Abstract
Purpose
Three-dimensional (3D) effects of the single plane osteotomies of the proximal femur are compared and analyzed by the trigonometric method.
Materials and Methods
The shape of proximal femur was simplified as a bent line. The bent line is the continuation of the three points-the center of the femoral head, the center of femoral neck at the base, and the center of the femoral shaft. Then rotated the proximal femur at the junction of the neck and shaft with the each rotation axis of X, Y, Z, defined the frontal plane as a XY plane, sagittal plane as a YZ plane, and transverse plane as a XZ plane.
Results
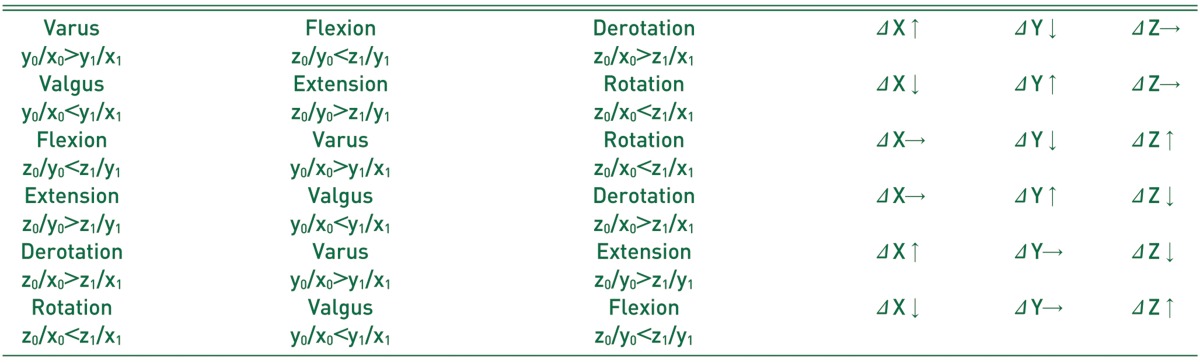
The varus osteotomy of the proximal femur in the frontal plane with the rotation axis 'Z' that meant the increase of the X coordinate and the decrease of Y coordinate with constant Z coordinate (Δx>Δy, Δz=0) resulted in decreased anteversion in the transverse plane and increased flexion in the sagittal plane. The derotation osteotomy (Δx>Δz, Δy=0) resulted in varus in the frontal plane and extension in the sagittal plane. The flexion osteotomy (Δz>Δy, Δx=0) resulted in increased anteversion in the transverse plane and varus in the frontal plane.
Conclusion
Single plane osteotomy for the proximal femur results in the angular correction in all three planes and may have the similar 3D effect of the certain double or triple osteotomy. So single plane osteotomy could be enough to correct some complex deformities.
Keywords: Proximal femur, Single plane osteotomy, Three-dimensional effects
INTRODUCTION
Due to the three-dimensional (3D) configuration of the femur neck and the head, it is unavoidable to have 3D effects on the femoral head by the femur osteotomy just after one plane osteotomy such as a varus or derotation osteotomy. The distal femur osteotomy of the frontal and sagittal plane causes clinically insignificant 3D effect on the femoral head.
Most of orthopedic surgeons know about the varus change of the neck-shaft angle of the anteroposterior (AP) hip X-ray by the internal rotation of the lower extremity1), but do not consider seriously about the 3D effect of the proximal femur osteotomy. The 3D effects of the single plane osteotomies of the proximal femur were compared and analyzed by the trigonometric method.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The shape of the right proximal femur was simplified as bent lines. The bent lines were the continuation of the three points; the center of the femoral head (H), the center of femoral neck at the base (N), and the center of the femoral shaft (S).
Then rotated the proximal femur at the junction of the neck and shaft with the each rotation axis of X, Y, Z, defined the frontal plane as a XY plane, sagittal plane as a YZ plane, and transverse plane as a XZ plane. The projected cervicofemoral angulation in the frontal plane was defined as 'α' that was AP neck-shaft angle, angleαis angle v plus 90, and angle v is valgus angle of femoral neck. In the sagittal plane 'β' was the flexion angle, in the transverse plane 'γ' the anteversion angle, the true neck shaft angle 'δ', and the angle between the femoral neck and the frontal plane 'φ' was the inclination angle (Fig. 1).
