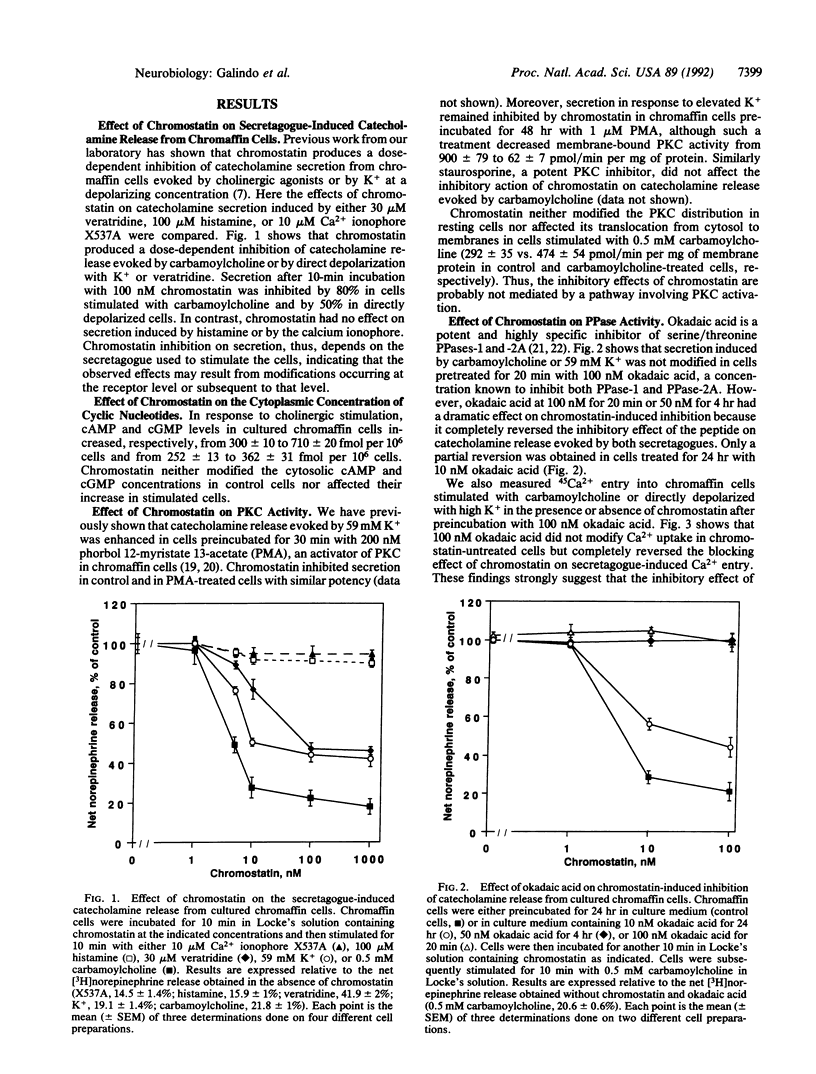
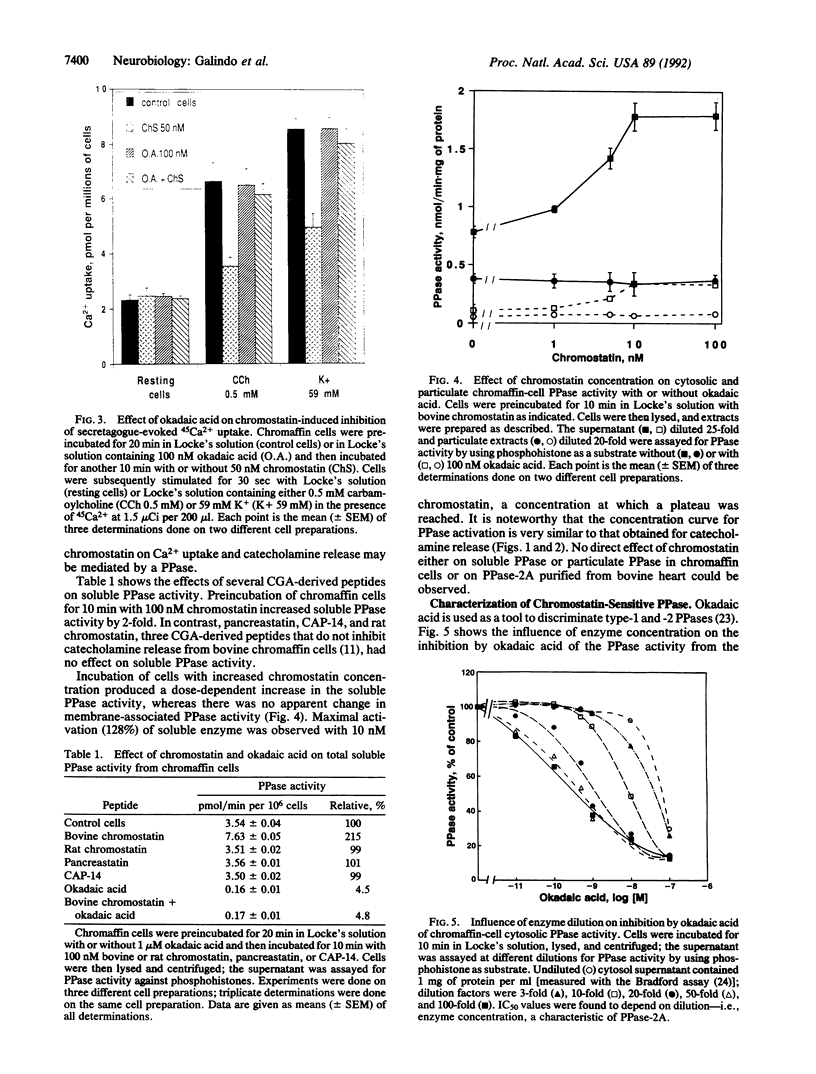
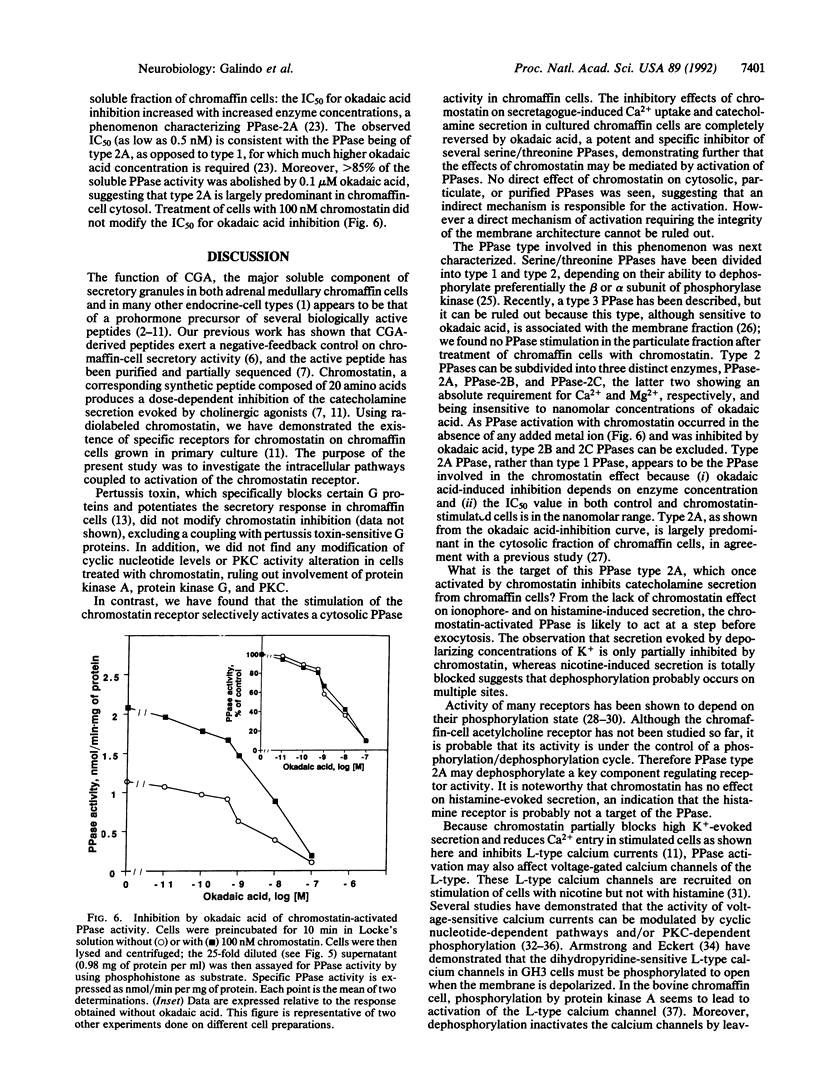
Abstract
Chromostatin is a 20-residue peptide derived from chromogranin A (CGA), the major soluble component of secretory granules in adrenal medullary chromaffin cells. One known biological function of chromostatin is to inhibit the secretagogue-evoked catecholamine secretion from chromaffin cells. Putative receptors are present on the chromaffin-cell plasma membrane, and the activation of such receptors leads to the inhibition of L-type voltage-sensitive calcium channels. We report here that exposure of chromaffin cells to chromostatin modifies neither cAMP and cGMP levels nor protein kinase C activity but does provoke the activation of soluble protein phosphatase (PPase) type 2A in a dose-dependent manner compatible with the peptide concentration inhibiting catecholamine secretion. The activation of the PPase as well as the inhibition of both secretagogue-induced Ca2+ entry and catecholamine secretion by chromostatin were all blocked by okadaic acid, a specific PPase inhibitor. We suggest that chromostatin directly or indirectly stimulates PPase-2A, dephosphorylating a target protein and lowering its activity in the secretory process.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armstrong D., Eckert R. Voltage-activated calcium channels that must be phosphorylated to respond to membrane depolarization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2518–2522. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Artalejo C. R., Ariano M. A., Perlman R. L., Fox A. P. Activation of facilitation calcium channels in chromaffin cells by D1 dopamine receptors through a cAMP/protein kinase A-dependent mechanism. Nature. 1990 Nov 15;348(6298):239–242. doi: 10.1038/348239a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Artalejo C. R., García A. G., Aunis D. Chromaffin cell calcium channel kinetics measured isotopically through fast calcium, strontium, and barium fluxes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 15;262(2):915–926. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bader M. F., Sontag J. M., Thiersé D., Aunis D. A reassessment of guanine nucleotide effects on catecholamine secretion from permeabilized adrenal chromaffin cells. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 5;264(28):16426–16434. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bader M. F., Thiersé D., Aunis D., Ahnert-Hilger G., Gratzl M. Characterization of hormone and protein release from alpha-toxin-permeabilized chromaffin cells in primary culture. J Biol Chem. 1986 May 5;261(13):5777–5783. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bialojan C., Takai A. Inhibitory effect of a marine-sponge toxin, okadaic acid, on protein phosphatases. Specificity and kinetics. Biochem J. 1988 Nov 15;256(1):283–290. doi: 10.1042/bj2560283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P. Classification of protein-serine/threonine phosphatases: identification and quantitation in cell extracts. Methods Enzymol. 1991;201:389–398. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)01035-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P., Holmes C. F., Tsukitani Y. Okadaic acid: a new probe for the study of cellular regulation. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Mar;15(3):98–102. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90192-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deftos L. J., Hogue-Angeletti R., Chalberg C., Tu S. A chromogranin A-derived peptide differentially regulates the secretion of calcitonin gene products. J Bone Miner Res. 1990 Sep;5(9):989–991. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.5650050913. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dohlman H. G., Thorner J., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Model systems for the study of seven-transmembrane-segment receptors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:653–688. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.60.070191.003253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Efendić S., Tatemoto K., Mutt V., Quan C., Chang D., Ostenson C. G. Pancreastatin and islet hormone release. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):7257–7260. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.7257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galindo E., Mendez M., Calvo S., Gonzalez-Garcia C., Ceña V., Hubert P., Bader M. F., Aunis D. Chromostatin receptors control calcium channel activity in adrenal chromaffin cells. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 5;267(1):407–412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galindo E., Rill A., Bader M. F., Aunis D. Chromostatin, a 20-amino acid peptide derived from chromogranin A, inhibits chromaffin cell secretion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 15;88(4):1426–1430. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.4.1426. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goh Y., Kurosawa A. Characterization and Ca2+ requirement of histamine-induced catecholamine secretion in cultured bovine chromaffin cells. J Neurochem. 1991 Oct;57(4):1249–1257. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1991.tb08286.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haavik J., Schelling D. L., Campbell D. G., Andersson K. K., Flatmark T., Cohen P. Identification of protein phosphatase 2A as the major tyrosine hydroxylase phosphatase in adrenal medulla and corpus striatum: evidence from the effects of okadaic acid. FEBS Lett. 1989 Jul 17;251(1-2):36–42. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81424-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemmings H. C., Jr, Nairn A. C., McGuinness T. L., Huganir R. L., Greengard P. Role of protein phosphorylation in neuronal signal transduction. FASEB J. 1989 Mar;3(5):1583–1592. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.3.5.2493406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homcy C. J., Vatner S. F., Vatner D. E. Beta-adrenergic receptor regulation in the heart in pathophysiologic states: abnormal adrenergic responsiveness in cardiac disease. Annu Rev Physiol. 1991;53:137–159. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.53.030191.001033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honkanen R. E., Zwiller J., Daily S. L., Khatra B. S., Dukelow M., Boynton A. L. Identification, purification, and characterization of a novel serine/threonine protein phosphatase from bovine brain. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 5;266(10):6614–6619. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huganir R. L., Greengard P. Regulation of neurotransmitter receptor desensitization by protein phosphorylation. Neuron. 1990 Nov;5(5):555–567. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(90)90211-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingebritsen T. S., Cohen P. The protein phosphatases involved in cellular regulation. 1. Classification and substrate specificities. Eur J Biochem. 1983 May 2;132(2):255–261. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07357.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishizuka J., Asada I., Poston G. J., Lluis F., Tatemoto K., Greeley G. H., Jr, Thompson J. C. Effect of pancreastatin on pancreatic endocrine and exocrine secretion. Pancreas. 1989;4(3):277–281. doi: 10.1097/00006676-198906000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Killilea S. D., Aylward J. H., Mellgren R. L., Lee E. Y. Purification and properties of bovine myocardial phosphorylase phosphatase (protein phosphatase C). Arch Biochem Biophys. 1978 Dec;191(2):638–646. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(78)90402-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klumpp S., Cohen P., Schultz J. E. Okadaic acid, an inhibitor of protein phosphatase 1 in Paramecium, causes sustained Ca2(+)-dependent backward swimming in response to depolarizing stimuli. EMBO J. 1990 Mar;9(3):685–689. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08160.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostyuk P. G. Metabolic control of ionic channels in the neuronal membrane. Neuroscience. 1984 Dec;13(4):983–989. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(84)90282-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis J. J., Goldenring J. R., Asher V. A., Modlin I. M. Pancreastatin: a novel peptide inhibitor of parietal cell signal transduction. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Sep 15;163(2):667–673. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92275-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meisler M. H., Langan T. A. Characterization of a phosphatase specific for phosphorylated histones and protamine. J Biol Chem. 1969 Sep 25;244(18):4961–4968. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Méry P. F., Lohmann S. M., Walter U., Fischmeister R. Ca2+ current is regulated by cyclic GMP-dependent protein kinase in mammalian cardiac myocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 15;88(4):1197–1201. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.4.1197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nunoki K., Florio V., Catterall W. A. Activation of purified calcium channels by stoichiometric protein phosphorylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6816–6820. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6816. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinhart P. H., Chung S., Martin B. L., Brautigan D. L., Levitan I. B. Modulation of calcium-activated potassium channels from rat brain by protein kinase A and phosphatase 2A. J Neurosci. 1991 Jun;11(6):1627–1635. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.11-06-01627.