Abstract
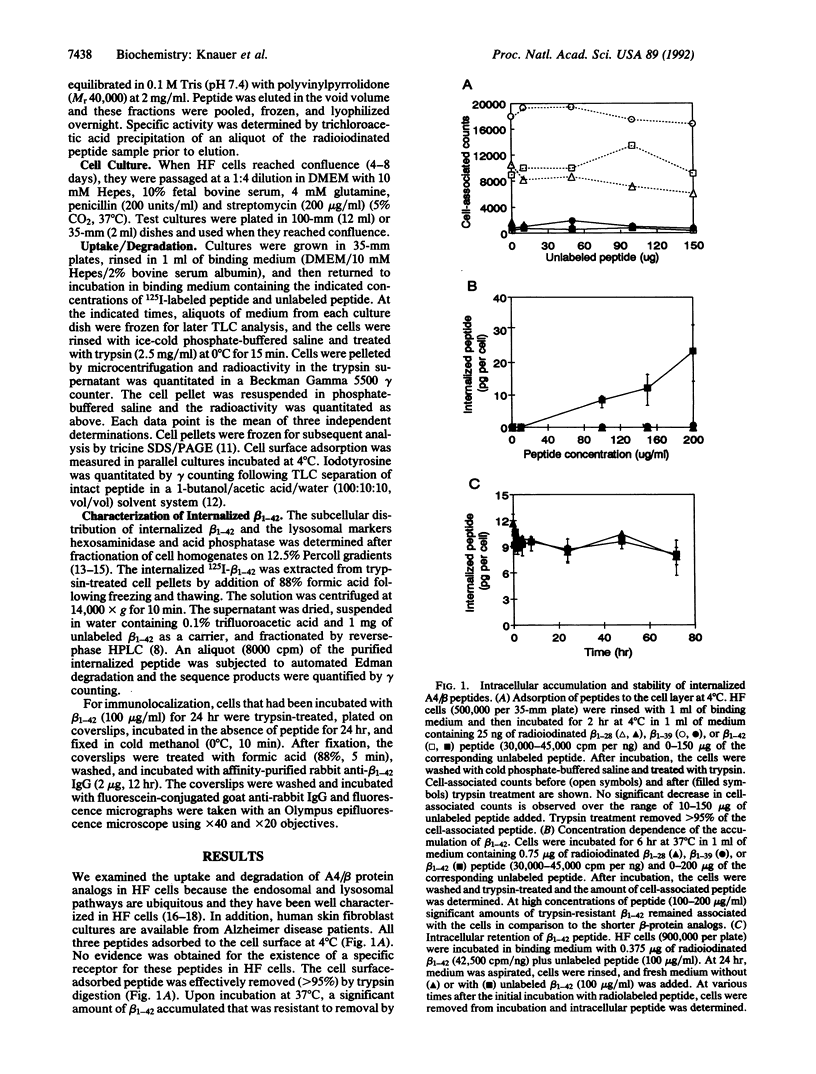
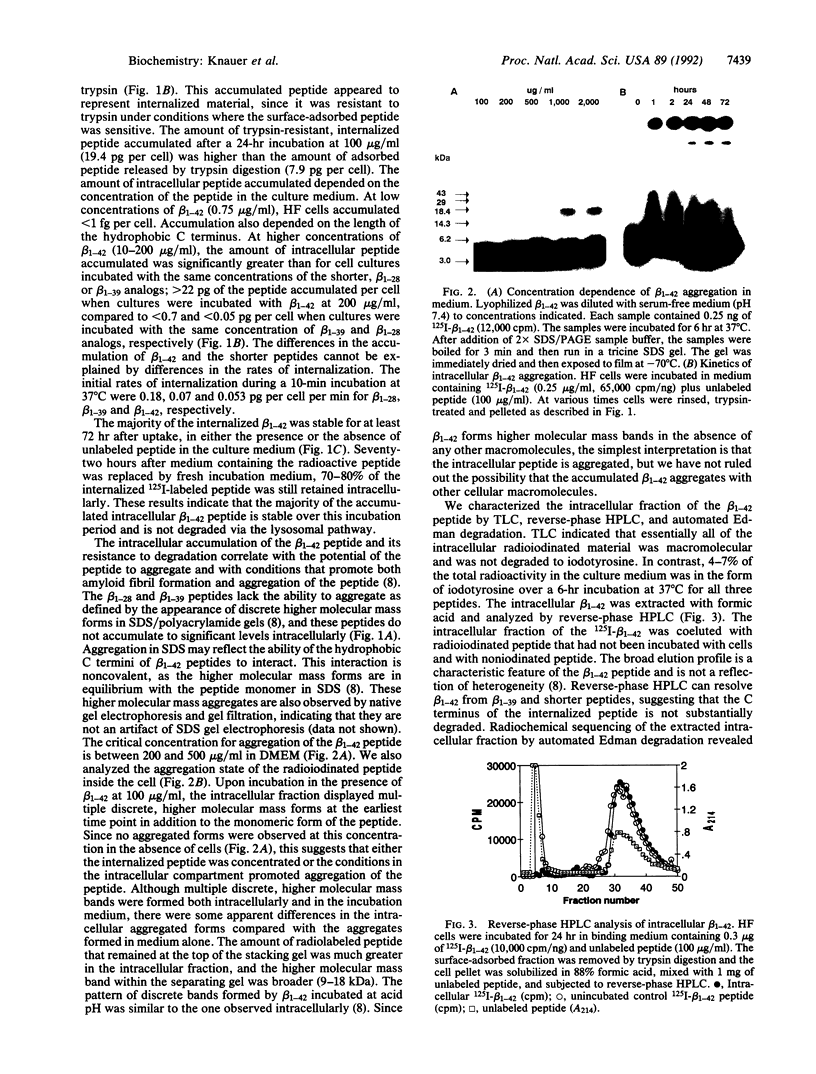
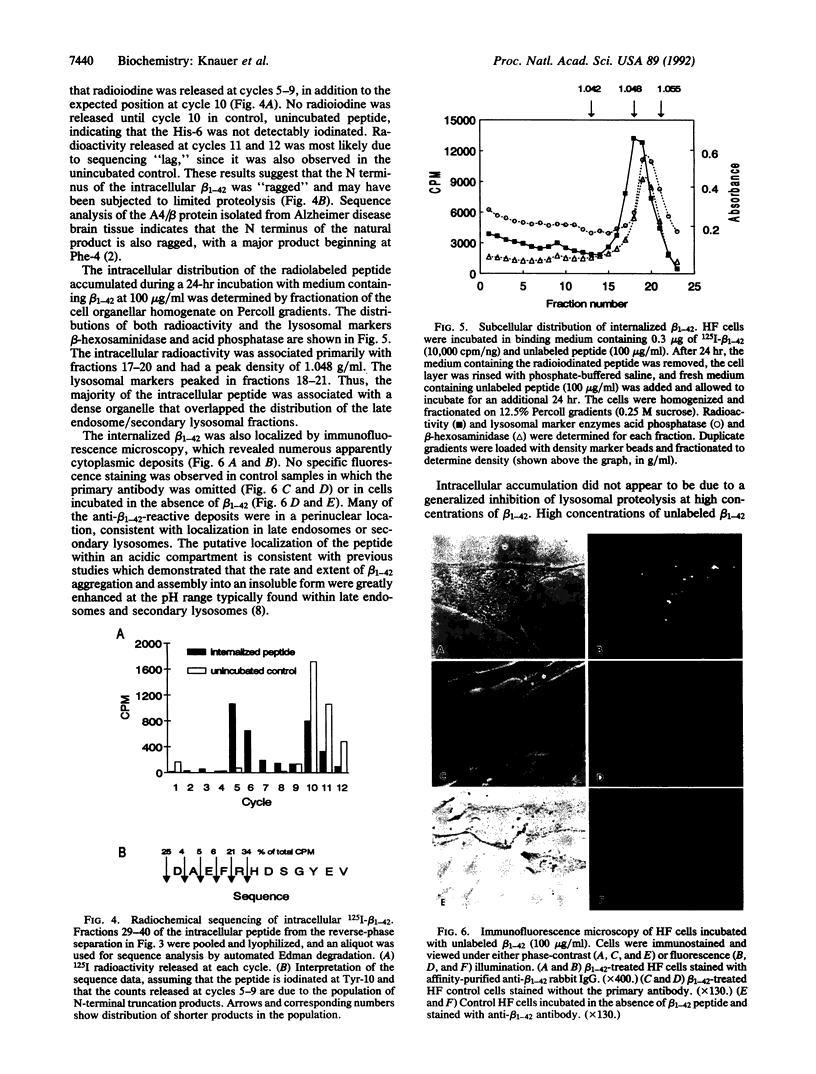
The A4 or beta protein is a peptide that constitutes the major protein component of senile plaques in Alzheimer disease. The A4/beta protein is derived from a larger, transmembrane amyloid precursor protein (APP). The putative abnormal processing events leading to amyloid accumulation are largely unknown. Here we report that a 42-residue synthetic peptide, beta 1-42, corresponding to one of the longer forms of the A4/beta protein, accumulates in cultured human skin fibroblasts and is stable for at least 3 days. The peptide appears to accumulate intracellularly, since it does not accumulate under conditions that prevent endocytosis and accumulation is correlated with the acquisition of resistance to removal by trypsin digestion. This intracellular accumulation is also correlated with the ability of the peptide to aggregate as determined by SDS/polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. At low concentrations of the beta 1-42 peptide, which favor the nonaggregated state, no accumulation is observed. Shorter peptide analogs (28 or 39 residues) that are truncated at the C terminus, which lack the ability to aggregate in SDS gels, fail to accumulate. The accumulated intracellular beta 1-42 peptide is in an aggregated state and is contained in a dense organellar compartment that overlaps the distribution of late endosomes or secondary lysosomes. Immunofluorescence of the internalized peptide in permeabilized cells reveals that it is contained in granular deposits, consistent with localization in late endosomes or secondary lysosomes. Sequence analysis indicates that some of the internalized peptide is subject to N-terminal trimming. These results suggest that the aggregated A4/beta protein may be resistant to degradation and suggest that the A4/beta protein may arise, at least in part, by endosomal or lysosomal processing of APP. Our results also suggest that relatively nonspecific proteolysis may be sufficient to generate the A4/beta protein if this part of APP is selectively resistant to proteolysis.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ajioka R. S., Kaplan J. Characterization of endocytic compartments using the horseradish peroxidase-diaminobenzidine density shift technique. J Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;104(1):77–85. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.1.77. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benowitz L. I., Rodriguez W., Paskevich P., Mufson E. J., Schenk D., Neve R. L. The amyloid precursor protein is concentrated in neuronal lysosomes in normal and Alzheimer disease subjects. Exp Neurol. 1989 Dec;106(3):237–250. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(89)90156-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burdick D., Soreghan B., Kwon M., Kosmoski J., Knauer M., Henschen A., Yates J., Cotman C., Glabe C. Assembly and aggregation properties of synthetic Alzheimer's A4/beta amyloid peptide analogs. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 5;267(1):546–554. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabral L., Unger W., Boulton M., Marshall J. A microsystem to assay lysosomal enzyme activities in cultured retinal pigment epithelial cells. Curr Eye Res. 1988 Nov;7(11):1097–1104. doi: 10.3109/02713688809001880. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cataldo A. M., Nixon R. A. Enzymatically active lysosomal proteases are associated with amyloid deposits in Alzheimer brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(10):3861–3865. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.10.3861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cataldo A. M., Thayer C. Y., Bird E. D., Wheelock T. R., Nixon R. A. Lysosomal proteinase antigens are prominently localized within senile plaques of Alzheimer's disease: evidence for a neuronal origin. Brain Res. 1990 Apr 16;513(2):181–192. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(90)90456-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esch F. S., Keim P. S., Beattie E. C., Blacher R. W., Culwell A. R., Oltersdorf T., McClure D., Ward P. J. Cleavage of amyloid beta peptide during constitutive processing of its precursor. Science. 1990 Jun 1;248(4959):1122–1124. doi: 10.1126/science.2111583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estus S., Golde T. E., Kunishita T., Blades D., Lowery D., Eisen M., Usiak M., Qu X. M., Tabira T., Greenberg B. D. Potentially amyloidogenic, carboxyl-terminal derivatives of the amyloid protein precursor. Science. 