Fig. 1. Schematic drawing of right proximal femur in bent lines.
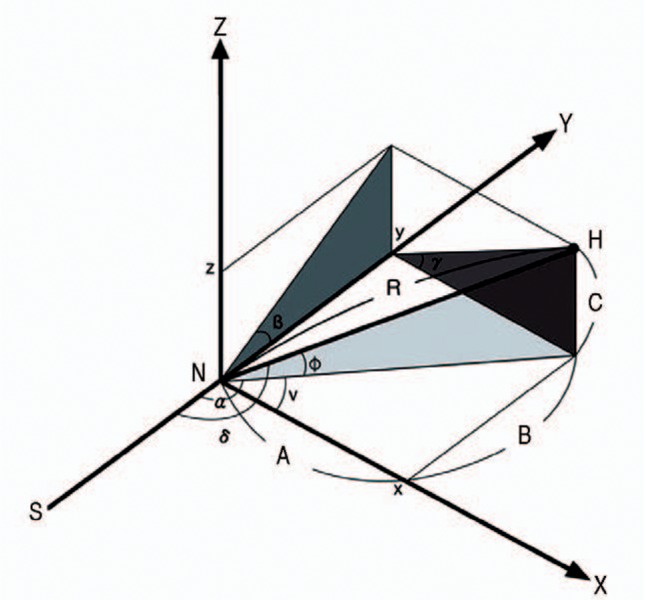
H: the center of the femoral head, N: the center of femoral neck at the base, S: the center of the femoral shaft, R: the length of the femoral neck (true head-neck distance), Y axis: the extension of the center of the femoral shaft, X axis: the vertical to Y axis in the frontal plane at the junction of femoral neck and the shaft, Z axis: the vertical to Y axis in the sagittal plane at the junction of femoral neck and the shaft.
So XY plane is frontal, YZ is sagittal, and XZ is transverse plane. The angle of femoral neck at XY, YZ and XZ plane has the value of α,β and γ respectively. Angle α is angle v plus 90, and angle v is valgus angle of femoral neck. Angle β is flexion angle and angle γ is anteversion angle of the femoral neck. The center of femoral head (H) is located in three-dimensional space and it has three coordinates of x, y, and z. A, B and C is the each value of x, y and z coordinate of the center of femoral head. Angle 'ϕ' is neck-frontal plane angle, and angle δ is true neck-shaft angle.
With just two angles of femoral neck among angles of three planes (v,β, andγ), the remaining one angle could be calculated by the following formulas.
tan v=B/A, tanβ=C/B, tanγ=C/A
tan v=tan γ/tan β, tan β=tan γ/tan v, tan γ=tan v · tan β
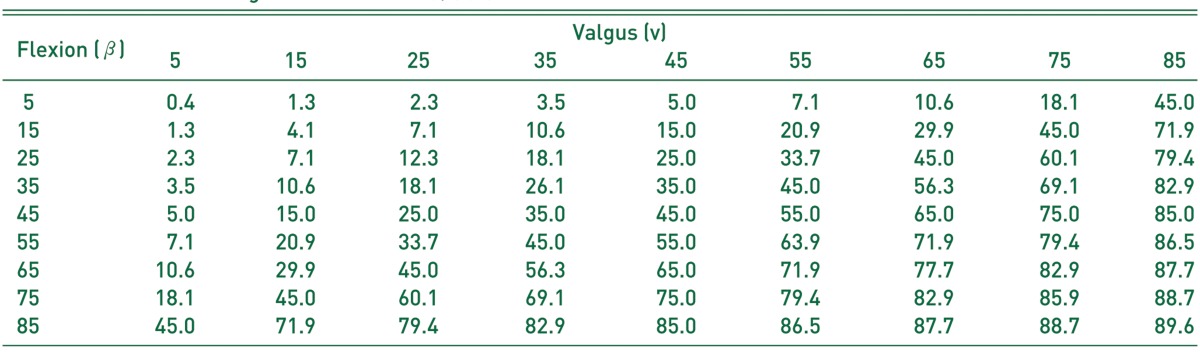
With these trigonometric formulas, the change of angle in each plane could be calculated (Table 1).
