The title molecule, bergapten, a psoralen/furanocoumarin derivative, possesses photocarcinogenic and photomutagenic activity. In the crystal, molecules are linked via C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds, forming a three-dimensional framework.
Keywords: crystal structure, bergapten, T. stictocarpum, psoralen, furanocoumarin, photobiological activity, C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds, π–π interactions
Abstract
The title compound, C12H8O4, is a furanocoumarin [systematic name: 4-methoxy-7H-furo[3,2-g]chromen-7-one], which was isolated from the Indian herb T. stictocarpum. The molecule is almost planar with an r.m.s. deviation of 0.024 Å for the hetero atoms of the fused-ring system. In the crystal, molecules are linked by C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds, forming a three-dimensional framework. There are offset π–π interactions present involving the coumarin moieties stacking along the a-axis direction [shortest inter-centroid distance = 3.717 (3) Å].
Chemical context
The title molecule, bergapten, is a linear furanocoumarin having a methoxy group in the benzene ring at position C5. This class of furano coumarins have absorption bands in the near UV region due to the presence of conjugated double bonds, and exhibit photomutagenic (Appendino, et al., 2004 ▸) and photocarcinogenic properties, binding with purine bases of DNA in living cells to yield photoadducts (Filomena et al., 2009 ▸). Based on this property, they are employed to treat numerous inflammatory skin diseases, such as atopic dermatitis, and pigment disorders like vitiligo and psoriasis by UV photodynamic therapy. In addition, due to their strong ability to absorb UV radiation, this class of molecules are utilized as photoprotective agents, to prevent the absorption of harmful UV radiation by the skin. A variety of sun-screen lotions are widely used in dermatological applications in the cosmetic and pharmaceutical industries (Chen et al., 2007 ▸, 2009 ▸). In addition, the in vitro antiproliferation activity and in vivo photoxicity of the title molecule has been reported against epithelial cancer cell lines, including HL60, A431 (Conconi et al., 1998 ▸). Bergapten (5-methoxy psoralen/methoxsalen) has been used successfully in combination with UV photodynamic therapy to mange psoriasis and vitiligo; it inhibits proliferation in human hepatocellular carcinoma cell line (March et al., 1993 ▸). Experimental results revealed that its phototoxicity and photomutagenicity is exerted via a Diels–Alder reaction binding the double bond of a purine base of DNA in a living cell with the double bonds of bergapten to yield mono- and di-adducts (Conforti et al., 2009 ▸).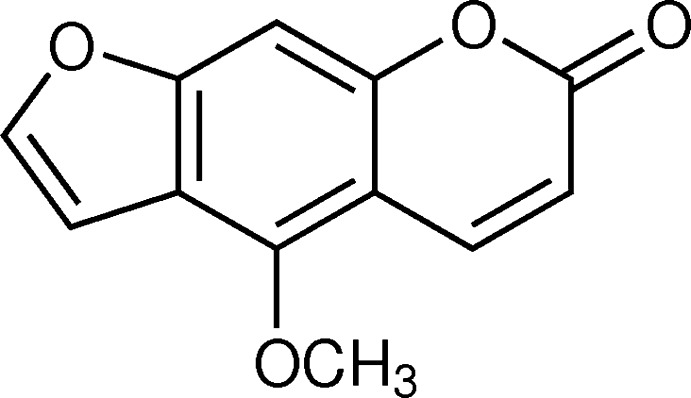
While this is the first report of the crystal structure of the title compound, its chemical structure was determined by spectrometric and spectroscopic analysis many years ago (Howell & Robertson, 1937 ▸; Ray et al., 1937 ▸; Lin et al., 1979 ▸; Confalone & Confalone, 1983 ▸).
