Abstract
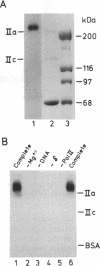
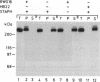
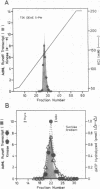
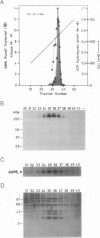
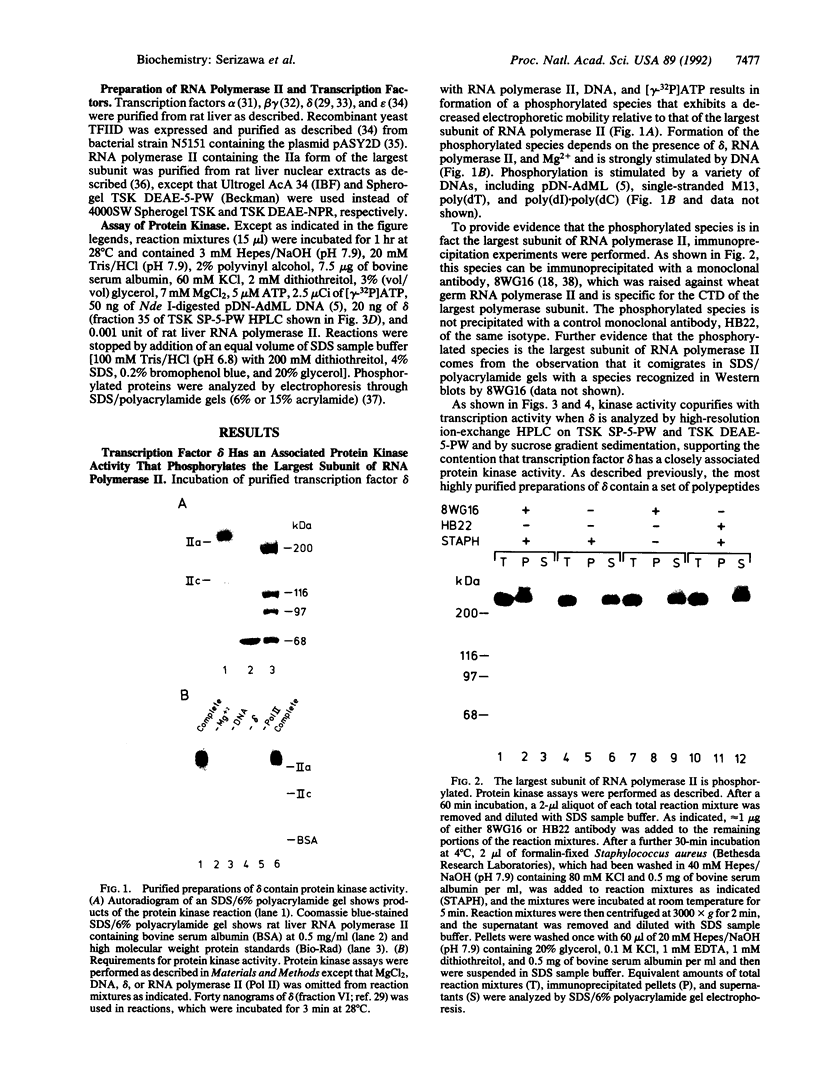
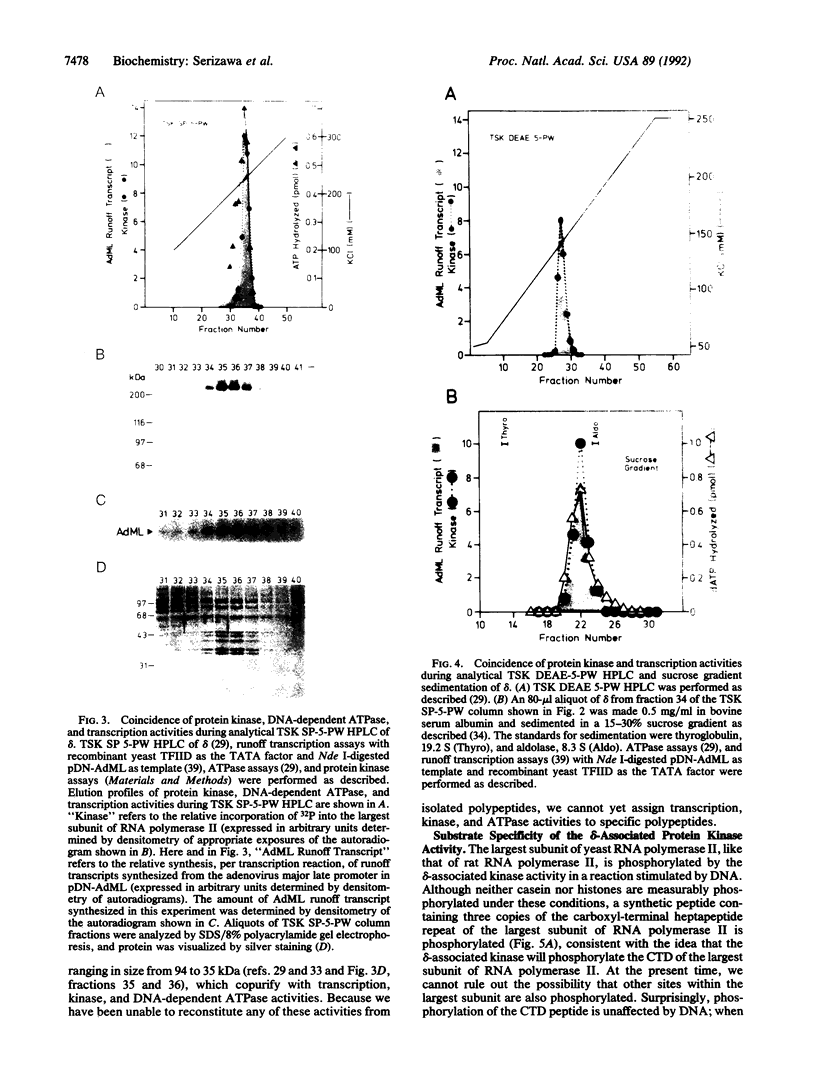
We previously purified RNA polymerase II transcription factor delta from rat liver and found that it has an associated DNA-dependent ATPase (dATPase) activity. In this report, we show that delta is also closely associated with a protein kinase activity that catalyzes phosphorylation of the largest subunit of RNA polymerase II. Kinase activity copurifies with transcription and DNA-dependent ATPase (dATPase) activities when delta is analyzed by anion- and cation-exchange HPLC as well as by sucrose gradient sedimentation, arguing that delta possesses all three activities. Phosphorylation of the largest subunits of both rat and yeast RNA polymerase II is stimulated by DNA, whereas phosphorylation of a synthetic peptide containing multiple copies of the carboxyl-terminal heptapeptide repeat is not. Although both ATP and GTP appear to function as phosphate donors, GTP is utilized less than 10% as well as ATP. These findings suggest that delta may exert its action in transcription at least in part through a mechanism involving phosphorylation of the largest subunit of RNA polymerase II.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arias J. A., Peterson S. R., Dynan W. S. Promoter-dependent phosphorylation of RNA polymerase II by a template-bound kinase. Association with transcriptional initiation. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 5;266(13):8055–8061. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartholomew B., Dahmus M. E., Meares C. F. RNA contacts subunits IIo and IIc in HeLa RNA polymerase II transcription complexes. J Biol Chem. 1986 Oct 25;261(30):14226–14231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bunick D., Zandomeni R., Ackerman S., Weinmann R. Mechanism of RNA polymerase II--specific initiation of transcription in vitro: ATP requirement and uncapped runoff transcripts. Cell. 1982 Jul;29(3):877–886. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90449-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buratowski S., Sharp P. A. Transcription initiation complexes and upstream activation with RNA polymerase II lacking the C-terminal domain of the largest subunit. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Oct;10(10):5562–5564. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.10.5562. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burton Z. F., Ortolan L. G., Greenblatt J. Proteins that bind to RNA polymerase II are required for accurate initiation of transcription at the adenovirus 2 major late promoter. EMBO J. 1986 Nov;5(11):2923–2930. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04588.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cadena D. L., Dahmus M. E. Messenger RNA synthesis in mammalian cells is catalyzed by the phosphorylated form of RNA polymerase II. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 15;262(26):12468–12474. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesnut J. D., Stephens J. H., Dahmus M. E. The interaction of RNA polymerase II with the adenovirus-2 major late promoter is precluded by phosphorylation of the C-terminal domain of subunit IIa. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 25;267(15):10500–10506. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cisek L. J., Corden J. L. Phosphorylation of RNA polymerase by the murine homologue of the cell-cycle control protein cdc2. Nature. 