Table 1. The Values of Angle of Anteversion (γ) (°)*.
*Calculated with valgus and flexion angle of femoral neck.
With the value of true head neck distance (R) and just two angles among three angle (v, β, and γ), could calculate the value of A, B, and C.
With two angles of femoral neck in three planes (v, β, γ) and true head-neck distance (R), could calculate three coordinates (A, B, C).
To avoid the confusion, the varus and valgus osteotomy was defined as the direction of movement of the distal femur after osteotomy in the frontal plane, the flexion and extension osteotomy in the sagittal plane and the external (derotation) and internal (rotation) rotation osteotomy in the transverse plane.
RESULTS
The varus osteotomy of the proximal femur in the frontal plane with the rotation axis 'Z' that meant the increase of the X coordinate and the decrease of Y coordinate with constant Z coordinate resulted in decreased anteversion in the transverse plane and increased flexion in the sagittal plane (Fig. 2).
Fig. 2. With the rotation axis Z, varus osteotomy results in the change of three-dimensional location of femoral head.
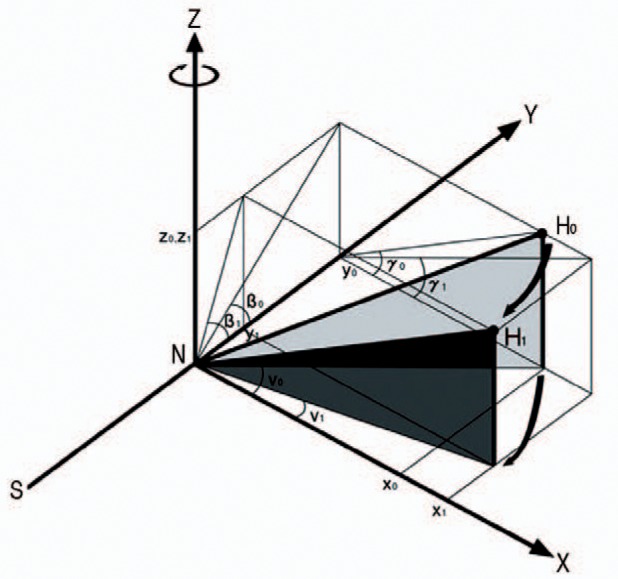
X coordinate is increased (x0<x1), Y coordinate is decreased (y0>y1), and Z coordinate is not changed (z0=z1). Therefore, angle of valgus and anteversion is decreased (v0>v1,γ0>γ1) and flexion angle (β0<β1) is increased.
H0 and H1: Center of femoral head before and after varus osteotomy.
v0 and v1: the valgus angle before and after varus osteotomy.
β0 and β1: the flexion angle before and after varus osteotomy.
γ0 and γ1: the angle of anteversion before and after varus osteotomy.
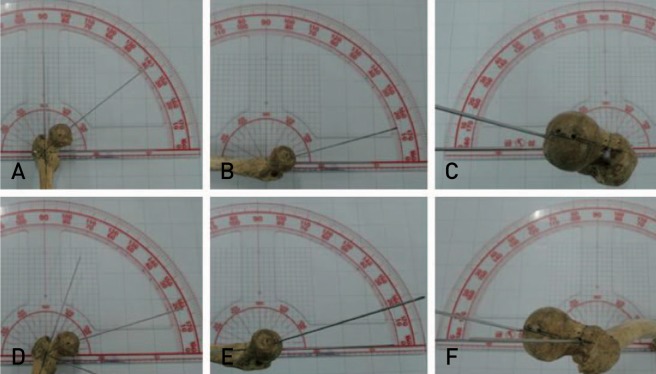
A real bone model with 2 K-wires representing x and y axis at the neck shaft junction, and 1 K-wire inserted along the center of the femur neck showed frontal neck-shaft angle of 128°(valgus angle 38°), sagittal neck-shaft angle of 15°, and transverse neck-shaft angle of 14° (Fig. 3A-C). With 20°varus rotation in the frontal plane, showed the change of the frontal neck-shaft angle to 108°(valgus angle 18°), sagittal neck-shaft angle to 17°, and transverse neck-shaft angle of 10° (Fig. 3D-F).
