 14% of the DWH spilled-oil (Chanton et al., 2014), although ∼22% could not be traced (Ramseur, 2010). The impact on deep-sea life was striking. Deep-sea sediments were classified as low to moderately polluted (Romero et al., 2015); pore-water from 1000 to 1400 m bsl exerted high toxicity levels and DNA mutagenesis (Paul et al., 2013); primary production and carbon export to the deep-sea was reduced (Prouty et al., 2016); in sea-food, concentration of certain petroleum-hydrocarbons was 1000 times above the threshold for human consumption (Sammarco et al., 2013).
Hydrocarbons enter deep-sea areas also through several geochemical routes (oil seeps, hydrothermal vents, gas hydrates, asphalt volcanoes; Jørgensen and Boetius, 2007). Several microorganisms proficiently use oil as an energy/carbon source preventing its accumulation into marine environments (Head et al., 2006). Natural niches characterized by fossil hydrocarbons determine microbial community structures featured by unique biochemical equilibria, which form over a time-span of centuries (Jørgensen and Boetius, 2007). Conversely, anthropogenically oil-affected sites are non-adapted environments where overabundant carbon loads are discharged within weeks/months. The enrichment of oil-degrading taxa jump-starting bioremediation coincides with a net loss of biodiversity (Kleindienst et al., 2015), which can hardly be recovered until excess oil has been depleted. The oligotrophic nature of marine environments (Garrison, 2015) limits oil bioassimilation, which is further impaired at the deep sea by low temperatures, O2 availability, and hydrostatic pressure (HP).
Review Objective
Lack of efficient oil recovery technologies at deep sea implies that bioremediation represents the only mean to combat contamination (Lu et al., 2012). The DWH spill was investigated through in situ studies employing next-generation sequencing techniques, which were partially backed-up by ex situ experiments. Despite supplying unprecedented information, both approaches failed to describe the exact metabolic routes and constraints in deep-sea bioremediation. In situ studies using molecular techniques could only provide information on potential activities while, with no exception, ex situ studies neglected the impact of one of the major drivers for biodiversity in marine environments, i.e., HP (Ghiglione et al., 2012). While previous overviews focused on microbial succession (Kimes et al., 2014), marine snow formation (Joye et al., 2014) and hydrocarbon fate (King et al., 2015) following the DWH, this mini-review aims at highlighting the open questions concerning the physiology of oil bioremediation at deep-sea HP conditions.
In Situ Molecular Studies: Deep-Sea Plume
Upon injection, DWH spilled-oil was composed of 74, 16, and 10% saturated, aromatic and polar hydrocarbons, respectively; gas represented 24% of the spill, while oil comprised 76% (alkanes being 32% of the total; Table 1). Fractionation due to physicochemical factors (and dispersants application; Kujawinski et al., 2011) resulted into different petroleum mixtures affecting water and sediment. The oil plume was mainly composed of gaseous and monoaromatic compounds (Table 1). A hydrocarbon-dependent microbial community restructuring was proposed for the plume. Following a first enrichment in Oceanospirillales and Pseudomonas (May 2010), the relative increase in aromatic hydrocarbons as compared to aliphatic and cycloalkanes following partial cap closure (June 4, 2010) coincided with a general shift in dominance to Colwellia, Cycloclasticus, Pseudoalteromonas and methylotrophs lasting until mid-August 2010 (Hazen et al., 2010; Valentine et al., 2010; Kessler et al., 2011; Lu et al., 2012; Mason et al., 2012; Dubinsky et al., 2013; Rivers et al., 2013; Kleindienst et al., 2015). Before partial closure of the well, metagenomic (Hazen et al., 2010; Lu et al., 2012; Mason et al., 2012) and metatranscriptomic (Mason et al., 2012; Rivers et al., 2013) analyses evidenced an upregulation of genes related to hydrocarbon degradation, although a consensus could not be reached. Upregulation of genes or pathways related to monoaromatics or PAH degradation was observed in all studies to different extents (Hazen et al., 2010; Lu et al., 2012; Mason et al., 2012; Rivers et al., 2013). Mason et al. (2012) found a higher level of gene and transcript reads related to the degradation of n-alkanes rather than aromatics, contrary to Hazen et al. (2010). The latter would be in contrast with data from the same group indicating that n-alkane and cycloalkane concentrations correlated with the enriched communities before partial closure (Dubinsky et al., 2013). Similarly, the upregulation of the cyclohexanone degradation pathway as detected in Mason et al. (2012) was negligible in Hazen et al. (2010). Upregulation of alkane-1 mono-oxygenases responsible for n-alkane activation was detected in all studies (Hazen et al., 2010; Lu et al., 2012; Mason et al., 2012; Rivers et al., 2013). Following activation, n-alkanes should enter beta-oxidation (Rojo, 2009), but genes related to this pathway were only partially upregulated in Mason et al. (2012) and Rivers et al. (2013). Upregulation of anaerobic hydrocarbon degradation genes (Lu et al., 2012) was consistent with that for nitrate reduction (Rivers et al., 2013), although O2 levels were marginally affected at that time (Camilli et al., 2010; Hazen et al., 2010). As 16S rRNA gene signatures persisted long after the plume had dissipated (Joye et al., 2014), such controversies concerning structure-function relationships highlight the need for more data integration (Widder et al., 2016).