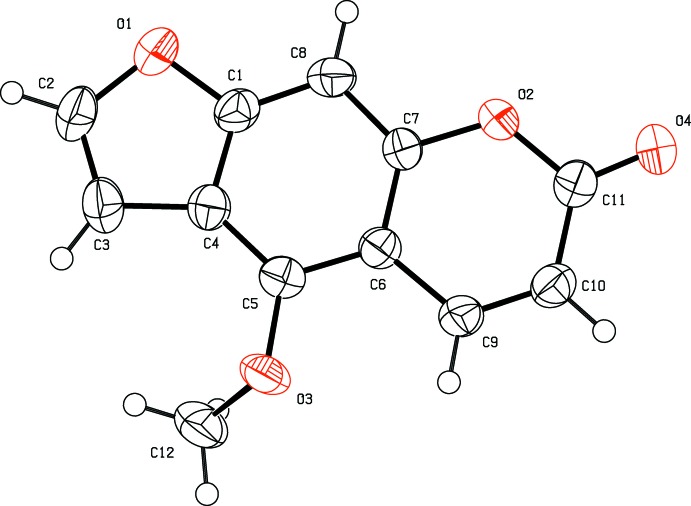
Structural commentary
The title compound (Fig. 1 ▸), belongs to the psoralen class of compounds and is composed of three fused rings viz. furan, benzene and pyrone. It is an almost planar molecule with an r.m.s. deviation of 0.024 Å for the atoms of the fused ring system, O1–O2/C1–C11. The methoxy C atom, C12, is displaced from this mean plane by 0.925 (5) Å, while atoms O3 and O4 are displaced from the mean plane by 0.069 (3) and 0.035 (3) Å, respectively.
Figure 1.
A view of the molecular structure of the title compound, with the atom labelling. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 50% probability level.
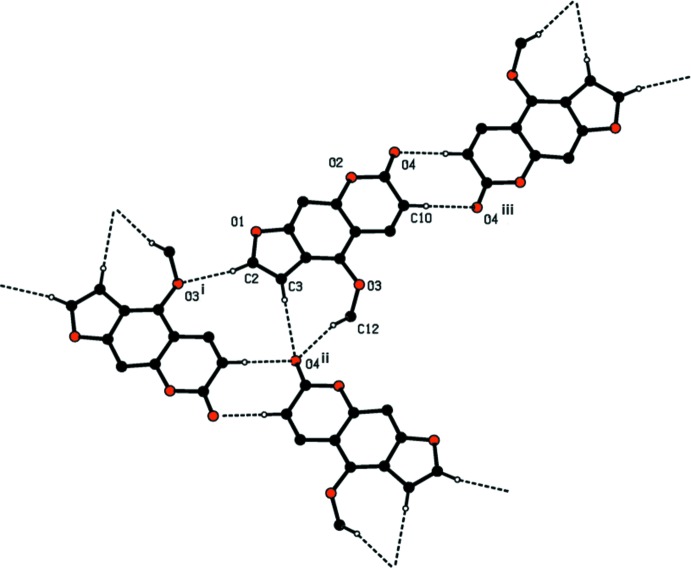
Supramolecular features
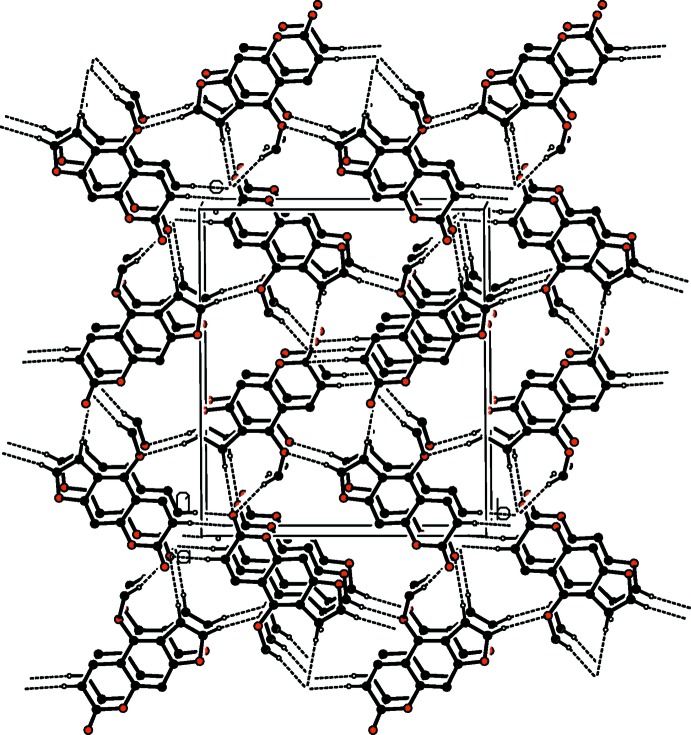
In the crystal, molecules are linked by a series of C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds, which are illustrated in Fig. 2 ▸ (see also Table 1 ▸). They form a three-dimensional network (Table 1 ▸ and Fig. 3 ▸). There are offset π–π interactions present involving the coumarin moieties stacking along the a-axis direction [shortest inter-centroid distance Cg2⋯Cg3i = 3.717 (3) Å, interplanar distance = 3.425 (2) Å, slippage = 1.356 Å, Cg2 and Cg3 are the centroids of rings O2/C6/C7/C9–C11 and C1/C4–C8, respectively, symmetry code: (i) x − 1, y, z].