Fig. 3. Three-dimensional neck-shaft angle of real bone models with neutral and 20° varus rotation position.
A neutral position shows frontal neck-shaft angle of 128° (A), sagittal neck-shaft angle of 15° (B), and transverse neck-shaft angle of 14° (C). With 20° varus rotation in the frontal plane, shows the change of the frontal neck-shaft angle to 108° (D), sagittal neck-shaft angle to 17° (E), and transverse neck-shaft angle of 10° (F).
If two angles were changed to any correction, the other one angle is definitely confined.
If varus (20°) correction was just carried out to the proximal femur with its angle of valgus 45°, flexion 25° and anteversion 25°, final angles of the neck in each plane was valgus 25°, flexion 40°and anteversion 20°. Using the Table 1, when we were planning the varus osteotomy (v was decreasing), also got flexion (βwas increasing) and derotation (γ was decreasing) effect. When valgus angle was less than 45°, varus osteotomy could cause the more flexion effect than derotation effect, because the decrement of Y axis was bigger than the increment of X axis. Reversely when valgus angle was more than 45°, varus osteotomy could cause the more derotation effect than flexion effect.
Like the same manner, the valgus osteotomy of the proximal femur caused increased anteversion and decreased flexion.
The derotation osteotomy of the proximal femur in the transverse plane with the rotation axis 'Y' that was performed by external rotation of the distal femur after osteotomy resulted in varus in the frontal plane and extension in the sagittal plane (Fig. 4).
Fig. 4. Derotation (γ0>γ1) osteotomy with the rotation axis Y results in varus change (v0>v1) and decreased flexion (β0>β1) of femoral head.
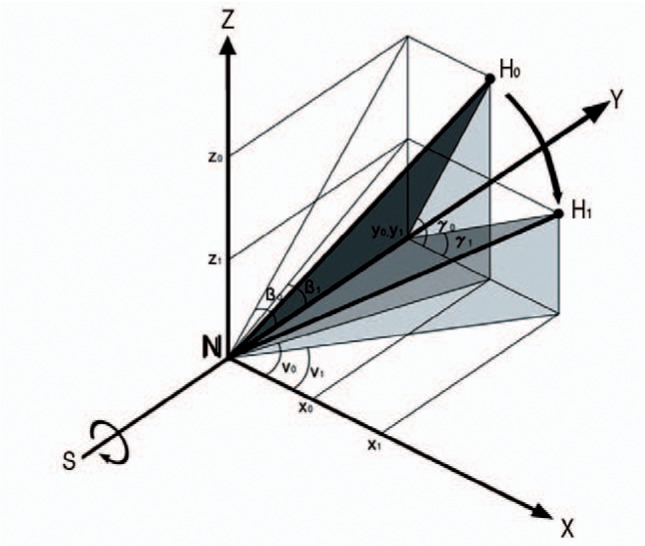
X coordinate is increased (x0<x1), Z coordinate is decreased (z0>z1), and Y coordinate is not changed (y0=y1). Therefore, angle of valgus and anteversion is decreased (v0>v1, γ0>γ1) and flexion angle (β0>β1) is decreased.
H0 and H1: Center of femoral head before and after derotation osteotomy.
v0 and v1: the valgus angle before and after derotation osteotomy.
β0 and β1: the flexion angle before and after derotation osteotomy.
γ0 and γ1: the angle of anteversion before and after derotation osteotomy.
On the contrary, the rotation osteotomy of the proximal femur caused valgus and flexion.
The flexion osteotomy of the proximal femur in the sagittal plane with the rotation axis 'X' resulted in increased anteversion in the transverse plane and varus in the frontal plane (Fig. 5).
Fig. 5. Flexion (β0<β1) osteotomy with the rotation axis X results in varus change (v0>v1) and increased anteversion (γ0<γ1) of femoral head.