1989 Jun 29;339(6227):679–684. doi: 10.1038/339679a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conaway J. W., Bond M. W., Conaway R. C. An RNA polymerase II transcription system from rat liver. Purification of an essential component. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 15;262(17):8293–8297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conaway J. W., Bradsher J. N., Conaway R. C. Mechanism of assembly of the RNA polymerase II preinitiation complex. Transcription factors delta and epsilon promote stable binding of the transcription apparatus to the initiator element. J Biol Chem. 1992 May 15;267(14):10142–10148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conaway J. W., Conaway R. C. A multisubunit transcription factor essential for accurate initiation by RNA polymerase II. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 5;264(4):2357–2362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conaway J. W., Conaway R. C. An RNA polymerase II transcription factor shares functional properties with Escherichia coli sigma 70. Science. 1990 Jun 22;248(4962):1550–1553. doi: 10.1126/science.2193400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conaway J. W., Conaway R. C. Initiation of eukaryotic messenger RNA synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 25;266(27):17721–17724. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conaway J. W., Hanley J. P., Garrett K. P., Conaway R. C. Transcription initiated by RNA polymerase II and transcription factors from liver. Structure and action of transcription factors epsilon and tau. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 25;266(12):7804–7811. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conaway J. W., Reines D., Conaway R. C. Transcription initiated by RNA polymerase II and purified transcription factors from liver. Cooperative action of transcription factors tau and epsilon in initial complex formation. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 5;265(13):7552–7558. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conaway R. C., Conaway J. W. ATP activates transcription initiation from promoters by RNA polymerase II in a reversible step prior to RNA synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 25;263(6):2962–2968. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conaway R. C., Conaway J. W. An RNA polymerase II transcription factor has an associated DNA-dependent ATPase (dATPase) activity strongly stimulated by the TATA region of promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(19):7356–7360. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.19.7356. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conaway R. C., Garrett K. P., Hanley J. P., Conaway J. W. Mechanism of promoter selection by RNA polymerase II: mammalian transcription factors alpha and beta gamma promote entry of polymerase into the preinitiation complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 15;88(14):6205–6209. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.14.6205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corden J. L. Tails of RNA polymerase II. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Oct;15(10):383–387. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90236-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards A. M., Darst S. A., Feaver W. J., Thompson N. E., Burgess R. R., Kornberg R. D. Purification and lipid-layer crystallization of yeast RNA polymerase II. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(6):2122–2126. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.6.2122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feaver W. J., Gileadi O., Kornberg R. D. Purification and characterization of yeast RNA polymerase II transcription factor b. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 5;266(28):19000–19005. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feaver W. J., Gileadi O., Li Y., Kornberg R. D. CTD kinase associated with yeast RNA polymerase II initiation factor b. Cell. 1991 Dec 20;67(6):1223–1230. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90298-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flanagan P. M., Kelleher R. J., Feaver W. J., Lue N. F., LaPointe J. W., Kornberg R. D. Resolution of factors required for the initiation of transcription by yeast RNA polymerase II. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 5;265(19):11105–11107. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flores O., Ha I., Reinberg D. Factors involved in specific transcription by mammalian RNA polymerase II. Purification and subunit composition of transcription factor IIF. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 5;265(10):5629–5634. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerard M., Fischer L., Moncollin V., Chipoulet J. M., Chambon P., Egly J. M. Purification and interaction properties of the human RNA polymerase B(II) general transcription factor BTF2. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 5;266(31):20940–20945. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ha I., Lane W. S., Reinberg D. Cloning of a human gene encoding the general transcription initiation factor IIB. Nature. 1991 Aug 22;352(6337):689–695. doi: 10.1038/352689a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inostroza J., Flores O., Reinberg D. Factors involved in specific transcription by mammalian RNA polymerase II. Purification and functional analysis of general transcription factor IIE. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 15;266(14):9304–9308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim W. Y., Dahmus M. E. The major late promoter of adenovirus-2 is accurately transcribed by RNA polymerases IIO, IIA, and IIB. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 25;264(6):3169–3176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laybourn P. J., Dahmus M. E. Phosphorylation of RNA polymerase IIA occurs subsequent to interaction with the promoter and before the initiation of transcription. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 5;265(22):13165–13173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laybourn P. J., Dahmus M. E. Transcription-dependent structural changes in the C-terminal domain of mammalian RNA polymerase subunit IIa/o. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 25;264(12):6693–6698. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. M., Greenleaf A. L. A protein kinase that phosphorylates the C-terminal repeat domain of the largest subunit of RNA polymerase II. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3624–3628. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. M., Greenleaf A. L. CTD kinase large subunit is encoded by CTK1, a gene required for normal growth of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Gene Expr. 1991 May;1(2):149–167. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu H., Flores O., Weinmann R., Reinberg D. The nonphosphorylated form of RNA polymerase II preferentially associates with the preinitiation complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 15;88(22):10004–10008. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.22.10004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malik S., Hisatake K., Sumimoto H., Horikoshi M., Roeder R. G. Sequence of general transcription factor TFIIB and relationships to other initiation factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 1;88(21):9553–9557. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.21.9553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohkuma Y., Sumimoto H., Horikoshi M., Roeder R. G. Factors involved in specific transcription by mammalian RNA polymerase II: purification and characterization of general transcription factor TFIIE. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(23):9163–9167. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.23.9163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne J. M., Laybourn P. J., Dahmus M. E. The transition of RNA polymerase II from initiation to elongation is associated with phosphorylation of the carboxyl-terminal domain of subunit IIa. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 25;264(33):19621–19629. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson S. R., Dvir A., Anderson C. W., Dynan W. S. DNA binding provides a signal for phosphorylation of the RNA polymerase II heptapeptide repeats. Genes Dev. 1992 Mar;6(3):426–438. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.3.426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawadogo M., Roeder R. G. Energy requirement for specific transcription initiation by the human RNA polymerase II system. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 25;259(8):5321–5326. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawadogo M., Sentenac A. RNA polymerase B (II) and general transcription factors. Annu Rev Biochem. 1990;59:711–754. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.59.070190.003431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt M. C., Kao C. C., Pei R., Berk A. J. Yeast TATA-box transcription factor gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):7785–7789. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.7785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigler P. B. Transcriptional activation. Acid blobs and negative noodles. Nature. 1988 May 19;333(6170):210–212. doi: 10.1038/333210a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson N. E., Aronson D. B., Burgess R. R. Purification of eukaryotic RNA polymerase II by immunoaffinity chromatography. Elution of active enzyme with protein stabilizing agents from a polyol-responsive monoclonal antibody. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 25;265(12):7069–7077. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson N. E., Steinberg T. H., Aronson D. B., Burgess R. R. Inhibition of in vivo and in vitro transcription by monoclonal antibodies prepared against wheat germ RNA polymerase II that react with the heptapeptide repeat of eukaryotic RNA polymerase II. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 5;264(19):11511–11520. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang W., Carey M., Gralla J. D. Polymerase II promoter activation: closed complex formation and ATP-driven start site opening. Science. 1992 Jan 24;255(5043):450–453. doi: 10.1126/science.1310361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zehring W. A., Lee J. M., Weeks J. R., Jokerst R. S., Greenleaf A. L. The C-terminal repeat domain of RNA polymerase II largest subunit is essential in vivo but is not required for accurate transcription initiation in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(11):3698–3702. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.11.3698. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang J., Corden J. L. Identification of phosphorylation sites in the repetitive carboxyl-terminal domain of the mouse RNA polymerase II largest subunit. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 5;266(4):2290–2296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]