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuter H. Calcium channel modulation by neurotransmitters, enzymes and drugs. Nature. 1983 Feb 17;301(5901):569–574. doi: 10.1038/301569a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarafian T., Pradel L. A., Henry J. P., Aunis D., Bader M. F. The participation of annexin II (calpactin I) in calcium-evoked exocytosis requires protein kinase C. J Cell Biol. 1991 Sep;114(6):1135–1147. doi: 10.1083/jcb.114.6.1135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon J. P., Aunis D. Biochemistry of the chromogranin A protein family. Biochem J. 1989 Aug 15;262(1):1–13. doi: 10.1042/bj2620001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon J. P., Bader M. F., Aunis D. Secretion from chromaffin cells is controlled by chromogranin A-derived peptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(5):1712–1716. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.5.1712. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sontag J. M., Sanderson P., Klepper M., Aunis D., Takeda K., Bader M. F. Modulation of secretion by dopamine involves decreases in calcium and nicotinic currents in bovine chromaffin cells. J Physiol. 1990 Aug;427:495–517. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1990.sp018184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sontag J. M., Thierse D., Rouot B., Aunis D., Bader M. F. A pertussis-toxin-sensitive protein controls exocytosis in chromaffin cells at a step distal to the generation of second messengers. Biochem J. 1991 Mar 1;274(Pt 2):339–347. doi: 10.1042/bj2740339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tatemoto K., Efendić S., Mutt V., Makk G., Feistner G. J., Barchas J. D. Pancreastatin, a novel pancreatic peptide that inhibits insulin secretion. Nature. 1986 Dec 4;324(6096):476–478. doi: 10.1038/324476a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trautwein W., Hescheler J. Regulation of cardiac L-type calcium current by phosphorylation and G proteins. Annu Rev Physiol. 1990;52:257–274. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.52.030190.001353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. W., Lipscombe D., Madison D. V., Bley K. R., Fox A. P. Multiple types of neuronal calcium channels and their selective modulation. Trends Neurosci. 1988 Oct;11(10):431–438. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(88)90194-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wand G. S., Takiyyuddin M., O'Connor D. T., Levine M. A. A proposed role for chromogranin A as a glucocorticoid-responsive autocrine inhibitor of proopiomelanocortin secretion. Endocrinology. 1991 Mar;128(3):1345–1351. doi: 10.1210/endo-128-3-1345. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White R. E., Schonbrunn A., Armstrong D. L. Somatostatin stimulates Ca(2+)-activated K+ channels through protein dephosphorylation. Nature. 1991 Jun 13;351(6327):570–573. doi: 10.1038/351570a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zwiller J., Ogasawara E. M., Nakamoto S. S., Boynton A. L. Stimulation by inositol trisphosphate and tetrakisphosphate of a protein phosphatase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Sep 15;155(2):767–772. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80561-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]