Abstract
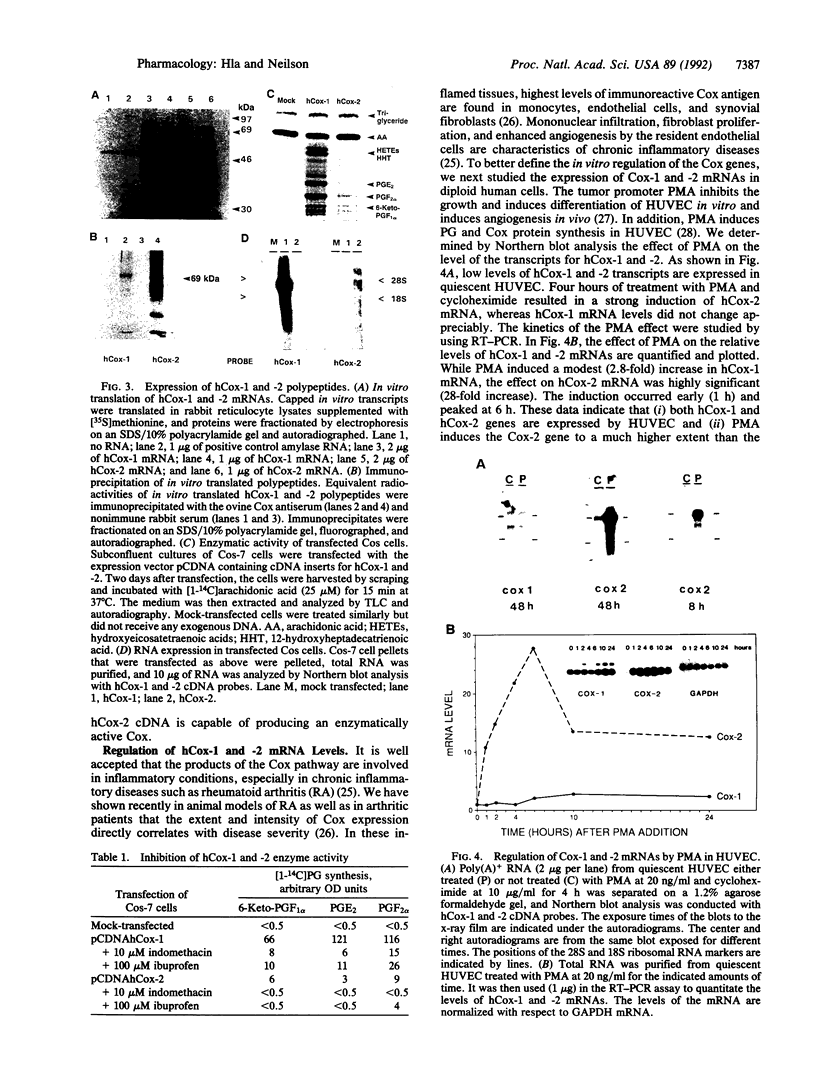
Cyclooxygenase (Cox), also known as prostaglandin (PG) H synthase (EC 1.14.99.1), catalyzes the rate-limiting step in the formation of inflammatory PGs. A major regulatory step in PG biosynthesis is at the level of Cox: growth factors, cytokines, and tumor promoters induce Cox activity. We have cloned the second form of the Cox gene (Cox-2) from human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC). The cDNA encodes a polypeptide of 604 amino acids that is 61% identical to the previously isolated human Cox-1 polypeptide. In vitro translation of the human (h)Cox-2 transcript in rabbit reticulocyte lysates resulted in the synthesis of a 70-kDa protein that is immunoprecipitated by antiserum to ovine Cox. Expression of the hCox-2 open reading frame in Cos-7 monkey kidney cells results in the elaboration of cyclooxygenase activity. hCox-2 cDNA hybridizes to a 4.5-kilobase mRNA species in HUVEC, whereas the hCox-1 cDNA hybridizes to 3- and 5.3-kilobase species. Both Cox-1 and Cox-2 mRNAs are expressed in HUVEC, vascular smooth muscle cells, monocytes, and fibroblasts. Cox-2 mRNA was preferentially induced by phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate and lipopolysaccharide in human endothelial cells and monocytes. Together, these data demonstrate that the Cox enzyme is encoded by at least two genes that are expressed and differentially regulated in a variety of cell types. High-level induction of the hCox-2 transcript in mesenchymal-derived inflammatory cells suggests a role in inflammatory conditions.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bailey J. M., Muza B., Hla T., Salata K. Restoration of prostacyclin synthase in vascular smooth muscle cells after aspirin treatment: regulation by epidermal growth factor. J Lipid Res. 1985 Jan;26(1):54–61. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeWitt D. L. Prostaglandin endoperoxide synthase: regulation of enzyme expression. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 May 8;1083(2):121–134. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(91)90032-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeWitt D. L., el-Harith E. A., Kraemer S. A., Andrews M. J., Yao E. F., Armstrong R. L., Smith W. L. The aspirin and heme-binding sites of ovine and murine prostaglandin endoperoxide synthases. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 25;265(9):5192–5198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu J. Y., Masferrer J. L., Seibert K., Raz A., Needleman P. The induction and suppression of prostaglandin H2 synthase (cyclooxygenase) in human monocytes. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 5;265(28):16737–16740. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goerig M., Habenicht A. J., Zeh W., Salbach P., Kommerell B., Rothe D. E., Nastainczyk W., Glomset J. A. Evidence for coordinate, selective regulation of eicosanoid synthesis in platelet-derived growth factor-stimulated 3T3 fibroblasts and in HL-60 cells induced to differentiate into macrophages or neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 25;263(36):19384–19391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habenicht A. J., Goerig M., Grulich J., Rothe D., Gronwald R., Loth U., Schettler G., Kommerell B., Ross R. Human platelet-derived growth factor stimulates prostaglandin synthesis by activation and by rapid de novo synthesis of cyclooxygenase. J Clin Invest. 1985 Apr;75(4):1381–1387. doi: 10.1172/JCI111839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris E. D., Jr Rheumatoid arthritis. Pathophysiology and implications for therapy. N Engl J Med. 1990 May 3;322(18):1277–1289. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199005033221805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III creates targeted breakpoints for DNA sequencing. Gene. 1984 Jun;28(3):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hla T., Farrell M., Kumar A., Bailey J. M. Isolation of the cDNA for human prostaglandin H synthase. Prostaglandins. 1986 Dec;32(6):829–845. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(86)90093-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hla T., Maciag T. An abundant transcript induced in differentiating human endothelial cells encodes a polypeptide with structural similarities to G-protein-coupled receptors. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 5;265(16):9308–9313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hla T., Maciag T. Cyclooxygenase gene expression is down-regulated by heparin-binding (acidic fibroblast) growth factor-1 in human endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Dec 15;266(35):24059–24063. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. An analysis of 5'-noncoding sequences from 699 vertebrate messenger RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 26;15(20):8125–8148. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.20.8125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kujubu D. A., Fletcher B. S., Varnum B. C., Lim R. W., Herschman H. R. TIS10, a phorbol ester tumor promoter-inducible mRNA from Swiss 3T3 cells, encodes a novel prostaglandin synthase/cyclooxygenase homologue. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 15;266(20):12866–12872. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin A. H., Bienkowski M. J., Gorman R. R. Regulation of prostaglandin H synthase mRNA levels and prostaglandin biosynthesis by platelet-derived growth factor. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 15;264(29):17379–17383. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maciag T., Kadish J., Wilkins L., Stemerman M. B., Weinstein R. Organizational behavior of human umbilical vein endothelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;94(3):511–520. doi: 10.1083/jcb.94.3.511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maier J. A., Hla T., Maciag T. Cyclooxygenase is an immediate-early gene induced by interleukin-1 in human endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 5;265(19):10805–10808. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masferrer J. L., Zweifel B. S., Seibert K., Needleman P. Selective regulation of cellular cyclooxygenase by dexamethasone and endotoxin in mice. J Clin Invest. 1990 Oct;86(4):1375–1379. doi: 10.1172/JCI114850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montesano R., Orci L. Phorbol esters induce angiogenesis in vitro from large-vessel endothelial cells. J Cell Physiol. 1987 Feb;130(2):284–291. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041300215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Needleman P., Turk J., Jakschik B. A., Morrison A. R., Lefkowith J. B. Arachidonic acid metabolism. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:69–102. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.000441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R. Control of protein exit from the endoplasmic reticulum. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1989;5:1–23. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.05.110189.000245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raz A., Wyche A., Siegel N., Needleman P. Regulation of fibroblast cyclooxygenase synthesis by interleukin-1. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 25;263(6):3022–3028. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossi V., Breviario F., Ghezzi P., Dejana E., Mantovani A. Prostacyclin synthesis induced in vascular cells by interleukin-1. Science. 1985 Jul 12;229(4709):174–176. doi: 10.1126/science.2409598. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sano H., Hla T., Maier J. A., Crofford L. J., Case J. P., Maciag T., Wilder R. L. In vivo cyclooxygenase expression in synovial tissues of patients with rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis and rats with adjuvant and streptococcal cell wall arthritis. J Clin Invest. 1992 Jan;89(1):97–108. doi: 10.1172/JCI115591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw G., Kamen R. A conserved AU sequence from the 3' untranslated region of GM-CSF mRNA mediates selective mRNA degradation. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):659–667. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90341-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimokawa T., Smith W. L. Essential histidines of prostaglandin endoperoxide synthase. His-309 is involved in heme binding. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 5;266(10):6168–6173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whiteley P. J., Needleman P. Mechanism of enhanced fibroblast arachidonic acid metabolism by mononuclear cell factor. J Clin Invest. 1984 Dec;74(6):2249–2253. doi: 10.1172/JCI111651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu K. K., Hatzakis H., Lo S. S., Seong D. C., Sanduja S. K., Tai H. H. Stimulation of de novo synthesis of prostaglandin G/H synthase in human endothelial cells by phorbol ester. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 15;263(35):19043–19047. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xie W. L., Chipman J. G., Robertson D. L., Erikson R. L., Simmons D. L. Expression of a mitogen-responsive gene encoding prostaglandin synthase is regulated by mRNA splicing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 1;88(7):2692–2696. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.7.2692. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]