Table 1.
Detected oil fractions in water and sediment deep-sea samples after the Deepwater Horizon spill.
| Deepwater Horizon spilled-oil composition at origin (15 MPa, 5°C) | Oil | Oil plume | Sediments | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| x109 g | % | |||||||||||||||
| 2010 | 2010 | 2010 | 2011 | |||||||||||||
| Sampling period | June 21 | May 9–16 | May 25–June 6 | May 25–June 2 | May 25–June 2 | June 11–21 | June 19–28 | August 18–October 4 | September | September 16–October 20 | December–February | May | November 16 | |||
| Methane | 100 | 14.3 | + | + | + | + | ||||||||||
| Ethane | 19 | 2.7 | + | + | + | |||||||||||
| Propane | 18 | 2.6 | + | + | + | |||||||||||
| Gas | Isobutane | 4.7 | 0.7 | + | ||||||||||||
| n-butane | 10 | 1.4 | + | |||||||||||||
| Isopentane | 5.6 | 0.8 | ||||||||||||||
| n-pentane | 7.3 | 1 | + | |||||||||||||
| n-alkanes | 81 | 11.6 | + | + | + | + | + | |||||||||
| Branched alkanes | 140 | 20.1 | + | |||||||||||||
| Cycloalkanes | 84 | 12.1 | + | |||||||||||||
| Oil | Alkylbenzenes and indenes | 48 | 6.9 | + | ||||||||||||
| BTEX | 19.2 | 2.8 | + | + | + | + | ||||||||||
| PAH | 21 | 3 | + | + | + | + | ||||||||||
| Unresolved/not defined | 139.6 | 20 | + | + | + | |||||||||||
| Polar | 54 | 7.7 | ||||||||||||||
| Total gas | 165 | 24 | ||||||||||||||
| Oil and gas | Total oil | 533 | 76 | |||||||||||||
| Total spill | 697 | 100 | ||||||||||||||
| Reference | Reddy et al., 2012 | Diercks et al., 2010 | Joye et al., 2011 | Hazen et al., 2010 | Lu et al., 2012 | Valentine et al., 2010 | Camilli et al., 2010 | Kessler et al., 2011 | Sammarco et al., 2013 | Mason et al., 2014 | Romero et al., 2015 | Liu et al., 2012 | Yergeau et al., 2015 | |||
While a microbial and molecular response to oil appears evident, the actual metabolic routes following hydrocarbons uptake are not. Lack of significant O2 respiration in the plume early in the spill contrasts with the enhanced cell number (Hazen et al., 2010; Mason et al., 2012; Kleindienst et al., 2015). Sustained aerobic biodegradation would be expected to result in increased CO2 production and decreased pH, but none of these phenomena were reported. The ease of hydrocarbon degradation would suggest the plume to be enriched in n-alkane degraders as proposed for gaseous compounds (Valentine et al., 2010) and the Oceanospirillales group found by Hazen et al. (2010), but the preferential molecular response to aromatics brings this hypothesis into question. The fate of n-alkanes (>C6) and the lack of a strong beta-oxidation upregulation in the plume remain unexplained.
Persistent O2 anomalies were observed following well closure (July 15, 2010). Their strong intensity was used to track the oil plume moving southwestward (Du and Kessler, 2012) and associated with heterotrophic degradation of high-molecular-weight organics rather than oil (Dubinsky et al., 2013)- possibly due to marine snow formation after the spill (Ziervogel et al., 2014)- or with aerobic degradation of gaseous hydrocarbons (Kessler et al., 2011). The latter would be consistent with enriched methylotrophs at that time (Kessler et al., 2011; Redmond and Valentine, 2012; Dubinsky et al., 2013; Kleindienst et al., 2015). However, actual CH4 respiration rates were inconsistent throughout the spill (Crespo-Medina et al., 2014) and CH4 mono-oxygenase upregulation before May–June 2010 is still under debate (Joye et al., 2014; Kimes et al., 2014; King et al., 2015). Joye et al. (2014) suggest that some presently unknown factor hampered CH4 respiration after mid-June. As it stands, venting to the atmosphere could not be excluded (Rivers et al., 2013).
In Situ Molecular Studies: Deep-Sea Sediments
Deepwater Horizon sediments were investigated through metagenomic analysis of seafloor (Mason et al., 2014) and sub-seafloor (Kimes et al., 2013) samples in September–October 2010. Superficial samples (0–1 cm) within 5 km of the wellhead were the most impacted, and were enriched in uncultured Gammaproteobacteria and Colwellia-related organisms similar to the ones in the plume, and in uncultured Rhodobacteraceae (Mason et al., 2014). Highly impacted sediments showed increased levels of monoaromatic degradation genes, no relation with PAH and O2 respiration, thus partly resembling results obtained for plume samples in May-June (Hazen et al., 2010; Lu et al., 2012; Rivers et al., 2013). Sub-seafloor samples (1–3 cm deep) close to the wellhead (0.5 and 6 km, Kimes et al., 2013) were enriched in several Deltaproteobacteria, although Alpha- and Gammaproteobacteria remained predominant (Kimes et al., 2013). Enhanced expression of the bssA gene was consistent with increased benzylsuccinate levels formed via the fumarate pathway. Conversely, no alkylsuccinate or alkylmalonate metabolites related to alkane degradation were found despite the corresponding assA gene being upregulated and alkanes up to n-docosane being detected (Kimes et al., 2013), reflecting the uncertain fate of n-alkanes (>C6) in the plume. Consistently, genes related to fatty acids metabolism were poorly expressed in seafloor sediments close to the wellhead (Kimes et al., 2013) and expression levels were comparable to pre-spill samples (Kimes et al., 2013). One year later, n-alkanes (C8–C38) were 10–1000 times more concentrated than PAH in the sediments (Liu et al., 2012), suggesting that the degradation of PAH was faster than that of n-alkanes (Yergeau et al., 2015; Table 1).