Figure 2.
A view of the various C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds (dashed lines; see Table 1 ▸ for details) in the crystal of the title compound.
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C2—H2⋯O3i | 0.93 | 2.49 | 3.406 (5) | 170 |
| C3—H3⋯O4ii | 0.93 | 2.57 | 3.484 (6) | 170 |
| C10—H10⋯O4iii | 0.93 | 2.51 | 3.387 (5) | 158 |
| C12—H12A⋯O4ii | 0.96 | 2.44 | 3.376 (5) | 165 |
Symmetry codes: (i) 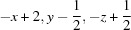 ; (ii)
; (ii) 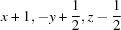 ; (iii)
; (iii) 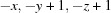 .
.
Figure 3.
A view along the a axis of the crystal packing of the title compound. Hydrogen bonds are drawn as dashed lines (see Table 1 ▸) and H atoms not involved in these interactions have been omitted for clarity.
Database survey
A search of the Cambridge Structural Database (CSD, Version 5.37, last update May 2016; Groom et al., 2016 ▸) gave 16 hits for the furanocoumarin skeleton with an O atom substituent in position 5, similar to the title compound. Two compounds closely resemble the title compound, viz. 5-hydroxypsolalen [JIXBOH; Ginderow, 1991 ▸] isolated from the bark of Citrus bergamia, and 5,8-dimethoxypsoralen [ISIMP (293 K); Gopalakrishna et al., 1977 ▸] and [ISIMP01 (120 K); Napolitano et al., 2003 ▸]. The latter was isolated from the roots and leaves of Adiscanthus fusciflorus (Rutaceae).
Synthesis and crystallization
The title compound was isolated as a colourless solid from the methanol extract of T. stictocarpum by means of column chromatography over silica gel by gradient elution with a mixture of binary solvents system hexane and ethyl acetate. It was purified by reverse phase high-pressure liquid chromatography. Colourless rod-like crystals, suitable crystals for X ray diffraction analysis, were obtained after the title compound was recrystallized three times from ethyl acetate:hexane (1:4) mixed solvents at room temperature by slow evaporation of the solvents (m.p. 469 K).
1H NMR data (CHCl3, 200 MHz) 8.13 (d, 1H, J = 9.8 Hz, H-9), 7.57 (d, 1H, J = 2.2 Hz, H-2), 7.11 (s, 1H, H-8), 7.05 (d, 1H, J = 2.2 Hz, H-3), 6.25 (d, 1H, J = 9.8 Hz, H-10), 4.26 (s, 3H, OCH3). EIMS (70 ev) data: m/z (%) 216 (100; base peak/molecular ion peak) [M +], 201 (25.2%) [M +−CH3), 188 (25.7) [M +−OCH3], 173 (25.6) [M +−(CH3–CO)], 145 (33.8) [M +−(OCH3–CO2)], 89(17.0).
Refinement
Crystal data, data collection and structure refinement details are summarized in Table 2 ▸. The C-bound H atoms were included in calculated positions and treated as riding atoms: C—H = 0.93–0.96 Å with U iso(H) = 1.5U eq(C-methyl) and 1.2Ueq(C) for other H atoms. The structure was refined as a two-component twin [180° rotation about the a* axis; BASF = 0.3955 (2)].