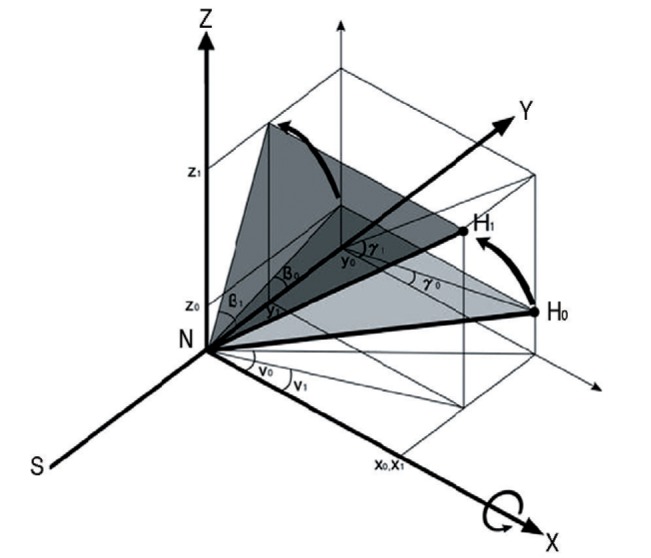
Z coordinate is increased (z0<z1), Y coordinate is decreased (y0>y1), and X coordinate is not changed (x0=x1). Therefore, angle of flexion and anteversion is increased (β0<β1, γ0<γ1) and valgus angle (v0>v1) is decreased.
H0 and H1: Center of femoral head before and after flexion osteotomy.
v0 and v1: the valgus angle before and after flexion osteotomy.
β0 and β1: the flexion angle before and after flexion osteotomy.
γ0 and γ1: the angle of anteversion before and after flexion osteotomy.
Reversely the extension osteotomy of the proximal femur caused valgus and decreased anteversion. The effects of the every single plane osteotomy were simplified in the diagram (Table 2).
Table 2. Three-dimensional Effects of Every Single Plane Osteotomy of the Proximal Femur.
X: X coordinate, Y: Y coordinate, Z: Z coordinate, ΔX: x1-x0, ΔY: y1-y0, ΔZ: z1-z0, ↑: increase, ↓: decrease, →: constant.
x0, y0, z0: x, y, z coordinate before osteotomy.
x1, y1, z1: x, y, z coordinate after osteotomy.
For example, varus single plane osteotomy resulted in increased X coordinate, decreased Y coordinate and constant Z coordinate (ΔX↑, ΔY↓, ΔZ→). This osteotomy makes not only decreased Y to X coordinate ratio (y0/x0>y1/x1: varus) but also increased Z to Y (z0/y0<z1/y1: flexion) and increased Z to X coordinate ratio (z0/x0>z1/x1: derotation).
In clinical practice, the site of the proximal femoral osteotomy could be distal to the neck-shaft junction, different 3D effects of this subtrochanteric osteotomy comparing to the head and neck junction osteotomy were inevitable except rotation or derotation osteotomy.
The subtrochanteric varus osteotomy could induce increase of ΔX and ΔY coordinates comparing to the varus osteotomy at the neck shaft junction with the same degrees correction (Fig. 6).
Fig. 6. The subtrochanteric varus osteotomy results in both increased change of ΔX and ΔY coordinates compared with varus osteotomy at the neck shaft junction.
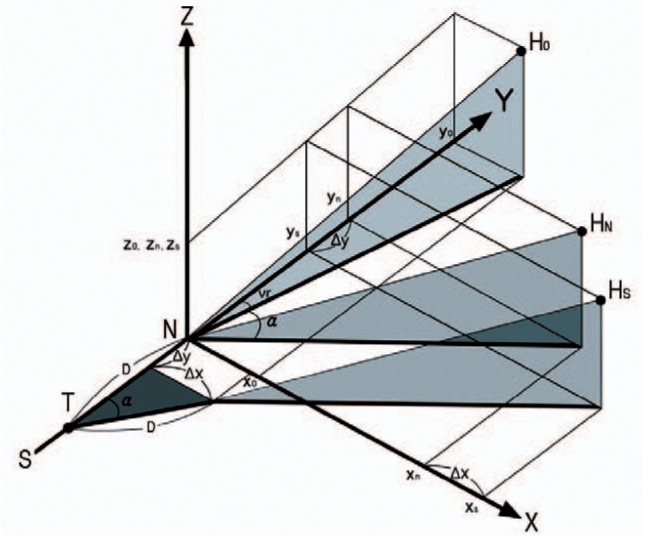
D: the distance between the base of neck and the level of subtrochanteric osteotomy, T: the level of subtrochanteric osteotomy, α: angle of varus correction, vr: varus angle of femoral neck before osteotomy.