As for the plume, CH4 respiration rates in sediments are uncertain. After 1 year, the upper (0–2 cm) sediments located 2–6 km from the wellhead were populated by Actinobacteria, Firmicutes, Chloroflexi and several type I methylotrophs (Liu and Liu, 2013). Provided that CH4 levels in the plume were low in October 2010 (Kessler et al., 2011; Crespo-Medina et al., 2014), it appears unlikely that plume-related CH4 could persist in sediments until May 2011. CH4 accumulation may result from long-term anaerobic hydrocarbon degradation (Widdel and Rabus, 2001), which would be in agreement with the presence of Desulfobacterium (Liu and Liu, 2013). Alternatively, acetotrophic methanogens may have been stimulated by an increase in acetate produced by acetogenic hydrocarbon-degrading SO4-reducing bacteria (SRB). Together with the upregulated nitrification in September–August 2010 (Mason et al., 2014), the available data suggest that persistent oil-contamination affects O2 seafloor levels indefinitely, supporting anaerobic benthic microbial activity.
Ex Situ Microbiology and Lab-Scale Hp Experiments
None of the ex situ experiments on DWH deep-sea samples applied HP (Hazen et al., 2010; Valentine et al., 2010; Bælum et al., 2012; Redmond and Valentine, 2012; Gutierrez et al., 2013b; McKay et al., 2013; Mason et al., 2014; Yergeau et al., 2015; Dombrowski et al., 2016). Despite the persistence of n-alkanes and mild beta-oxidation upregulation, ex situ14C-experiments reported high n-alkane degradation in sediment (Mason et al., 2014) and water samples (Yergeau et al., 2015). Oiled beach sands were enriched in Gammaproteobacteria (Alcanivorax, Marinobacter) and Alphaproteobacteria (Rhodobacteraceae; Kostka et al., 2011). While some Rhodobacteraceae were found in deep-sea waters (Dubinsky et al., 2013) and sediments (Mason et al., 2014), neither Marinobacter nor Alcanivorax were enriched, contrary to other Alteromonadales and Oceanospirillales (Hazen et al., 2010; Dubinsky et al., 2013; Yang et al., 2014). Other hydrocarbonoclastic Oceanospirillales as Thalassolituus, Oleiphilus, Neptunomonas, or Oleispira were only reported because they consist of species closely related to the Oceanospirillales group identified in the plume (97%, Oleispira antarctica and T. oleivorans; Hazen et al., 2010). These isolates degrade long-chain hydrocarbons (Joye et al., 2014), which were not particularly enriched in the plume (Table 1). Low temperature was proposed to account for this (Redmond and Valentine, 2012), although species as O. antarctica are psychrophilic (Yakimov et al., 2003) and many of these genera populate hydrocarbon-seeps in the Gulf of Mexico (King et al., 2013).
The reason why these predominant hydrocarbonoclastic genera were not enriched at deep-sea is currently unknown. A moderately piezophilic Marinobacter hydrocarbonoclasticus strain could grow on C16 at 35 MPa (∼3 times higher than DWH plume HP; Grossi et al., 2010). As Alcanivorax abundance in bathypelagic water (Gutierrez et al., 2013b) and sediments was low (Kimes et al., 2013) and unrelated to hydrocarbons (Kimes et al., 2013) its contribution to deep-sea bioremediation was considered negligible (Gutierrez et al., 2013b). Alcanivorax isolates were obtained from decompressed water samples (Gutierrez et al., 2013b) resembling results and HP conditions for oil mousses (Liu and Liu, 2013) and beach sands (Kostka et al., 2011). Alcanivorax species isolated from 2682 to 5000 m bsl (up to 50 MPa, Liu and Shao, 2005; Lai et al., 2011) could not grow below 10°C, i.e., at much higher temperature values than those registered for these depths (<4°C). Another Alcanivorax strain was isolated from 668 m bsl (∼6.7 MPa, Lai et al., 2013). However, the isolation protocols employed in these studies did not apply HP. The first HP experiments on Alcanivorax were reported by the present group (Scoma and Boon, 2016; Scoma et al., 2016a,b). A mild increase to 5 MPa (∼500 m bsl) was sufficient to impair cell replication in Alcanivorax dieselolei and A. jadensis. Increase to 10 MPa in A. dieselolei (approximately the oil plume HP) further impaired growth, in concomitance with a general downregulation of its genome expression. The few upregulated pathways related to protein translation, energy production and Na+ transporters (Scoma et al., 2016a,b). Similarly, in the type strain Alcanivorax borkumensis SK2 the increased cell damage at 10 MPa was consistent with the intracellular accumulation of the piezolyte ectoine, and further studies on hypo- and hyper-osmotic stimulation highlighted that enhanced cell metabolism or integrity did not improve growth at 10 MPa (Scoma and Boon, 2016).
