Abstract
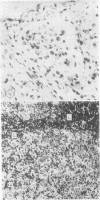
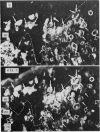
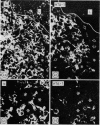
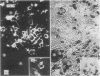
The immunological phenotype of the cells involved in skin and lymph node lesions from two cases of histiocytosis X (H-X) were analysed by immunofluorescence techniques using combinations of heterologous and monoclonal antisera to Ia-like antigen and human cortical thymocyte (HTA-1) determinant. These cells were also characterised by a new technique using simultaneous immunofluorescence and enzyme histochemistry for acid phosphatase (ACPase). The major cell type in the lesions was found to express the same Ia+, HTA-1+ phenotype as normal epidermal Langerhans' cells (LC) and was unreactive for ACPase. Additional cell types included Ia-, HTA-1- multinucleate giant cells and residual lymphoid populations. These findings endorse previous concepts that H-X is a proliferation of abnormal LC and emphasise the heterogeneous nature of the cells involved in the disease.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Basset F., Turiaf M. J. Identification par la microscopie électronique de particules de nature probablement virale dans les liaisons granulomateuses d'une histiocytose "X" pulmonaire. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1965 Nov 3;261(18):3701–3703. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berman B., France D. S. Histochemical analysis of Langerhans' cells. Am J Dermatopathol. 1979 Fall;1(3):215–221. doi: 10.1097/00000372-197900130-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elema J. D., Poppema S. Infantile histiocytosis X. Cancer. 1978 Aug;42(2):555–565. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197808)42:2<555::aid-cncr2820420223>3.0.co;2-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fithian E., Kung P., Goldstein G., Rubenfeld M., Fenoglio C., Edelson R. Reactivity of Langerhans cells with hybridoma antibody. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2541–2544. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gianotti F., Caputo R. Skin ultrastructure in Hand-Schüller-Christian disease. Report on abnormal Langerhans' cells. Arch Dermatol. 1969 Sep;100(3):342–349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halper J. P., Knowles D. M., 2nd, Wang C. Y. Ia antigen expression by human malignant lymphomas: correlation with conventional lymphoid markers. Blood. 1980 Mar;55(3):373–382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imamura M., Muroya K. Lymph node ultrastructure in Hand-Schüller-Christian disease. Cancer. 1971 Apr;27(4):956–964. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197104)27:4<956::aid-cncr2820270431>3.0.co;2-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janossy G., Thomas J. A., Bollum F. J., Granger S., Pizzolo G., Bradstock K. F., Wong L., McMichael A., Ganeshaguru K., Hoffbrand A. V. The human thymic microenvironment: an immunohistologic study. J Immunol. 1980 Jul;125(1):202–212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janossy G., Tidman N., Selby W. S., Thomas J. A., Granger S., Kung P. C., Goldstein G. Human T lymphocytes of inducer and suppressor type occupy different microenvironments. Nature. 1980 Nov 6;288(5786):81–84. doi: 10.1038/288081a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaubert F., Barbey S., Nogues C., Monnet J. P., Grun M., Nezelof C. Histiocyte X positivity for nonspecific esterase. J Histochem Cytochem. 1980 Jan;28(1):45–46. doi: 10.1177/28.1.6153192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz S. I., Tamaki K., Sachs D. H. Epidermal Langerhans cells are derived from cells originating in bone marrow. Nature. 1979 Nov 15;282(5736):324–326. doi: 10.1038/282324a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly R. H., Balfour B. M., Armstrong J. A., Griffiths S. Functional anatomy of lymph nodes. II. Peripheral lymph-borne mononuclear cells. Anat Rec. 1978 Jan;190(1):5–21. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091900103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LICHTENSTEIN L. Histiocytosis X; integration of eosinophilic granuloma of bone, Letterer-Siwe disease, and Schüller-Christian disease as related manifestations of a single nosologic entity. AMA Arch Pathol. 1953 Jul;56(1):84–102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert I. A., Suitters A. J., Janossy G., Thomas J. A., Palmer S., Gordon Smith E. Lymphoid infiltrates in skin in graft-versus-host disease. Lancet. 1981 Dec 12;2(8259):1352–1352. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)91378-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leder L. D. Subtle clues to diagnosis by histochemistry. Histiocytosis X. Am J Dermatopathol. 1979 Winter;1(4):365–369. doi: 10.1097/00000372-197900140-00015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nesbit M. E., Jr, O'Leary M., Dehner L. P., Ramsay N. K. The immune system and the histiocytosis syndromes. Am J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 1981 Summer;3(2):141–149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowden G., Lewis M. G., Sullivan A. K. Ia antigen expression on human epidermal Langerhans cells. Nature. 1977 Jul 21;268(5617):247–248. doi: 10.1038/268247a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowden G., Phillips T. M., Lewis M. G., Wilkinson R. D. Target role of Langerhans cells in mycosis fungoides: transmission and immuno-electron microscopic studies. J Cutan Pathol. 1979 Oct;6(5):364–382. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0560.1979.tb01159.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stingl G., Wolff-Schreiner E. C., Pichler W. J., Gschnait F., Knapp W., Wolff K. Epidermal Langerhans cells bear Fc and C3 receptors. Nature. 1977 Jul 21;268(5617):245–246. doi: 10.1038/268245a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorbecke G. J., Silberberg-Sinakin I., Flotte T. J. Langerhans cells as macrophages in skin and lymphoid organs. J Invest Dermatol. 1980 Jul;75(1):32–43. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12521083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. W., Dorfman R. F. Lymphadenopathy as the initial manifestation of histiocytosis X. Am J Surg Pathol. 1979 Oct;3(5):405–421. doi: 10.1097/00000478-197910000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff H. H. Subtle clues to diagnosis of skin diseases by electron microscopy. Langerhans' cell granules in histiocytosis X. Am J Dermatopathol. 1979 Spring;1(1):77–81. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]