x0, y0, z0: x, y, z coordinates before osteotomy.
xn, yn, zn: x, y, z coordinates after varus osteotomy at the neck shaft junction.
xs, ys, zs: x, y, z coordinates after varus osteotomy at the subtrochanteric level.
The change of Y coordinate after subtrochanteric varus osteotomy was more decreased than that of neckshaft junction varus osteotomy; ΔY=D (1-Cos α). The change of X coordinate after subtrochanteric varus osteotomy was more increased than that of neck-shaft junction varus osteotomy; Δx=D sin α.
DISCUSSION
There are many examples of 3D effects of the proximal femur by one plane movements, such as the internal rotation of femur causes the varus change of the proximal femur. For measuring a femoral anteversion, Kane et al.2) used a single roentgenographic measurement of femoral anteversion by projecting the femur longitudinally from the knee to hip with 10°to 20°abduction of the thighs and reported +1°to -6°differences from the real anteversion. These results are expected by the 3D effect of the abduction of the thighs that causes varus of the femur head, so the decreased anteversion of the femur is resulted from abduction of thighs.
Howell et al.3) calculated the angle of anteversion and varus of proximal femur in Perthes' disease by a method using single AP radiograph. They suggested that the ratio of major and minor axis of ellipse created by epiphyseal plate of femoral head on AP radiograph depends on anteversion and true neck-shaft angle.
Nelitz et al.4) stated that proximal derotation osteotomy resulted in increased varus angulation of the hip and distal derotation osteotomy resulted in increased valgus angulation of the knee due to antecurvatum of femoral shaft.
With the valgus in the AP X-ray and increased anteversion in computed tomography scan, some cases show a decreased flexion in the lateral X-ray and a normal range of AP neck-frontal plane angle, that means a normal Z coordinate, decreased X coordinate, and increased Y coordinate. The varus osteotomy with rotation axis Z is enough and no need to correct the anteversion because the increased anteversion is a pure reflection of the valgus.
With the valgus and anteversion, some cases show an increased Y coordinate, a decreased X coordinate and an increased Z coordinate. The derotation osteotomy can change the valgus also; there is no need to add the varus osteotomy to the derotation osteotomy. Some cases show an increased Y and Z coordinate with a marked decreased X coordinate. Both valgus and derotation osteotomies are necessary because the varus osteotomy or the derotation osteotomy only is not enough to correct the deformity in these cases. The normal values of the three coordinates of the proximal femur will be needed to plan any kind of corrective osteotomy in case of complex deformity.
Liu et al.5) reported that the angle of neck-frontal plane (angle 'φ') or inclination could be calculated using the true or apparent neck-shaft angle and angle of version. And they stated that varus osteotomy decreased anteversion and valgus osteotomy increased anteversion due to the relationship with version and neck-shaft angle.
Some papers suggested different measurements methods of femoral anteversion by biplane radiography6,7,8,9,10,11). With these two angulations, true femoral neck-shaft angulation and angle of anteversion could be calculated like Table 1.
The subtrochanteric varus osteotomy could induce more vertical shortening and increased medial offset than the neck-shaft junction varus osteotomy. The subtrochanteric valgus osteotomy could induce less vertical lengthening and decreased medial offset than the neck-shaft junction valgus osteotomy. The subtrochanteric flexion osteotomy could induce more vertical shortening and increased anteversion than the neck-shaft junction varus osteotomy.