Hydrostatic pressure affects enzyme folding (Oger and Jebbar, 2010), cellular components (Bartlett et al., 1995) and functions, which may be gradually downregulated, triggered (Clouston and Wills, 1970; Kalchayanand et al., 2002; Ishii et al., 2004) or non-linearly induced (Pagàn and Mackey, 2000). Sphingobium yanoikuyae growth was suddenly impaired at >8.8 MPa when supplying naphthalene (or glucose, Schedler et al., 2014). A. borkumensis cultures growing on C12 were inactivated at 5 MPa but could grow at 10 MPa (Scoma et al., 2016b). Both growth and C16 degradation rates were reduced at 15 MPa in Rhodococcus qingshengii (Schedler et al., 2014). HP impact on oil biodegradation rates has been critically overlooked. Hazen et al. (2010) proposed half-lives of 6 days for plume-related n-alkanes supported by ex situ ambient pressure experiments, while in situ measurements indicated 1 month half-lives for water-soluble petroleum-hydrocarbons (Reddy et al., 2012). The main constraints to deep-sea oil bioremediation are yet to be elucidated. Injection of 3 × 106 liters of COREXIT dispersant at deep sea implies that bioavailability was considered a major issue. The negligible degradation rates of its key components and its unknown effect on deep-sea environments (Kujawinski et al., 2011) challenge this assumption. Understanding whether biosurfactant production or microbial adhesion to hydrocarbons is limited by HP and/or temperature may already assist policymakers in establishing efficient protocols for deep-sea bioremediation.
Future Perspectives
The limited literature on lab-scale oil degradation under HP (Schwarz et al., 1974, 1975; Grossi et al., 2010; Schedler et al., 2014; Scoma and Boon, 2016; Scoma et al., 2016a,b) does not explain how microbes cooperate/compete for petroleum-hydrocarbons, extracellular metabolites, O2 or nutrients.
The main structure-function mechanisms shaping microbial communities following deep-sea spills are unclear. Cell growth in the plume was proposed as a main response to oil release (Hazen et al., 2010; Mason et al., 2012; Kleindienst et al., 2015). However, metadata also indicated an enhanced response to stress (Hazen et al., 2010; Rivers et al., 2013) including starvation (Lu et al., 2012; Rivers et al., 2013), carbon storage (Rivers et al., 2013), and resistance to metals (Hazen et al., 2010; Lu et al., 2012). Similar results were obtained with sediments (Kimes et al., 2013; Mason et al., 2014; Yergeau et al., 2015). The M. hydrocarbonoclasticus tested at 35 MPa by Grossi et al. (2010) used C16 to feed both growth and the accumulation of intracellular wax esters. However, microbial dynamics may respond to compounds not typically analyzed in field samples as polar compounds (Reddy et al., 2012).
State-of-the-art technology can already be used to face the problem of deep-sea oil bioremediation by integrating molecular, physiological, and biochemical tools in a fully controlled environment. In situ hydrocarbon degradation rates must be confirmed by ex situ HP experiments in vivo and in vitro. Recent reports on methanotroph enrichments stressed the importance of cultivation techniques (Dedysh et al., 2012), supporting the use of synthetic communities to highlight the contribution of different individual genera to biodegradation activities. Some microbial representatives produce EPS to increase oil bioavailability for the benefit of the whole community (Gutierrez et al., 2013a). Enriched communities may be composed of opportunistic microbes which do not contribute to oil remediation. Defining the exact role of primary oil degraders with respect to other genera is key to addressing the specific requirements of each representative, and may explain how deep-sea areas are evolving following oil spills. Continuously operated HP systems may prevent accumulation of toxic compounds and provide more accurate data on microbial kinetics (Zhang et al., 2010, 2011). Isotopic experiments under HP should clarify whether oil fuels cell division, production of secondary metabolites or other unexpected activities. Improved biodegradation rates through the supply of critical nutrients should be compared with the impact of dispersants. The fate of tar components should be characterized, together with the role of SRB in long-term exposed sediments. These considerations must extend to temperature, as warmer seas may possess a different microbial potential (e.g., the warm bathypelagic Mediterranean sea). Deep-sea HP and low temperature impact the physicochemical state of the oil (Reddy et al., 2012) affecting its bioavailability. Low temperature is expected to slow microbial kinetics and select for psychrophiles (Atlas and Bartha, 1972). Provided that deep-sea oil bioremediation is affected by the interplay between several biological and physical factors, laboratory experiments must consider HP and temperature simultaneously to mimic deep-sea conditions.
Author Contributions
AS conceived the project and wrote the review. MY and NB discussed and supervised the project and co-wrote the review.
Conflict of Interest Statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Acknowledgments
Research leading to these findings was conducted with the financial support of the FP7-EU project Kill Spill (grant agreement, No. 312139, “Integrated Biotechnological Solutions for Combating Marine Oil Spills”). Mr. Tim Lacoere is acknowledged for Figure 1.
