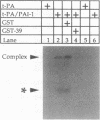
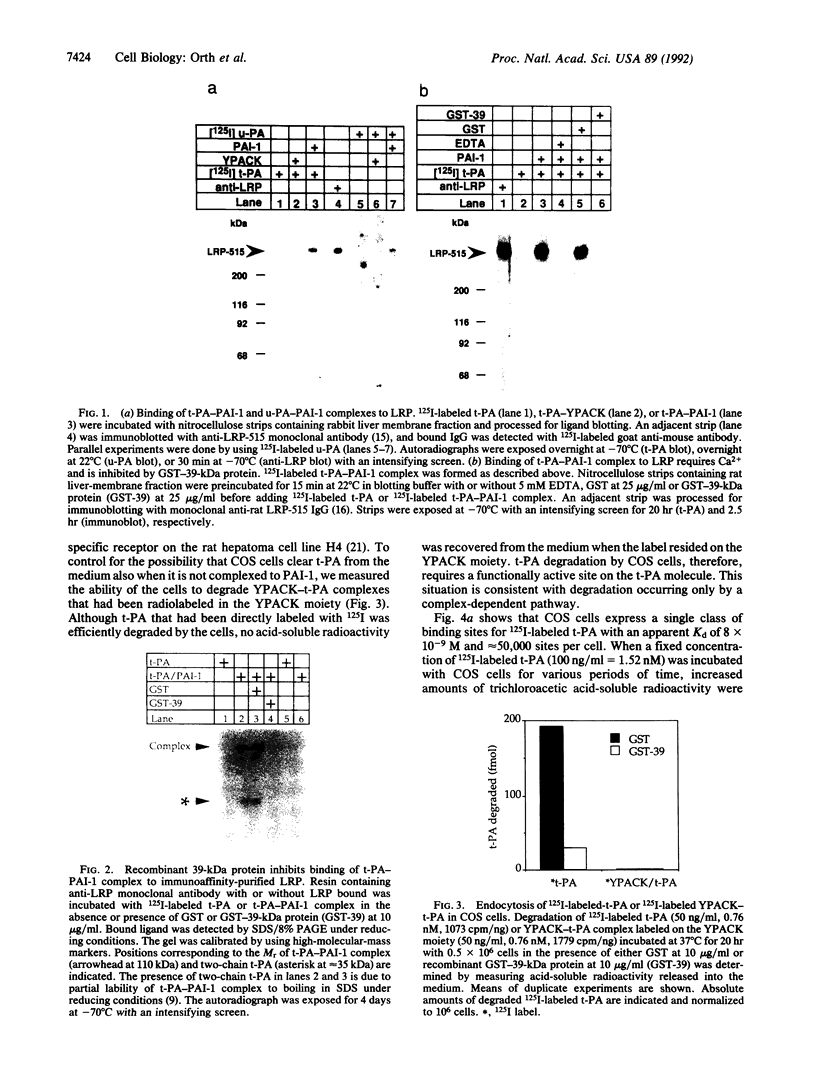
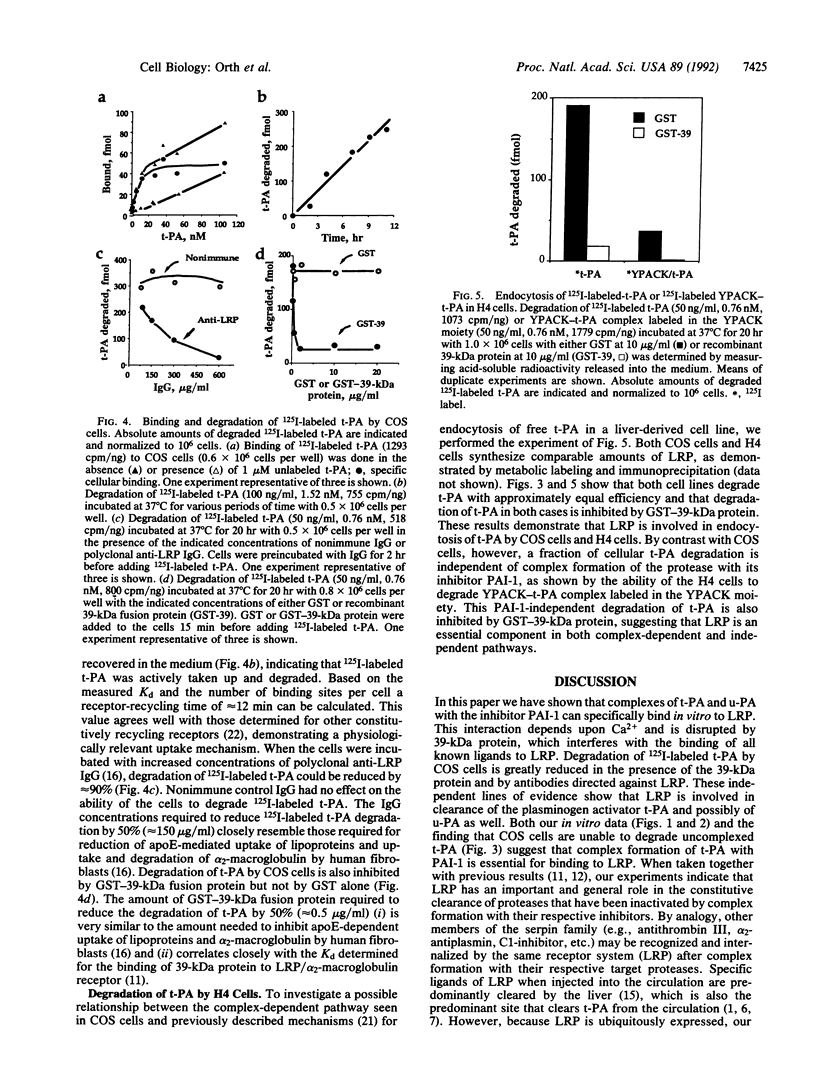
Abstract
Tissue-type plasminogen activator and urokinase are serine proteases secreted by many cell types that participate in biological processes, such as tissue restructuring, cell migration, and tumor metastasis. Clinically, these proteases are used to dissolve coronary fibrin clots that are the proximal causes of acute myocardial infarction. In vivo, the activity of these enzymes is controlled by plasminogen-activator inhibitors, members of the serpin family of protease inhibitors. This study shows that tissue-type plasminogen activator-inhibitor complexes bind in solution to low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein (LRP), a large heterodimeric ubiquitous membrane receptor. In cultured cells, endocytosis and degradation of these complexes is reduced by polyclonal antibodies directed against LRP and inhibited by a M(r) 39,000 protein that binds to LRP and inhibits its interaction with previously known ligands, including apolipoprotein E and alpha 2-macroglobulin. We propose a role for LRP in the clearance of plasminogen activator-inhibitor complexes that is analogous to its function in the endocytosis of alpha 2-macroglobulin-protease complexes.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bassel-Duby R., Jiang N. Y., Bittick T., Madison E., McGookey D., Orth K., Shohet R., Sambrook J., Gething M. J. Tyrosine 67 in the epidermal growth factor-like domain of tissue-type plasminogen activator is important for clearance by a specific hepatic receptor. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 15;267(14):9668–9677. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett W. F., Paoni N. F., Keyt B. A., Botstein D., Jones A. J., Presta L., Wurm F. M., Zoller M. J. High resolution analysis of functional determinants on human tissue-type plasminogen activator. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 15;266(8):5191–5201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. A receptor-mediated pathway for cholesterol homeostasis. Science. 1986 Apr 4;232(4746):34–47. doi: 10.1126/science.3513311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bu G., Williams S., Strickland D. K., Schwartz A. L. Low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein/alpha 2-macroglobulin receptor is an hepatic receptor for tissue-type plasminogen activator. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 15;89(16):7427–7431. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.16.7427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cubellis M. V., Wun T. C., Blasi F. Receptor-mediated internalization and degradation of urokinase is caused by its specific inhibitor PAI-1. EMBO J. 1990 Apr;9(4):1079–1085. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08213.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danø K., Andreasen P. A., Grøndahl-Hansen J., Kristensen P., Nielsen L. S., Skriver L. Plasminogen activators, tissue degradation, and cancer. Adv Cancer Res. 1985;44:139–266. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60028-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estreicher A., Mühlhauser J., Carpentier J. L., Orci L., Vassalli J. D. The receptor for urokinase type plasminogen activator polarizes expression of the protease to the leading edge of migrating monocytes and promotes degradation of enzyme inhibitor complexes. J Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;111(2):783–792. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.2.783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hekman C. M., Loskutoff D. J. Endothelial cells produce a latent inhibitor of plasminogen activators that can be activated by denaturants. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 25;260(21):11581–11587. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herz J., Goldstein J. L., Strickland D. K., Ho Y. K., Brown M. S. 39-kDa protein modulates binding of ligands to low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein/alpha 2-macroglobulin receptor. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 5;266(31):21232–21238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herz J., Kowal R. C., Ho Y. K., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. Low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein mediates endocytosis of monoclonal antibodies in cultured cells and rabbit liver. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 5;265(34):21355–21362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korninger C., Stassen J. M., Collen D. Turnover of human extrinsic (tissue-type) plasminogen activator in rabbits. Thromb Haemost. 1981 Oct;46(3):658–661. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kowal R. C., Herz J., Weisgraber K. H., Mahley R. W., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. Opposing effects of apolipoproteins E and C on lipoprotein binding to low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 25;265(18):10771–10779. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kristensen T., Moestrup S. K., Gliemann J., Bendtsen L., Sand O., Sottrup-Jensen L. Evidence that the newly cloned low-density-lipoprotein receptor related protein (LRP) is the alpha 2-macroglobulin receptor. FEBS Lett. 1990 Dec 10;276(1-2):151–155. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80530-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lijnen H. R., Collen D. Strategies for the improvement of thrombolytic agents. Thromb Haemost. 1991 Jul 12;66(1):88–110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madison E. L., Goldsmith E. J., Gerard R. D., Gething M. J., Sambrook J. F. Serpin-resistant mutants of human tissue-type plasminogen activator. Nature. 1989 Jun 29;339(6227):721–724. doi: 10.1038/339721a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moestrup S. K., Gliemann J. Analysis of ligand recognition by the purified alpha 2-macroglobulin receptor (low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein). Evidence that high affinity of alpha 2-macroglobulin-proteinase complex is achieved by binding to adjacent receptors. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 25;266(21):14011–14017. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moestrup S. K., Kaltoft K., Sottrup-Jensen L., Gliemann J. The human alpha 2-macroglobulin receptor contains high affinity calcium binding sites important for receptor conformation and ligand recognition. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 25;265(21):12623–12628. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morton P. A., Owensby D. A., Sobel B. E., Schwartz A. L. Catabolism of tissue-type plasminogen activator by the human hepatoma cell line Hep G2. Modulation by plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 5;264(13):7228–7235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morton P. A., Owensby D. A., Wun T. C., Billadello J. J., Schwartz A. L. Identification of determinants involved in binding of tissue-type plasminogen activator-plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1 complexes to HepG2 cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 25;265(24):14093–14099. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ploug M., Behrendt N., Løber D., Danø K. Protein structure and membrane anchorage of the cellular receptor for urokinase-type plasminogen activator. Semin Thromb Hemost. 1991 Jul;17(3):183–193. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1002608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ploug M., Rønne E., Behrendt N., Jensen A. L., Blasi F., Danø K. Cellular receptor for urokinase plasminogen activator. Carboxyl-terminal processing and membrane anchoring by glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 25;266(3):1926–1933. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rijken D. C., Otter M., Kuiper J., van Berkel T. J. Receptor-mediated endocytosis of tissue-type plasminogen activator (t-PA) by liver cells. Thromb Res Suppl. 1990;10:63–71. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(90)90379-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saksela O., Rifkin D. B. Cell-associated plasminogen activation: regulation and physiological functions. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1988;4:93–126. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.04.110188.000521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sappino A. P., Huarte J., Belin D., Vassalli J. D. Plasminogen activators in tissue remodeling and invasion: mRNA localization in mouse ovaries and implanting embryos. J Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;109(5):2471–2479. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.5.2471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens R. W., Pöllänen J., Tapiovaara H., Leung K. C., Sim P. S., Salonen E. M., Rønne E., Behrendt N., Danø K., Vaheri A. Activation of pro-urokinase and plasminogen on human sarcoma cells: a proteolytic system with surface-bound reactants. J Cell Biol. 1989 May;108(5):1987–1995. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.5.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strickland D. K., Ashcom J. D., Williams S., Burgess W. H., Migliorini M., Argraves W. S. Sequence identity between the alpha 2-macroglobulin receptor and low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein suggests that this molecule is a multifunctional receptor. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 15;265(29):17401–17404. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiman B., Chmielewska J., Rånby M. Inactivation of tissue plasminogen activator in plasma. Demonstration of a complex with a new rapid inhibitor. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 25;259(6):3644–3647. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wing L. R., Hawksworth G. M., Bennett B., Booth N. A. Clearance of t-PA, PAI-1, and t-PA-PAI-1 complex in an isolated perfused rat liver system. J Lab Clin Med. 1991 Feb;117(2):109–114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Mourik J. A., Lawrence D. A., Loskutoff D. J. Purification of an inhibitor of plasminogen activator (antiactivator) synthesized by endothelial cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 10;259(23):14914–14921. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]