1992 Feb 7;255(5045):726–728. doi: 10.1126/science.1738846. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenner G. G., Wong C. W. Alzheimer's disease: initial report of the purification and characterization of a novel cerebrovascular amyloid protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 May 16;120(3):885–890. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(84)80190-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golde T. E., Estus S., Younkin L. H., Selkoe D. J., Younkin S. G. Processing of the amyloid protein precursor to potentially amyloidogenic derivatives. Science. 1992 Feb 7;255(5045):728–730. doi: 10.1126/science.1738847. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein B., Wofsy C., Bell G. Interactions of low density lipoprotein receptors with coated pits on human fibroblasts: estimate of the forward rate constant and comparison with the diffusion limit. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5695–5698. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horvat A., Baxandall J., Touster O. The isolation of lysosomes from Ehrlich ascites tumor cells following pretreatment of mice with Triton WR-1339. J Cell Biol. 1969 Aug;42(2):469–479. doi: 10.1083/jcb.42.2.469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang J., Lemaire H. G., Unterbeck A., Salbaum J. M., Masters C. L., Grzeschik K. H., Multhaup G., Beyreuther K., Müller-Hill B. The precursor of Alzheimer's disease amyloid A4 protein resembles a cell-surface receptor. Nature. 1987 Feb 19;325(6106):733–736. doi: 10.1038/325733a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitaguchi N., Takahashi Y., Tokushima Y., Shiojiri S., Ito H. Novel precursor of Alzheimer's disease amyloid protein shows protease inhibitory activity. Nature. 1988 Feb 11;331(6156):530–532. doi: 10.1038/331530a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masters C. L., Simms G., Weinman N. A., Multhaup G., McDonald B. L., Beyreuther K. Amyloid plaque core protein in Alzheimer disease and Down syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):4245–4249. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.4245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKinley D. N., Wiley H. S. Reassessment of fluid-phase endocytosis and diacytosis in monolayer cultures of human fibroblasts. J Cell Physiol. 