Table 2. Experimental details.
| Crystal data | |
| Chemical formula | C12H8O4 |
| M r | 216.18 |
| Crystal system, space group | Monoclinic, P21/c |
| Temperature (K) | 299 |
| a, b, c (Å) | 3.8486 (8), 14.676 (2), 16.866 (3) |
| β (°) | 92.12 (2) |
| V (Å3) | 952.0 (3) |
| Z | 4 |
| Radiation type | Mo Kα |
| μ (mm−1) | 0.12 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.44 × 0.08 × 0.02 |
| Data collection | |
| Diffractometer | Oxford Diffraction Xcalibur with a Sapphire CCD detector |
| Absorption correction | Multi-scan (CrysAlis RED; Oxford Diffraction, 2009 ▸)’ |
| T min, T max | 0.951, 0.998 |
| No. of measured, independent and observed [I > 2σ(I)] reflections | 7096, 7096, 3811 |
| R int | 0.08 |
| (sin θ/λ)max (Å−1) | 0.602 |
| Refinement | |
| R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)], wR(F 2), S | 0.055, 0.138, 0.86 |
| No. of reflections | 7096 |
| No. of parameters | 147 |
| H-atom treatment | H-atom parameters constrained |
| Δρmax, Δρmin (e Å−3) | 0.19, −0.22 |
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, Global. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989016011221/su5310sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989016011221/su5310Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989016011221/su5310Isup3.cml
CCDC reference: 1491854
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Professor Dr Hartmut, FG Strukturforschung, Material-und Geowissenschaften, Technische Universit at Darmstadt, Petersenstress 23, 64287 Darmstadt, for his kind co-operation in the data collection and for providing diffractometer time.
supplementary crystallographic information
Crystal data
| C12H8O4 | Dx = 1.508 Mg m−3 |
| Mr = 216.18 | Melting point: 469 K |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 3.8486 (8) Å | Cell parameters from 870 reflections |
| b = 14.676 (2) Å | θ = 2.8–27.9° |
| c = 16.866 (3) Å | µ = 0.12 mm−1 |
| β = 92.12 (2)° | T = 299 K |
| V = 952.0 (3) Å3 | Needle, colourless |
| Z = 4 | 0.44 × 0.08 × 0.02 mm |
| F(000) = 448 |
Data collection
| Oxford Diffraction Xcalibur with a Sapphire CCD detector diffractometer | 7096 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 3811 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Graphite monochromator | Rint = 0.08 |
| Rotation method data acquisition using ω and phi scans. | θmax = 25.4°, θmin = 2.8° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlis RED; Oxford Diffraction, 2009)' | h = −4→4 |
| Tmin = 0.951, Tmax = 0.998 | k = −17→17 |
| 7096 measured reflections | l = −20→20 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.055 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.138 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 0.86 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0738P)2] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 7096 reflections | (Δ/σ)max = 0.002 |