Footnotes
Funding. This work was funded by FP-7 project Kill Spill (No. 312139, “Integrated Biotechnological Solutions for Combating Marine Oil Spills”).
References
- Atlas R. M., Bartha R. (1972). Biodegradation of petroleum in seawater at low temperatures. Can. J. Microbiol. 18 1851–1855. 10.1139/m72-289 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartlett D. H., Kato C., Horikoshi K. (1995). High pressure influences on gene and protein expression. Res. Microbiol. 146 697–706. 10.1016/0923-2508(96)81066-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buist I., Trudel K., Morrison J., Aurand D. (1997). Laboratory studies of the properties of in-situ burn residues. Int. Oil Spill Conf. Proc. 1997 149–156. 10.7901/2169-3358-1997-1-149 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Bælum J., Borglin S., Chakraborty R., Fortney J. L., Lamendella R., Mason O. U., et al. (2012). Deep-sea bacteria enriched by oil and dispersant from the Deepwater Horizon spill. Environ. Microbiol. 14 2405–2416. 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2012.02780.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camilli R., Reddy C. M., Yoerger D. R., Van Mooy B. A., Jakuba M. V., Kinsey J. C., et al. (2010). Tracking hydrocarbon plume transport and biodegradation at Deepwater Horizon. Science 330 201–204. 10.1126/science.1195223 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chanton J., Zhao T., Rosenheim B. E., Joye S., Bosman S., Brunner C., et al. (2014). Using natural abundance radiocarbon to trace the flux of petrocarbon to the seafloor following the Deepwater Horizon oil spill. Environ. Sci. Technol. 49 847–854. 10.1021/es5046524 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clouston J. G., Wills P. A. (1970). Kinetics of initiation of germination of Bacillus pumilus spores by hydrostatic pressure. J. Bacteriol. 103 140–143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crespo-Medina M., Meile C. D., Hunter K. S., Diercks A. R., Asper V., Orphan V. J., et al. (2014). The rise and fall of methanotrophy following a deepwater oil-well blowout. Nat. Geosci. 7 423–427. 10.1038/ngeo2156 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Dedysh S. N., Kulichevskaya I. S., Serkebaeva Y. M., Mityaeva M. A., Sorokin V. V., Suzina N. E., et al. (2012). Bryocella elongata gen. nov., sp. nov., a member of subdivision 1 of the Acidobacteria isolated from a methanotrophic enrichment culture, and emended description of Edaphobacter aggregans Koch et al. 2008. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 62 654–664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diercks A. R., Highsmith R. C., Asper V. L., Joung D., Zhou Z., Guo L., et al. (2010). Characterization of subsurface polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons at the Deepwater Horizon site. Geophys. Res. Lett. 37:L20602 10.1029/2010GL045046 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Dombrowski N., Donaho J. A., Gutierrez T., Seitz K. W., Teske A. P., Baker B. J. (2016). Reconstructing metabolic pathways of hydrocarbon-degrading bacteria from the Deepwater Horizon oil spill. Nat. Microbiol. 1:16057 10.1038/nmicrobiol.2016.57 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Du M., Kessler J. D. (2012). Assessment of the spatial and temporal variability of bulk hydrocarbon respiration following the Deepwater Horizon oil spill. Environ. Sci. Technol. 46 10499–10507. 10.1021/es301363k [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubinsky E. A., Conrad M. E., Chakraborty R., Bill M., Borglin S. E., Hollibaugh J. T., et al. (2013). Succession of hydrocarbon-degrading bacteria in the aftermath of the Deepwater Horizon oil spill in the Gulf of Mexico. Environ. Sci. Technol. 47 10860–10867. 10.1021/es401676y [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Federal Interagency Solution Group (2010). Oil Budget Calculator Science and Engineering team 2010. Oil Budget Calculator Technical Documentation. Available at: www.noaanews.noaa.gov/stories2010/PDFs/OilBudgetCalc_Full_HQ-Print_111110.pdf [Google Scholar]
- Garrison T. (2015). Oceanography: An Invitation to Marine Science. Boston, MA: Cengage Learning. [Google Scholar]
- Ghiglione J. F., Galand P. E., Pommier T., Pedrós-Alió C., Maas E. W., Bakker K., et al. (2012). Pole-to-pole biogeography of surface and deep marine bacterial communities. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 109 17633–17638. 10.1073/pnas.1208160109 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossi V., Yakimov M. M., Al Ali B., Tapilatu Y., Cuny P., Goutx M., et al. (2010). Hydrostatic pressure affects membrane and storage lipid compositions of the piezotolerant hydrocarbon-degrading Marinobacter hydrocarbonoclasticus strain# 5. Environ. Microbiol. 12 2020–2033. 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2010.02213.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutierrez T., Berry D., Yang T., Mishamandani S., McKay L., Teske A., et al. (2013a). Role of bacterial exopolysaccharides (EPS) in the fate of the oil released during the Deepwater Horizon oil spill. PLoS ONE 8:e67717 10.1371/journal.pone.0067717 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutierrez T., Singleton D. R., Berry D., Yang T., Aitken M. D., Teske A. (2013b). Hydrocarbon-degrading bacteria enriched by the Deepwater Horizon oil spill identified by cultivation and DNA-SIP. ISME J. 7 2091–2104. 