1988 Sep;136(3):389–397. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041360302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponte P., Gonzalez-DeWhitt P., Schilling J., Miller J., Hsu D., Greenberg B., Davis K., Wallace W., Lieberburg I., Fuller F. A new A4 amyloid mRNA contains a domain homologous to serine proteinase inhibitors. Nature. 1988 Feb 11;331(6156):525–527. doi: 10.1038/331525a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prelli F., Castaño E., Glenner G. G., Frangione B. Differences between vascular and plaque core amyloid in Alzheimer's disease. J Neurochem. 1988 Aug;51(2):648–651. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1988.tb01087.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schägger H., von Jagow G. Tricine-sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis for the separation of proteins in the range from 1 to 100 kDa. Anal Biochem. 1987 Nov 1;166(2):368–379. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90587-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sisodia S. S., Koo E. H., Beyreuther K., Unterbeck A., Price D. L. Evidence that beta-amyloid protein in Alzheimer's disease is not derived by normal processing. Science. 1990 Apr 27;248(4954):492–495. doi: 10.1126/science.1691865. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka S., Nakamura S., Ueda K., Kameyama M., Shiojiri S., Takahashi Y., Kitaguchi N., Ito H. Three types of amyloid protein precursor mRNA in human brain: their differential expression in Alzheimer's disease. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Dec 15;157(2):472–479. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(88)80273-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiley H. S., Cunningham D. D. Epidermal growth factor stimulates fluid phase endocytosis in human fibroblasts through a signal generated at the cell surface. J Cell Biochem. 1982;19(4):383–394. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240190407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisniewski H. M., Barcikowska M., Kida E. Phagocytosis of beta/A4 amyloid fibrils of the neuritic neocortical plaques. Acta Neuropathol. 1991;81(5):588–590. doi: 10.1007/BF00310142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