| 147 parameters | Δρmax = 0.19 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.22 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refined as a 2-component twin. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| O1 | 0.7447 (9) | 0.00489 (18) | 0.37565 (18) | 0.0525 (10) | |
| O2 | 0.3156 (8) | 0.26727 (18) | 0.50579 (14) | 0.0399 (9) | |
| O3 | 0.7860 (9) | 0.28906 (17) | 0.24893 (16) | 0.0510 (10) | |
| O4 | 0.1046 (9) | 0.3863 (2) | 0.56614 (18) | 0.0617 (11) | |
| C1 | 0.6682 (13) | 0.0956 (3) | 0.3822 (3) | 0.0392 (13) | |
| C2 | 0.8854 (13) | −0.0043 (3) | 0.3016 (3) | 0.0534 (15) | |
| H2 | 0.9619 | −0.0595 | 0.2814 | 0.064* | |
| C3 | 0.8989 (13) | 0.0740 (3) | 0.2626 (3) | 0.0477 (14) | |
| H3 | 0.9832 | 0.0833 | 0.2123 | 0.057* | |
| C4 | 0.7573 (13) | 0.1417 (3) | 0.3137 (2) | 0.0369 (12) | |
| C5 | 0.6975 (12) | 0.2354 (3) | 0.3111 (2) | 0.0344 (12) | |
| C6 | 0.5523 (11) | 0.2781 (3) | 0.3757 (2) | 0.0304 (11) | |
| C7 | 0.4677 (11) | 0.2262 (3) | 0.4418 (2) | 0.0348 (12) | |
| C8 | 0.5234 (12) | 0.1339 (3) | 0.4477 (3) | 0.0397 (13) | |
| H8 | 0.4679 | 0.1003 | 0.4922 | 0.048* | |
| C9 | 0.4692 (12) | 0.3738 (3) | 0.3771 (3) | 0.0373 (13) | |
| H9 | 0.5221 | 0.4101 | 0.3339 | 0.045* | |
| C10 | 0.3191 (12) | 0.4114 (3) | 0.4385 (2) | 0.0431 (13) | |
| H10 | 0.2654 | 0.4732 | 0.4371 | 0.052* | |
| C11 | 0.2370 (13) | 0.3592 (3) | 0.5074 (3) | 0.0433 (13) | |
| C12 | 0.6549 (14) | 0.2653 (3) | 0.1726 (2) | 0.0652 (17) | |
| H12A | 0.7936 | 0.2173 | 0.1516 | 0.098* | |
| H12B | 0.6630 | 0.3175 | 0.1384 | 0.098* | |
| H12C | 0.4187 | 0.2450 | 0.1758 | 0.098* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O1 | 0.075 (3) | 0.0265 (17) | 0.056 (2) | 0.0074 (19) | 0.006 (2) | −0.0024 (16) |
| O2 | 0.054 (2) | 0.0343 (18) | 0.0321 (16) | 0.0034 (18) | 0.0073 (19) | 0.0003 (14) |
| O3 | 0.081 (3) | 0.0419 (18) | 0.0300 (17) | −0.0206 (19) | 0.005 (2) | 0.0006 (15) |
| O4 | 0.089 (3) | 0.052 (2) | 0.045 (2) | 0.018 (2) | 0.025 (2) | −0.0027 (18) |
| C1 | 0.045 (4) | 0.029 (3) | 0.043 (3) | 0.000 (3) | −0.007 (3) | 0.000 (2) |
| C2 | 0.063 (4) | 0.040 (3) | 0.058 (3) | 0.009 (3) | 0.010 (3) | −0.013 (3) |
| C3 | 0.054 (4) | 0.041 (3) | 0.048 (3) | −0.001 (3) | 0.007 (3) | −0.006 (2) |
| C4 | 0.040 (3) | 0.032 (3) | 0.039 (3) | −0.002 (3) | −0.001 (3) | −0.0073 (19) |
| C5 | 0.036 (3) | 0.037 (3) | 0.030 (2) | −0.006 (3) | 0.001 (3) | 0.001 (2) |
| C6 | 0.029 (3) | 0.029 (2) | 0.033 (2) | −0.002 (2) | −0.002 (2) | −0.001 (2) |
| C7 | 0.041 (3) | 0.033 (3) | 0.031 (2) | −0.002 (3) | 0.005 (2) | −0.002 (2) |
| C8 | 0.049 (4) | 0.033 (3) | 0.038 (3) | −0.002 (3) | 0.004 (3) | 0.008 (2) |
| C9 | 0.047 (3) | 0.030 (3) | 0.035 (3) | −0.004 (2) | 0.002 (3) | 0.005 (2) |
| C10 | 0.056 (4) | 0.029 (2) | 0.044 (3) | 0.004 (3) | 0.001 (3) | 0.003 (2) |
