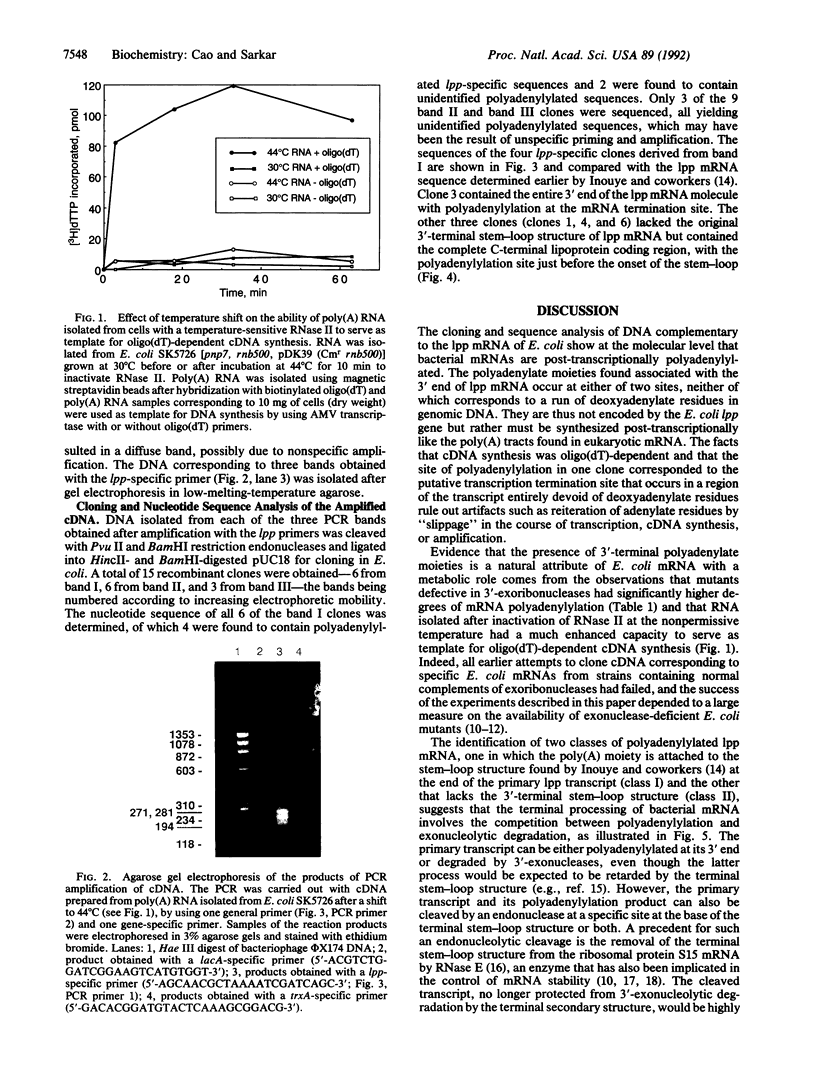
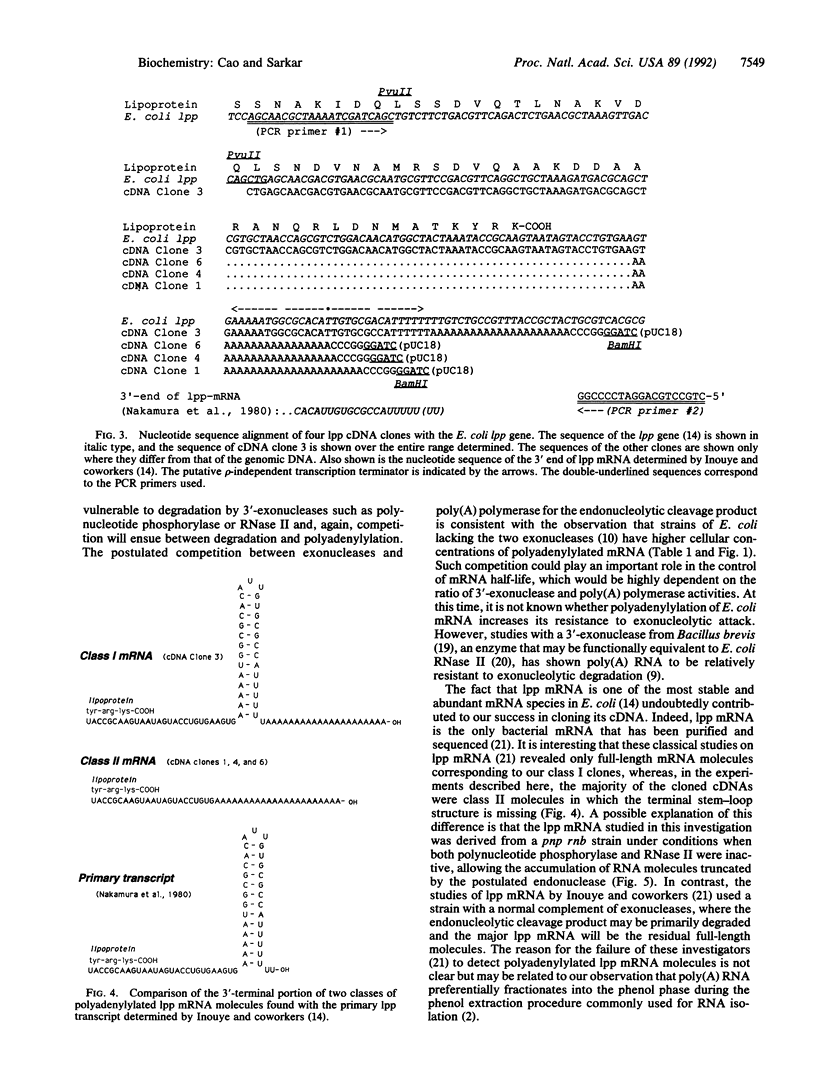
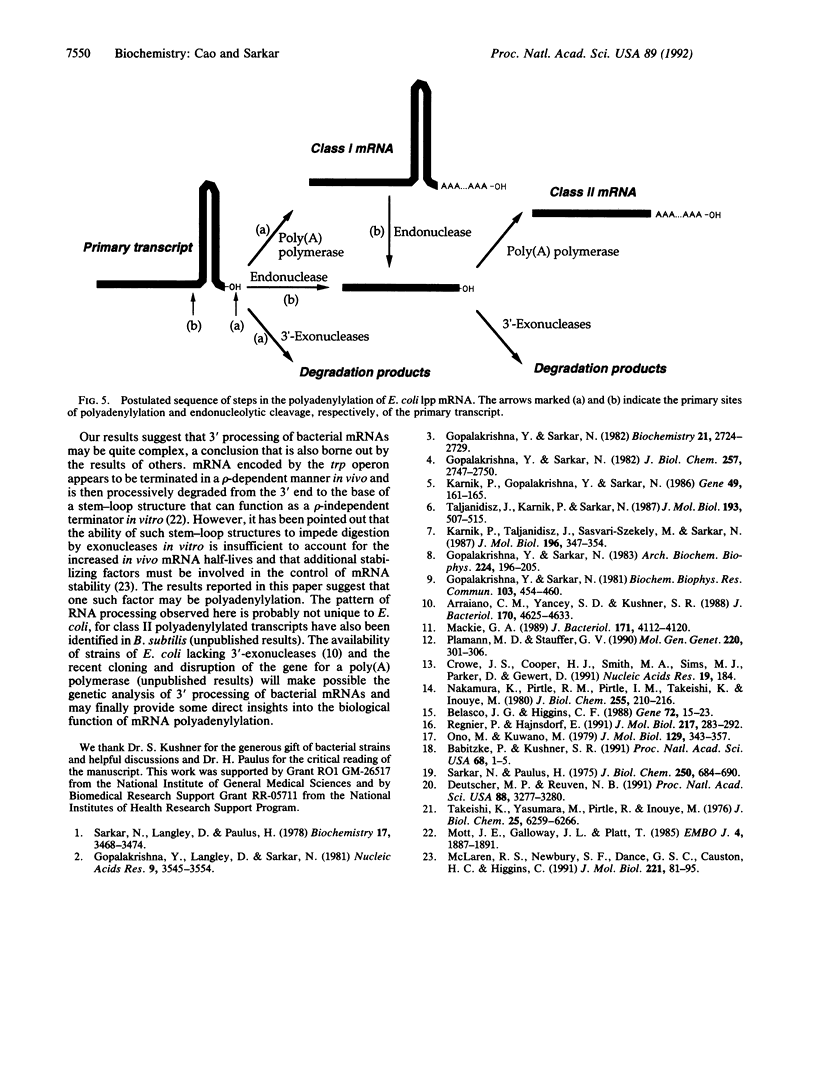
Abstract
Although it has been known for some time that bacterial mRNA molecules carry polyadenylate moieties at their 3' ends, nothing is known about the molecular structure of bacterial poly(A) RNA. To define the polyadenylylation site of a specific bacterial mRNA, we took advantage of the presence of elevated levels of poly(A) RNA in cells of Escherichia coli deficient in exoribonucleases and synthesized DNA complementary to polyadenylylated lipoprotein mRNA, encoded by the lpp gene, by using avian myeloblastosis virus reverse transcriptase and an oligo(dT)-containing primer. The 5'-terminal portion of the cDNA was amplified by the polymerase chain reaction and appropriate oligonucleotide primers, and the amplified DNA was cloned in pUC18 and subjected to nucleotide sequence analysis. Four clones were found to contain the entire 3'-terminal coding region of lpp mRNA, with poly(A) attached to either of two sites in the downstream untranslated region of the transcript. In one type of clone, the polyadenylate moiety was attached at the putative transcription termination site of lpp mRNA, whereas other clones lacked the stem-loop structure of the rho-independent transcription terminator and the polyadenylate moiety was attached to the residue just preceding the terminal stem-loop of the primary transcript. A model for the polyadenylylation of bacterial mRNA is proposed in which poly(A) polymerase and exonucleases compete for the 3' ends of mRNA molecules.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arraiano C. M., Yancey S. D., Kushner S. R. Stabilization of discrete mRNA breakdown products in ams pnp rnb multiple mutants of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1988 Oct;170(10):4625–4633. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.10.4625-4633.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babitzke P., Kushner S. R. The Ams (altered mRNA stability) protein and ribonuclease E are encoded by the same structural gene of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 1;88(1):1–5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belasco J. G., Higgins C. F. Mechanisms of mRNA decay in bacteria: a perspective. Gene. 1988 Dec 10;72(1-2):15–23. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90123-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowe J. S., Cooper H. J., Smith M. A., Sims M. J., Parker D., Gewert D. Improved cloning efficiency of polymerase chain reaction (PCR) products after proteinase K digestion. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jan 11;19(1):184–184. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.1.184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deutscher M. P., Reuven N. B. Enzymatic basis for hydrolytic versus phosphorolytic mRNA degradation in Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 15;88(8):3277–3280. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.8.3277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gopalakrishna Y., Langley D., Sarkar N. Detection of high levels of polyadenylate-containing RNA in bacteria by the use of a single-step RNA isolation procedure. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 24;9(14):3545–3554. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.14.3545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gopalakrishna Y., Sarkar N. Characterization of polyadenylate-containing ribonucleic acid from Bacillus subtilis. Biochemistry. 1982 May 25;21(11):2724–2729. doi: 10.1021/bi00540a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gopalakrishna Y., Sarkar N. Selective resistance of bacterial polyadenylate-containing RNA to hydrolysis by guanosine 3'-5'-monophosphate-sensitive nuclease of Bacillus brevis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Nov 30;103(2):454–460. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)90474-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gopalakrishna Y., Sarkar N. Synthesis of polyadenylate-containing RNA in vitro in permeable cells of Escherichia coli B. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1983 Jul 1;224(1):196–205. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(83)90204-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gopalakrishna Y., Sarkar N. The synthesis of DNA complementary to polyadenylate-containing RNA from Bacillus subtilis. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 25;257(6):2747–2750. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karnik P., Gopalakrishna Y., Sarkar N. Construction of a cDNA library from polyadenylated RNA of Bacillus subtilis and the determination of some 3'-terminal sequences. Gene. 1986;49(1):161–165. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90397-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karnik P., Taljanidisz J., Sasvari-Szekely M., Sarkar N. 3'-terminal polyadenylate sequences of Escherichia coli tryptophan synthetase alpha-subunit messenger RNA. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jul 20;196(2):347–354. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90695-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackie G. A. Stabilization of the 3' one-third of Escherichia coli ribosomal protein S20 mRNA in mutants lacking polynucleotide phosphorylase. J Bacteriol. 1989 Aug;171(8):4112–4120. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.8.4112-4120.