Abstract
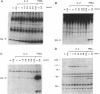
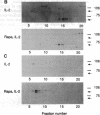
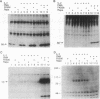
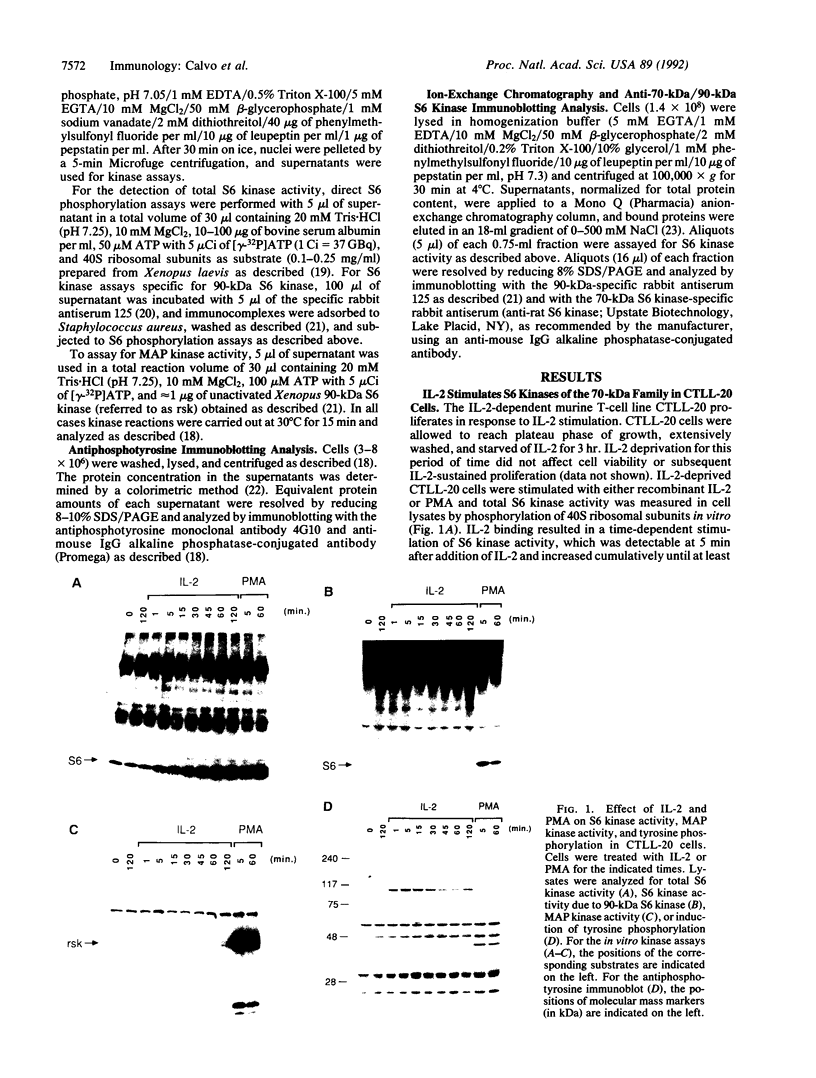
Binding of interleukin 2 (IL-2) to its receptor generates intracellular signals, including the activation of tyrosine and serine/threonine kinases. In this study the activation of the serine/threonine-specific ribosomal protein S6 kinases in response to IL-2 was analyzed in the murine T-cell line CTLL-20, a model system of IL-2-dependent proliferation. Two major classes of S6 kinases have been characterized: the 90-kDa (rsk) family and the 70-kDa family. In response to the addition of recombinant IL-2, total S6 kinase activity was increased. This S6 kinase activity could not be immunoprecipitated by an antiserum specific for S6 kinases of the 90-kDa family, exhibited a chromatographic behavior characteristic of 70-kDa S6 kinases, and was recognized by a 70-kDa S6 kinase-specific antiserum. Thus, IL-2 binding to its receptor induces specific activation of the 70-kDa family of S6 kinases. Rapamycin, a macrolide immunosuppressant that inhibits IL-2-dependent proliferation, inhibited IL-2-stimulated 70-kDa S6 kinase activity subsequent to early increases in tyrosine kinase activity. These findings imply that the targets of rapamycin include molecules involved in the activation of 70-kDa S6 kinases. These observations further suggest that S6 kinases of the 70-kDa family participate in signal transmission pathways subsequent to IL-2 binding to its receptor.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson N. G., Maller J. L., Tonks N. K., Sturgill T. W. Requirement for integration of signals from two distinct phosphorylation pathways for activation of MAP kinase. Nature. 1990 Feb 15;343(6259):651–653. doi: 10.1038/343651a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banerjee P., Ahmad M. F., Grove J. R., Kozlosky C., Price D. J., Avruch J. Molecular structure of a major insulin/mitogen-activated 70-kDa S6 protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(21):8550–8554. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.21.8550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bierer B. E., Mattila P. S., Standaert R. F., Herzenberg L. A., Burakoff S. J., Crabtree G., Schreiber S. L. Two distinct signal transmission pathways in T lymphocytes are inhibited by complexes formed between an immunophilin and either FK506 or rapamycin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(23):9231–9235. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.23.9231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calvo V., Bierer B. E., Vik T. A. T cell receptor activation of a ribosomal S6 kinase activity. Eur J Immunol. 1992 Feb;22(2):457–462. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830220225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cosman D., Cerretti D. P., Larsen A., Park L., March C., Dower S., Gillis S., Urdal D. Cloning, sequence and expression of human interleukin-2 receptor. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):768–771. doi: 10.1038/312768a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dumont F. J., Staruch M. J., Koprak S. L., Melino M. R., Sigal N. H. Distinct mechanisms of suppression of murine T cell activation by the related macrolides FK-506 and rapamycin. J Immunol. 1990 Jan 1;144(1):251–258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erikson E., Maller J. L. Purification and characterization of a protein kinase from Xenopus eggs highly specific for ribosomal protein S6. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 5;261(1):350–355. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erikson R. L. Structure, expression, and regulation of protein kinases involved in the phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 5;266(10):6007–6010. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans S. W., Farrar W. L. Interleukin 2 and diacylglycerol stimulate phosphorylation of 40 S ribosomal S6 protein. Correlation with increased protein synthesis and S6 kinase activation. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 5;262(10):4624–4630. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fruman D. A., Klee C. B., Bierer B. E., Burakoff S. J. Calcineurin phosphatase activity in T lymphocytes is inhibited by FK 506 and cyclosporin A. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 1;89(9):3686–3690. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.9.3686. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grove J. R., Banerjee P., Balasubramanyam A., Coffer P. J., Price D. J., Avruch J., Woodgett J. R. Cloning and expression of two human p70 S6 kinase polypeptides differing only at their amino termini. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Nov;11(11):5541–5550. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.11.5541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanekom C., Nel A., Gittinger C., Rheeder A., Landreth G. Complexing of the CD-3 subunit by a monoclonal antibody activates a microtubule-associated protein 2 (MAP-2) serine kinase in Jurkat cells. Biochem J. 1989 Sep 1;262(2):449–456. doi: 10.1042/bj2620449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatakeyama M., Tsudo M., Minamoto S., Kono T., Doi T., Miyata T., Miyasaka M., Taniguchi T. Interleukin-2 receptor beta chain gene: generation of three receptor forms by cloned human alpha and beta chain cDNA's. Science. 1989 May 5;244(4904):551–556. doi: 10.1126/science.2785715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones S. W., Erikson E., Blenis J., Maller J. L., Erikson R. L. A Xenopus ribosomal protein S6 kinase has two apparent kinase domains that are each similar to distinct protein kinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(10):3377–3381. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.10.3377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozma S. C., Ferrari S., Bassand P., Siegmann M., Totty N., Thomas G. Cloning of the mitogen-activated S6 kinase from rat liver reveals an enzyme of the second messenger subfamily. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(19):7365–7369. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.19.7365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard W. J., Depper J. M., Crabtree G. R., Rudikoff S., Pumphrey J., Robb R. J., Krönke M., Svetlik P. B., Peffer N. J., Waldmann T. A. Molecular cloning and expression of cDNAs for the human interleukin-2 receptor. Nature. 1984 Oct 18;311(5987):626–631. doi: 10.1038/311626a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu J., Farmer J. D., Jr, Lane W. S., Friedman J., Weissman I., Schreiber S. L. Calcineurin is a common target of cyclophilin-cyclosporin A and FKBP-FK506 complexes. Cell. 1991 Aug 23;66(4):807–815. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90124-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikaido T., Shimizu A., Ishida N., Sabe H., Teshigawara K., Maeda M., Uchiyama T., Yodoi J., Honjo T. Molecular cloning of cDNA encoding human interleukin-2 receptor. Nature. 1984 Oct 18;311(5987):631–635. doi: 10.1038/311631a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robb R. J., Greene W. C., Rusk C. M. Low and high affinity cellular receptors for interleukin 2. Implications for the level of Tac antigen. J Exp Med. 1984 Oct 1;160(4):1126–1146. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.4.1126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber S. L. Chemistry and biology of the immunophilins and their immunosuppressive ligands. Science. 1991 Jan 18;251(4991):283–287. doi: 10.1126/science.1702904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel J. P., Sharon M., Smith P. L., Leonard W. J. The IL-2 receptor beta chain (p70): role in mediating signals for LAK, NK, and proliferative activities. Science. 1987 Oct 2;238(4823):75–78. doi: 10.1126/science.3116668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith K. A. Interleukin 2. Annu Rev Immunol. 1984;2:319–333. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.02.040184.001535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturgill T. W., Ray L. B., Erikson E., Maller J. L. Insulin-stimulated MAP-2 kinase phosphorylates and activates ribosomal protein S6 kinase II. Nature. 1988 Aug 25;334(6184):715–718. doi: 10.1038/334715a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweet L. J., Alcorta D. A., Erikson R. L. Two distinct enzymes contribute to biphasic S6 phosphorylation in serum-stimulated chicken embryo fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):2787–2792. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.2787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vik T. A., Sweet L. J., Erikson R. L. Coinfection of insect cells with recombinant baculovirus expressing pp60v-src results in the activation of a serine-specific protein kinase pp90rsk. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(7):2685–2689. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.7.2685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang H. M., Smith K. A. The interleukin 2 receptor. Functional consequences of its bimolecular structure. J Exp Med. 1987 Oct 1;166(4):1055–1069. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.4.1055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]