| C11 | 0.046 (4) | 0.036 (3) | 0.048 (3) | 0.007 (3) | 0.006 (3) | −0.001 (2) |
| C12 | 0.099 (5) | 0.060 (3) | 0.037 (3) | −0.013 (4) | 0.001 (3) | −0.003 (2) |
Geometric parameters (Å, º)
| O1—C1 | 1.369 (5) | C4—C5 | 1.394 (6) |
| O1—C2 | 1.386 (5) | C5—C6 | 1.391 (5) |
| O2—C7 | 1.385 (4) | C6—C7 | 1.398 (5) |
| O2—C11 | 1.383 (5) | C6—C9 | 1.442 (5) |
| O3—C5 | 1.365 (4) | C7—C8 | 1.374 (5) |
| O3—C12 | 1.409 (4) | C8—H8 | 0.9300 |
| O4—C11 | 1.200 (5) | C9—C10 | 1.325 (5) |
| C1—C8 | 1.376 (5) | C9—H9 | 0.9300 |
| C1—C4 | 1.393 (6) | C10—C11 | 1.435 (5) |
| C2—C3 | 1.327 (6) | C10—H10 | 0.9300 |
| C2—H2 | 0.9300 | C12—H12A | 0.9600 |
| C3—C4 | 1.435 (6) | C12—H12B | 0.9600 |
| C3—H3 | 0.9300 | C12—H12C | 0.9600 |
| C1—O1—C2 | 105.1 (3) | C8—C7—O2 | 116.2 (4) |
| C7—O2—C11 | 122.6 (3) | C8—C7—C6 | 123.7 (4) |
| C5—O3—C12 | 117.9 (3) | O2—C7—C6 | 120.1 (4) |
| O1—C1—C8 | 123.8 (4) | C1—C8—C7 | 114.2 (4) |
| O1—C1—C4 | 110.2 (4) | C1—C8—H8 | 122.9 |
| C8—C1—C4 | 126.0 (4) | C7—C8—H8 | 122.9 |
| C3—C2—O1 | 112.7 (4) | C10—C9—C6 | 121.4 (4) |
| C3—C2—H2 | 123.7 | C10—C9—H9 | 119.3 |
| O1—C2—H2 | 123.7 | C6—C9—H9 | 119.3 |
| C2—C3—C4 | 106.2 (4) | C9—C10—C11 | 121.7 (4) |
| C2—C3—H3 | 126.9 | C9—C10—H10 | 119.1 |
| C4—C3—H3 | 126.9 | C11—C10—H10 | 119.1 |
| C5—C4—C1 | 117.3 (4) | O4—C11—O2 | 116.1 (4) |
| C5—C4—C3 | 136.9 (4) | O4—C11—C10 | 127.2 (4) |
| C1—C4—C3 | 105.8 (4) | O2—C11—C10 | 116.8 (4) |
| O3—C5—C6 | 117.4 (4) | O3—C12—H12A | 109.5 |
| O3—C5—C4 | 123.2 (4) | O3—C12—H12B | 109.5 |
| C6—C5—C4 | 119.4 (4) | H12A—C12—H12B | 109.5 |
| C5—C6—C7 | 119.4 (4) | O3—C12—H12C | 109.5 |
| C5—C6—C9 | 123.2 (4) | H12A—C12—H12C | 109.5 |
| C7—C6—C9 | 117.4 (4) | H12B—C12—H12C | 109.5 |
| C2—O1—C1—C8 | −179.8 (5) | C4—C5—C6—C9 | −177.6 (4) |
| C2—O1—C1—C4 | 0.3 (5) | C11—O2—C7—C8 | −178.5 (4) |
| C1—O1—C2—C3 | −0.2 (6) | C11—O2—C7—C6 | 0.9 (6) |
| O1—C2—C3—C4 | 0.0 (6) | C5—C6—C7—C8 | 0.8 (6) |
| O1—C1—C4—C5 | −179.6 (4) | C9—C6—C7—C8 | 178.3 (4) |
| C8—C1—C4—C5 | 0.5 (7) | C5—C6—C7—O2 | −178.5 (4) |
| O1—C1—C4—C3 | −0.3 (5) | C9—C6—C7—O2 | −1.1 (6) |
| C8—C1—C4—C3 | 179.8 (5) | O1—C1—C8—C7 | −179.9 (5) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | 179.2 (6) | C4—C1—C8—C7 | −0.1 (7) |
| C2—C3—C4—C1 | 0.2 (6) | O2—C7—C8—C1 | 178.7 (4) |
| C12—O3—C5—C6 | −126.8 (4) | C6—C7—C8—C1 | −0.6 (7) |
| C12—O3—C5—C4 | 55.5 (6) | C5—C6—C9—C10 | 177.4 (5) |
| C1—C4—C5—O3 | 177.3 (4) | C7—C6—C9—C10 | 0.1 (7) |
| C3—C4—C5—O3 | −1.7 (9) | C6—C9—C10—C11 | 1.1 (7) |
| C1—C4—C5—C6 | −0.3 (7) | C7—O2—C11—O4 | 179.7 (4) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | −179.3 (5) | C7—O2—C11—C10 | 0.3 (6) |
| O3—C5—C6—C7 | −178.0 (4) | C9—C10—C11—O4 | 179.3 (5) |
| C4—C5—C6—C7 | −0.3 (6) | C9—C10—C11—O2 | −1.3 (7) |
| O3—C5—C6—C9 | 4.7 (6) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, º)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C2—H2···O3i | 0.93 | 2.49 | 3.406 (5) | 170 |
