(The American Journal of Human Genetics 90, 457–466; March 9, 2012)
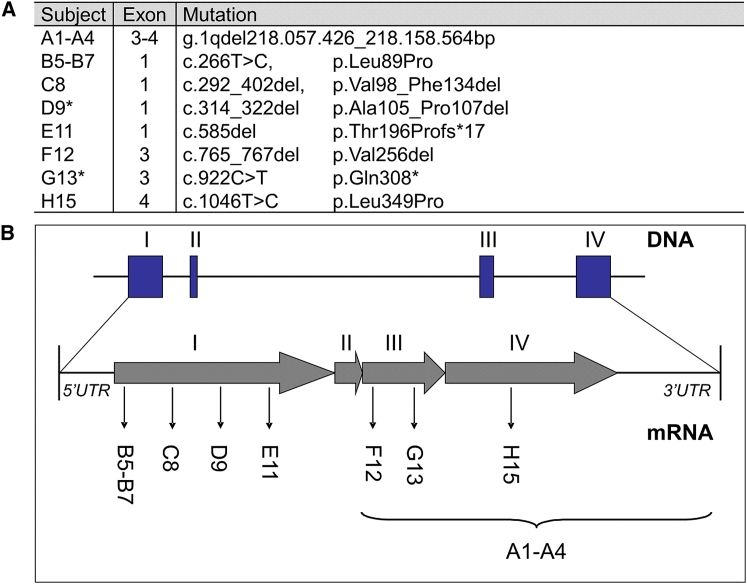
In this article, Figure 1 contained an error regarding the position of the deletion detected in the affected individuals of family A. The no-call SNPs between the coordinates 218,057,426 and 218,158,564 (GRCh36) suggest that exons 3 and 4 of SLC30A10 are deleted, whereas the original figure showed that exons 1 and 2 were deleted. The corrected Figure 1 and its legend are shown here. The authors regret the error.
Figure 1.
SLC30A10 Mutations in Affected Families with a Syndrome of Hepatic Cirrhosis, Dystonia, Polycythemia, and Hypermanganesemia
(A) Mutations in SLC30A10 identified by DNA sequencing. (For families D and G no DNA was available for analysis of deceased siblings D-II-3 and G-II-1.)
(B) Genomic structure of the exons encoding SLC30A10 and positions of identified mutations. The large deletion spanning exons 3 and 4 in family A is indicated by a bracket.