The subtrochanteric extension osteotomy could induce less vertical lengthening and more decreased anteversion than the neck-shaft junction varus osteotomy. But the rotation or derotation osteotomy in the subtrochanteric site has no 3D difference with the neck-shaft junction osteotomy due to the same rotation axis.
Single plane osteotomy had single rotation axis X, Y or Z. After single plane osteotomy, one coordinate which was on the rotation axis was not changed, but the rest two coordinates which were not on the rotation axis were changed. Of the rest two coordinates, one was increased and the other was decreased. This increase and decrease of the two coordinates in single plane osteotomy could change the location of the femoral head and the angle of femoral neck in all three planes (XY, YZ, and XZ plane). Single plane osteotomy could control just two coordinates, while double or triple osteotomy controlled all three coordinates. Thus, single plane osteotomy had the effect of correction in three planes (3D effect), but it was limited owing to the fixed one coordinate.
Clinical relevance of this study is that a combined deformity correction osteotomy is simplified by the single plane osteotomy in case of the synchronous deformity. For example, if there is valgus and increased anteversion deformity of the femoral head, we might correct the whole deformity by just varus osteotomy or derotation osteotomy alone. But if there is varus and increased anteversion deformity of the femoral head, we have to do combined valgus and derotation osteotomy to correct the deformity.
Using Table 1, we can expect the remaining plane neckshaft angle after changing the 2 plane neck-shaft angles by corrective osteotomy of the proximal femur. For example, if we make AP neck-shaft angle and anteversion angle to 135°and 15°each by the osteotomy, then we find that lateral neck-shaft angle is fixed to 15°
CONCLUSION
Single plane osteotomy for the proximal femur results in the angular correction in all three planes and may have the similar 3D effect of the certain double or triple osteotomy. So single plane osteotomy could be enough to correct some complex deformities.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was supported by the Dong-A University research fund.
References
- 1.Abel MF, Sutherland DH, Wenger DR, Mubarak SJ. Evaluation of CT scans and 3-D reformatted images for quantitative assessment of the hip. J Pediatr Orthop. 1994;14:48–53. doi: 10.1097/01241398-199401000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Kane TJ, Henry G, Furry D. A simple roentgenographic measurement of femoral anteversion. A short note. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1992;74:1540–1542. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Howell FR, Newman RJ, Wang HL, Nevelo¨s AB, Dickson RA. The three-dimensional anatomy of the proximal femur in Perthes’ disease. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1989;71:408–412. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.71B3.2722931. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Nelitz M, Wehner T, Steiner M, Du¨rselen L, Lippacher S. The effects of femoral external derotational osteotomy on frontal plane alignment. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2014;22:2740–2746. doi: 10.1007/s00167-013-2618-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Liu RW, Toogood P, Hart DE, Davy DT, Cooperman DR. The effect of varus and valgus osteotomies on femoral version. J Pediatr Orthop. 2009;29:666–675. doi: 10.1097/BPO.0b013e3181b769b5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Ogata K, Goldsand EM. A simple biplanar method of measuring femoral anteversion and neck-shaft angle. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1979;61:846–851. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Burr DB, Cook LT, Martin NL, Asher M. Measurement accuracy of proximal femoral geometry using biplanar radiography. J Pediatr Orthop. 1981;1:171–179. doi: 10.1097/01241398-198110000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Lee DY, Lee CK, Cho TJ. A new method for measurement of femoral anteversion. A comparative study with other radiographic methods. Int Orthop. 1992;16:277–281. doi: 10.1007/BF00182711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Hermann KL, Egund N. Measuring anteversion in the femoral neck from routine radiographs. Acta Radiol. 1998;39:410–415. doi: 10.1080/02841859809172455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Kuo TY, Skedros JG, Bloebaum RD. Measurement of femoral anteversion by biplane radiography and computed tomography imaging: comparison with an anatomic reference. Invest Radiol. 2003;38:221–229. doi: 10.1097/01.RLI.0000059542.90854.EF. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Sugano N, Noble PC, Kamaric E. A comparison of alternative methods of measuring femoral anteversion. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1998;22:610–614. doi: 10.1097/00004728-199807000-00019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]