10.1038/ismej.2013.98 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazen T. C., Dubinsky E. A., DeSantis T. Z., Andersen G. L., Piceno Y. M., Singh N., et al. (2010). Deep-sea oil plume enriches indigenous oil-degrading bacteria. Science 330 204–208. 10.1126/science.1195979 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Head I. M., Jones D. M., Röling W. F. (2006). Marine microorganisms make a meal of oil. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 4 173–182. 10.1038/nrmicro1348 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishii A., Sato T., Wachi M., Nagai K., Kato C. (2004). Effects of high hydrostatic pressure on bacterial cytoskeleton FtsZ polymers in vivo and in vitro. Microbiology 150 1965–1972. 10.1099/mic.0.26962-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jernelov A. (2010). How to defend against future oil spills. Nature 466 182–183. 10.1038/466182a [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jézéquel R., Simon R., Pirot V. (2014). “Development of a burning bench dedicated to in situ burning study: assessment of oil nature and weathering effect,” in Proceedings of the 37th AMOP Technical Seminar on Environmental Contamination and Response, Environment Canada, Ottawa, ON, 555–566. [Google Scholar]
- Joint Analysis Group [JAG] (2010). Review of R/V Brooks McCall Data to Examine Subsurface Oil. NOAA Report Silver Spring, MD: NOAA. [Google Scholar]
- Jørgensen B. B., Boetius A. (2007). Feast and famine - microbial life in the deep-sea bed. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 5 770–781. 10.1038/nrmicro1745 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joye S. B., MacDonald I. R., Leifer I., Asper V. (2011). Magnitude and oxidation potential of hydrocarbon gases released from the BP oil well blowout. Nat. Geosci. 4 160–164. 10.1038/ngeo1067 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Joye S. B., Teske A. P., Kostka J. E. (2014). Microbial dynamics following the Macondo oil well blowout across Gulf of Mexico environments. BioScience 64 766–777. 10.1093/biosci/biu121 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Kalchayanand N., Frethem C., Dunne P., Sikes A., Ray B. (2002). Hydrostatic pressure and bacteriocin-triggered cell wall lysis of Leuconostoc mesenteroides. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 3 33–40. 10.1016/S1466-8564(02)00004-8 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler J. D., Valentine D. L., Redmond M. C., Du M., Chan E. W., Mendes S. D., et al. (2011). A persistent oxygen anomaly reveals the fate of spilled methane in the deep Gulf of Mexico. Science 331 312–315. 10.1126/science.1199697 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimes N. E., Callaghan A. V., Aktas D. F., Smith W. L., Sunner J., Golding B., et al. (2013). Metagenomic analysis and metabolite profiling of deep-sea sediments from the Gulf of Mexico following the Deepwater Horizon oil spill. Front. Microbiol. 4:50 10.3389/fmicb.2013.00050 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimes N. E., Callaghan A. V., Suflita J. M., Morris P. J. (2014). Microbial transformation of the Deepwater Horizon oil spill - past, present, and future perspectives. Front. Microbiol. 5:603 10.3389/fmicb.2014.00603 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King G. M., Kostka J. E., Hazen T. C., Sobecky P. A. (2015). Microbial responses to the Deepwater Horizon oil spill: from coastal wetlands to the deep sea. Annu. Review Mar. Sci. 7 377–401. 10.1146/annurev-marine-010814-015543 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King G. M., Smith C. B., Tolar B., Hollibaugh J. T. (2013). Analysis of composition and structure of coastal to mesopelagic bacterioplankton communities in the northern Gulf of Mexico. Front. Microbiol. 3:438 10.3389/fmicb.2012.00438 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleindienst S., Grim S., Sogin M., Bracco A., Crespo-Medina M., Joye S. B. (2015). Diverse, rare microbial taxa responded to the Deepwater Horizon deep-sea hydrocarbon plume. ISME J. 10 400–415. 10.1038/ismej.2015.121 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostka J. E., Prakash O., Overholt W. A., Green S. J., Freyer G., Canion A., et al. (2011). Hydrocarbon-degrading bacteria and the bacterial community response in Gulf of Mexico beach sands impacted by the Deepwater Horizon oil spill. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 77 7962–7974. 10.1128/AEM.05402-11 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kujawinski E. B., Kido Soule M. C., Valentine D. L., Boysen A. K., Longnecker K., Redmond M. C. (2011). Fate of dispersants associated with the Deepwater Horizon oil spill. Environ. Sci. Technol. 45 1298–1306. 10.1021/es103838p [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai Q., Wang J., Gu L., Zheng T., Shao Z. (2013). Alcanivorax marinus sp. nov., isolated from deep sea water of Indian Ocean. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 63 4428–4432. 10.1099/ijs.0.049957-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai Q., Wang L., Liu Y., Fu Y., Zhong H., Wang B., et al. (2011). Alcanivorax pacificus sp. nov., isolated from a deep-sea pyrene-degrading consortium. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 61 1370–1374. 10.1099/ijs.0.022368-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu C., Shao Z. (2005). Alcanivorax dieselolei sp. nov., a novel alkane-degrading bacterium isolated from sea water and deep-sea sediment. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 55 1181–1186. 