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaren R. S., Newbury S. F., Dance G. S., Causton H. C., Higgins C. F. mRNA degradation by processive 3'-5' exoribonucleases in vitro and the implications for prokaryotic mRNA decay in vivo. J Mol Biol. 1991 Sep 5;221(1):81–95. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mott J. E., Galloway J. L., Platt T. Maturation of Escherichia coli tryptophan operon mRNA: evidence for 3' exonucleolytic processing after rho-dependent termination. EMBO J. 1985 Jul;4(7):1887–1891. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03865.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura K., Pirtle R. M., Pirtle I. L., Takeishi K., Inouye M. Messenger ribonucleic acid of the lipoprotein of the Escherichia coli outer membrane. II. The complete nucleotide sequence. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jan 10;255(1):210–216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono M., Kuwano M. A conditional lethal mutation in an Escherichia coli strain with a longer chemical lifetime of messenger RNA. J Mol Biol. 1979 Apr 15;129(3):343–357. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90500-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plamann M. D., Stauffer G. V. Escherichia coli glyA mRNA decay: the role of 3' secondary structure and the effects of the pnp and rnb mutations. Mol Gen Genet. 1990 Jan;220(2):301–306. doi: 10.1007/BF00260498. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Régnier P., Hajnsdorf E. Decay of mRNA encoding ribosomal protein S15 of Escherichia coli is initiated by an RNase E-dependent endonucleolytic cleavage that removes the 3' stabilizing stem and loop structure. J Mol Biol. 1991 Jan 20;217(2):283–292. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90542-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar N., Langley D., Paulus H. Isolation and characterization of polyadenylate-containing RNA from Bacillus brevis. Biochemistry. 1978 Aug 22;17(17):3468–3474. doi: 10.1021/bi00610a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar N., Paulus H. A guanosine 3':5'-monophosphate-sensitive nuclease from Bacillus brevis. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jan 25;250(2):684–690. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeishi K., Yasumura M., Pirtle R., Inouye M. Isolation and identification of the messenger ribonucleic acid for a structural lipoprotein of the Escherichia coli outer membrane. J Biol Chem. 1976 Oct 25;251(20):6259–6266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taljanidisz J., Karnik P., Sarkar N. Messenger ribonucleic acid for the lipoprotein of the Escherichia coli outer membrane is polyadenylated. J Mol Biol. 1987 Feb 5;193(3):507–515. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90263-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