| C3—H3···O4ii | 0.93 | 2.57 | 3.484 (6) | 170 |
| C10—H10···O4iii | 0.93 | 2.51 | 3.387 (5) | 158 |
| C12—H12A···O4ii | 0.96 | 2.44 | 3.376 (5) | 165 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+2, y−1/2, −z+1/2; (ii) x+1, −y+1/2, z−1/2; (iii) −x, −y+1, −z+1.
References
- Appendino, G., Bianchi, F., Bader, A., Campagnuolo, C., Fattorusso, E., Taglialatela-Scafati, O., Blanco-Molina, M., Macho, A., Fiebich, B. L., Bremner, P., Heinrich, M., Ballero, M. & Muñoz, E. (2004). J. Nat. Prod. 67, 532–536. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y., Fan, G., Zhang, Q., Wu, H. & Wu, Y. (2007). J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 43, 926–936. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Chen, D., Wang, J., Jiang, Y., Zhou, T., Fan, G. & Wu, Y. (2009). J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 50, 695–702. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Conconi, M. T., Montesi, F. & Parnigotto, P. P. (1998). Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 82, 193–198. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Confalone, P. N. & Confalone, D. L. (1983). Tetrahedron, 39, 1265–1271.
- Conforti, F., Marrelli, M., Menichini, F., Bonesi, M., Statti, G., Provenzano, E. & Menichini, F. (2009). Curr. Drug Ther. 4, 38–58.
- Ginderow, D. (1991). Acta Cryst. C47, 2144–2146.
- Gopalakrishna, E. M., Watson, W. H., Bittner, M. & Silva, M. (1977). J. Cryst. Mol. Struct. 7, 107–114.
- Groom, C. R., Bruno, I. J., Lightfoot, M. P. & Ward, S. C. (2016). Acta Cryst. B72, 171–179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Howell, W. N. & Robertson, A. (1937). J. Chem. Soc. pp. 293–294.
- Liu, Y., Thom, E. & Liebman, A. A. (1979). J. Heterocycl. Chem. 16, 799–801.
- March, K. L., Patton, B. L., Wilensky, R. L. & Hathaway, D. R. (1993). Circulation, 87, 184–191. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Napolitano, H. B., Silva, M., Ellena, J., Rocha, W. C., Vieira, P. C., Thiemann, O. H. & Oliva, G. (2003). Acta Cryst. E59, o1506–o1508.
- Oxford Diffraction (2009). CrysAlis CCD and CrysAlis RED. Oxford Diffraction Ltd, Abingdon, England.
- Ray, J. N., Silooja, S. S. & Vaid, V. R. (1937). J. Chem. Soc. 1, 813–816.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2015). Acta Cryst. C71, 3–8.
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablock(s) I, Global. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989016011221/su5310sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablock(s) I. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989016011221/su5310Isup2.hkl
Supporting information file. DOI: 10.1107/S2056989016011221/su5310Isup3.cml
CCDC reference: 1491854
Additional supporting information: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report