10.1099/ijs.0.63443-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu Z., Liu J. (2013). Evaluating bacterial community structures in oil collected from the sea surface and sediment in the northern Gulf of Mexico after the Deepwater Horizon oil spill. Microbiol. Open 2 492–504. 10.1002/mbo3.89 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu Z., Liu J., Zhu Q., Wu W. (2012). The weathering of oil after the Deepwater Horizon oil spill: insights from the chemical composition of the oil from the sea surface, salt marshes and sediments. Environ. Res. Lett. 7:035302 10.1088/1748-9326/7/3/035302 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Lu Z., Deng Y., Van Nostrand J. D., He Z., Voordeckers J., Zhou A., et al. (2012). Microbial gene functions enriched in the Deepwater Horizon deep-sea oil plume. ISME J. 6 451–460. 10.1038/ismej.2011.91 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason O. U., Hazen T. C., Borglin S., Chain P. S., Dubinsky E. A., Fortney J. L., et al. (2012). Metagenome, metatranscriptome and single-cell sequencing reveal microbial response to Deepwater Horizon oil spill. ISME J. 6 1715–1727. 10.1038/ismej.2012.59 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason O. U., Scott N. M., Gonzalez A., Robbins-Pianka A., Bælum J., Kimbrel J., et al. (2014). Metagenomics reveals sediment microbial community response to Deepwater Horizon oil spill. ISME J. 8 1464–1475. 10.1038/ismej.2013.254 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay L. J., Gutierrez T., Teske A. P. (2013). Development of a group-specific 16S rRNA-targeted probe set for the identification of Marinobacter by fluorescence in situ hybridization. Deep Sea Res. II 129 360–367. 10.1016/j.dsr2.2013.10.009 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Oger P. M., Jebbar M. (2010). The many ways of coping with pressure. Res. Microbiol. 161 799–809. 10.1016/j.resmic.2010.09.017 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pagàn R., Mackey B. (2000). Relationship between membrane damage and cell death in pressure-treated Escherichia coli cells: differences between exponential- and stationary-phase cells and variation among strains. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 66 2829–2834. 10.1128/AEM.66.7.2829-2834.2000 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parinos C., Gogou A., Bouloubassi I., Pedrosa-Pàmies R., Hatzianestis I., Sanchez-Vidal A., et al. (2013). Occurrence, sources and transport pathways of natural and anthropogenic hydrocarbons in deep-sea sediments of the Eastern Mediterranean Sea. Biogeosciences 10 6069–6089. 10.5194/bg-10-6069-2013 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Passow U., Ziervogel K., Asper V., Diercks A. (2012). Marine snow formation in the aftermath of the Deepwater Horizon oil spill in the Gulf of Mexico. Environ. Res. Lett. 7 035301 10.1088/1748-9326/7/3/035301 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Patton J., Rigler M., Boehm P., Fiest D. (1981). Ixtoc 1 oil spill: flaking of surface mousse in the Gulf of Mexico. Nature 290 235–238. 10.1038/290235a0 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Paul J. H., Hollander D., Coble P., Daly K. L., Murasko S., English D., et al. (2013). Toxicity and mutagenicity of Gulf of Mexico waters during and after the Deepwater Horizon oil spill. Environ. Sci. Technol. 47 9651–9659. 10.1021/es401761h [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prouty N. G., Campbell P. L., Mienis F., Duineveld G., Demopoulos A. W., Ross S. W., et al. (2016). Impact of Deepwater Horizon Spill on food supply to deep-sea benthos communities. Estuar. Coast Shelf Sci. 169 248–264. 10.1016/j.ecss.2015.11.008 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Ramseur J. L. (2010). Deepwater Horizon Oil Spill: the Fate of the Oil. Washington, DC: Congressional Research Service, Library of Congress. [Google Scholar]
- Reddy C. M., Arey J. S., Seewald J. S., Sylva S. P., Lemkau K. L., Nelson R. K., et al. (2012). Composition and fate of gas and oil released to the water column during the Deepwater Horizon oil spill. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 109 20229–20234. 10.1073/pnas.1101242108 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redmond M. C., Valentine D. L. (2012). Natural gas and temperature structured a microbial community response to the Deepwater Horizon oil spill. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 109 20292–20297. 10.1073/pnas.1108756108 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivers A. R., Sharma S., Tringe S. G., Martin J., Joye S. B., Moran M. A. (2013). Transcriptional response of bathypelagic marine bacterioplankton to the Deepwater Horizon oil spill. ISME J. 7 2315–2329. 10.1038/ismej.2013.129 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rojo F. (2009). Degradation of alkanes by bacteria. Environ. Microbiol. 11 2477–2490. 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2009.01948.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romero I. C., Schwing P. T., Brooks G. R., Larson R. A., Hastings D. W., Ellis G., et al. (2015). Hydrocarbons in deep-sea sediments following the 2010 Deepwater Horizon blowout in the northeast Gulf of Mexico. PLoS ONE 10:e0128371 10.1371/journal.pone.0128371 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sammarco P. W., Kolian S. R., Warby R. A., Bouldin J. L., Subra W. A., Porter S. A., et al. (2013). Distribution and concentrations of petroleum hydrocarbons associated with the BP/Deepwater Horizon Oil Spill, Gulf of Mexico. Mar. Poll. Bull. 73 129–143. 