Abstract
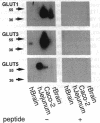
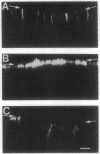
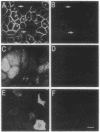
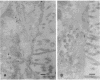
We have examined the expression and cellular location of facilitated glucose transporter proteins (GLUT1, -3, and -5) in a human colonic epithelial cell line (Caco-2) by using peptide-specific antibodies. A differential cellular distribution of these transporters was observed in differentiated (greater than 14 days postconfluence) Caco-2 cells by immunofluorescence and immunoelectron microscopy. GLUT1 was localized primarily to the basolateral membrane, whereas GLUT3 was predominantly localized to the apical membrane. GLUT5, which was detected in only approximately 40% of fully differentiated Caco-2 cells, was found primarily in the apical membrane but was also present in both basolateral and intracellular membranes. A Na(+)-independent glucose transport system in the apical membrane of Caco-2 cells has been described previously [Blais, A., Bissonnette, A. & Berteloot, A. (1987) J. Membr. Biol. 99, 113-125], and we propose that GLUT3 mediates this process. The amino acid sequence identity (57%) and structural conservation between GLUT1 and GLUT3 may make these transporters an ideal model system for examining the molecular basis for polarized sorting of membrane proteins.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bell G. I., Kayano T., Buse J. B., Burant C. F., Takeda J., Lin D., Fukumoto H., Seino S. Molecular biology of mammalian glucose transporters. Diabetes Care. 1990 Mar;13(3):198–208. doi: 10.2337/diacare.13.3.198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bendayan M. Double immunocytochemical labeling applying the protein A-gold technique. J Histochem Cytochem. 1982 Jan;30(1):81–85. doi: 10.1177/30.1.6172469. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blais A., Bissonnette P., Berteloot A. Common characteristics for Na+-dependent sugar transport in Caco-2 cells and human fetal colon. J Membr Biol. 1987;99(2):113–125. doi: 10.1007/BF01871231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown D. A., Rose J. K. Sorting of GPI-anchored proteins to glycolipid-enriched membrane subdomains during transport to the apical cell surface. Cell. 1992 Feb 7;68(3):533–544. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90189-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casanova J. E., Apodaca G., Mostov K. E. An autonomous signal for basolateral sorting in the cytoplasmic domain of the polymeric immunoglobulin receptor. Cell. 1991 Jul 12;66(1):65–75. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90139-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson N. O., Hausman A. M., Ifkovits C. A., Buse J. B., Gould G. W., Burant C. F., Bell G. I. Human intestinal glucose transporter expression and localization of GLUT5. Am J Physiol. 1992 Mar;262(3 Pt 1):C795–C800. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1992.262.3.C795. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James D. E., Strube M., Mueckler M. Molecular cloning and characterization of an insulin-regulatable glucose transporter. Nature. 1989 Mar 2;338(6210):83–87. doi: 10.1038/338083a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lisanti M. P., Le Bivic A., Saltiel A. R., Rodriguez-Boulan E. Preferred apical distribution of glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol (GPI) anchored proteins: a highly conserved feature of the polarized epithelial cell phenotype. J Membr Biol. 1990 Feb;113(2):155–167. doi: 10.1007/BF01872889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mostov K., Apodaca G., Aroeti B., Okamoto C. Plasma membrane protein sorting in polarized epithelial cells. J Cell Biol. 1992 Feb;116(3):577–583. doi: 10.1083/jcb.116.3.577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeffer S. R., Rothman J. E. Biosynthetic protein transport and sorting by the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:829–852. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.004145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piper R. C., Hess L. J., James D. E. Differential sorting of two glucose transporters expressed in insulin-sensitive cells. Am J Physiol. 1991 Mar;260(3 Pt 1):C570–C580. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1991.260.3.C570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piper R. C., Tai C., Slot J. W., Hahn C. S., Rice C. M., Huang H., James D. E. The efficient intracellular sequestration of the insulin-regulatable glucose transporter (GLUT-4) is conferred by the NH2 terminus. J Cell Biol. 1992 May;117(4):729–743. doi: 10.1083/jcb.117.4.729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slot J. W., Geuze H. J., Gigengack S., Lienhard G. E., James D. E. Immuno-localization of the insulin regulatable glucose transporter in brown adipose tissue of the rat. J Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;113(1):123–135. doi: 10.1083/jcb.113.1.123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorens B., Cheng Z. Q., Brown D., Lodish H. F. Liver glucose transporter: a basolateral protein in hepatocytes and intestine and kidney cells. Am J Physiol. 1990 Dec;259(6 Pt 1):C279–C285. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1990.259.2.C279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto T., Seino Y., Fukumoto H., Koh G., Yano H., Inagaki N., Yamada Y., Inoue K., Manabe T., Imura H. Over-expression of facilitative glucose transporter genes in human cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Jul 16;170(1):223–230. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91263-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Genderen I. L., van Meer G., Slot J. W., Geuze H. J., Voorhout W. F. Subcellular localization of Forssman glycolipid in epithelial MDCK cells by immuno-electronmicroscopy after freeze-substitution. J Cell Biol. 1991 Nov;115(4):1009–1019. doi: 10.1083/jcb.115.4.1009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]