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2013.05.029 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schedler M., Hiessl R., Valladares Juárez A. G., Gust G., Müller R. (2014). Effect of high pressure on hydrocarbon-degrading bacteria. AMB Express 4 1–7. 10.1186/s13568-014-0077-0 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz J. R., Walker J. D., Colwell R. R. (1974). Deep-sea bacteria: growth and utilization of hydrocarbons at ambient and in situ pressure. Appl. Microbiol. 28 982–986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz J. R., Walker J. D., Colwell R. R. (1975). Deep-sea bacteria: growth and utilization of n-hexadecane at in situ temperature and pressure. Can. J. Microbiol. 21 682–687. 10.1139/m75-098 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scoma A., Barbato M., Borin S., Daffonchio D., Boon N. (2016b). An impaired metabolic response to hydrostatic pressure explains A. borkumensis recorded distribution in the deep marine water column. Sci. Rep. (in press) 10.1038/srep31316 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scoma A., Barbato M., Hernandez-Sanabria E., Mapelli F., Daffonchio D., Borin S., et al. (2016a). Microbial oil-degradation under mild hydrostatic pressure (10 MPa): which pathways are impacted in piezosensitive hydrocarbonoclastic bacteria? Sci. Rep. 6:23526 10.1038/srep23526 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scoma A., Boon N. (2016). Osmotic stress confers cell protection to hydrostatic pressure but impairs growth in Alcanivorax borkumensis SK2. Front. Microbiol. 7:729 10.3389/fmicb.2016.00729 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thibodeaux L. J., Valsaraj K. T., John V. T., Papadopoulos K. D., Pratt L. R., Pesika N. S. (2011). Marine oil fate: knowledge gaps, basic research, and development needs; A perspective based on the Deepwater Horizon spill. Environ. Eng. Sci. 28 87–93. 10.1089/ees.2010.0276 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Tkalich P., Huda K., Hoong Gin K. Y. (2003). A multiphase oil spill model. J. Hydraul. Res. 41 115–125. 10.1080/00221680309499955 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- U.S. Geological Survey (2010). Deepwater Horizon MC252 Gulf Incident Oil Budget: Government Estimates - through August 01 (day 104). Available at: www.noaanews.noaa.gov/stories2010/PDFs/DeepwaterHorizonOilBudget20100801.pdf [Google Scholar]
- Valentine D. L., Kessler J. D., Redmond M. C., Mendes S. D., Heintz M. B., Farwell C., et al. (2010). Propane respiration jump-starts microbial response to a deep oil spill. Science 330 208–211. 10.1126/science.1196830 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Z., Fingas M. F., Landriault M., Sigouin L., Lambert P., Turpin R., et al. (1999). PAH Distribution in the 1994 and 1997 mobile burn products and determination of the diesel PAH destruction efficiencies. Int. Oil Spill Conf. Proc. 1999 1287–1292. 10.7901/2169-3358-1999-1-1287 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Widdel F., Rabus R. (2001). Anaerobic biodegradation of saturated and aromatic hydrocarbons. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 12 259–276. 10.1016/S0958-1669(00)00209-3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widder S., Allen R. J., Pfeiffer T., Curtis T. P., Wiuf C., Sloan W. T., et al. (2016). Challenges in microbial ecology: building predictive understanding of community function and dynamics. ISME J. 10.1038/ismej.2016.45 [Epub ahead of print]. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang T., Nigro L. M., Gutierrez T., D’Ambrosio L., Joye S. B., Highsmith R., et al. (2014). Pulsed blooms and persistent oil-degrading bacterial populations in the water column during and after the Deepwater Horizon blowout. Deep Sea Res. Part II Top. Stud. Oceanogr. 129 282–291. 10.1016/j.dsr2.2014.01.014 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Yakimov M. M., Giuliano L., Gentile G., Crisafi E., Chernikova T. N., Abraham W. R., et al. (2003). Oleispira antarctica gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel hydrocarbonoclastic marine bacterium isolated from Antarctic coastal sea water. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 53 779–785. 10.1099/ijs.0.02366-0 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yergeau E., Maynard C., Sanschagrin S., Champagne J., Juck D., Lee K., et al. (2015). Microbial community composition, functions, and activities in the Gulf of Mexico 1 year after the deepwater horizon accident. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 81 5855–5866. 10.1128/AEM.01470-15 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Y., Henriet J. P., Bursens J., Boon N. (2010). Stimulation of in vitro anaerobic oxidation of methane rate in a continuous high-pressure bioreactor. Biores. Technol. 101 3132–3138. 10.1016/j.biortech.2009.11.103 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Y., Maignien L., Zhao X., Wang F., Boon N. (2011). Enrichment of a microbial community performing anaerobic oxidation of methane in a continuous high-pressure bioreactor. BMC Microbiol. 11:137 10.1186/1471-2180-11-137 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziervogel K., Joye S. B., Arnosti C. (2014). Microbial enzymatic activity and secondary production in sediments affected by the sedimentation pulse following the Deepwater Horizon oil spill. Deep Sea Res. II 129 241–248. 10.1016/j.dsr2.2014.04.003 [DOI] [Google Scholar]