Abstract
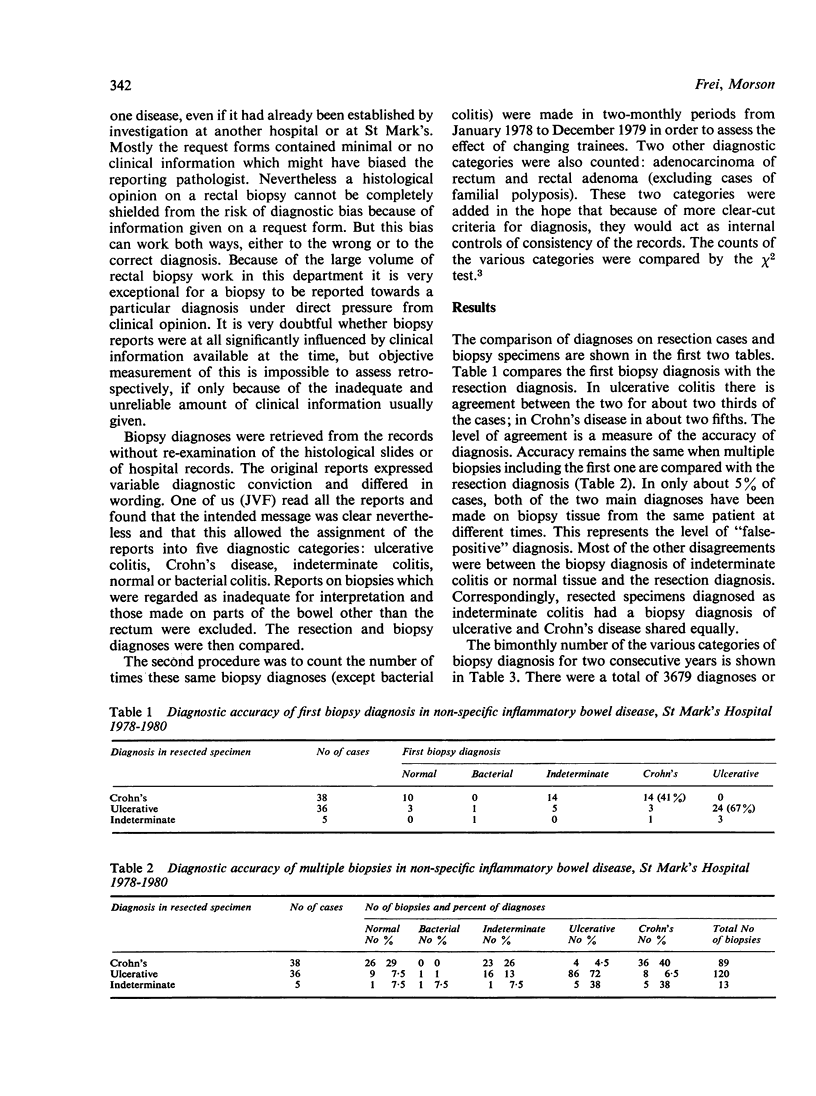
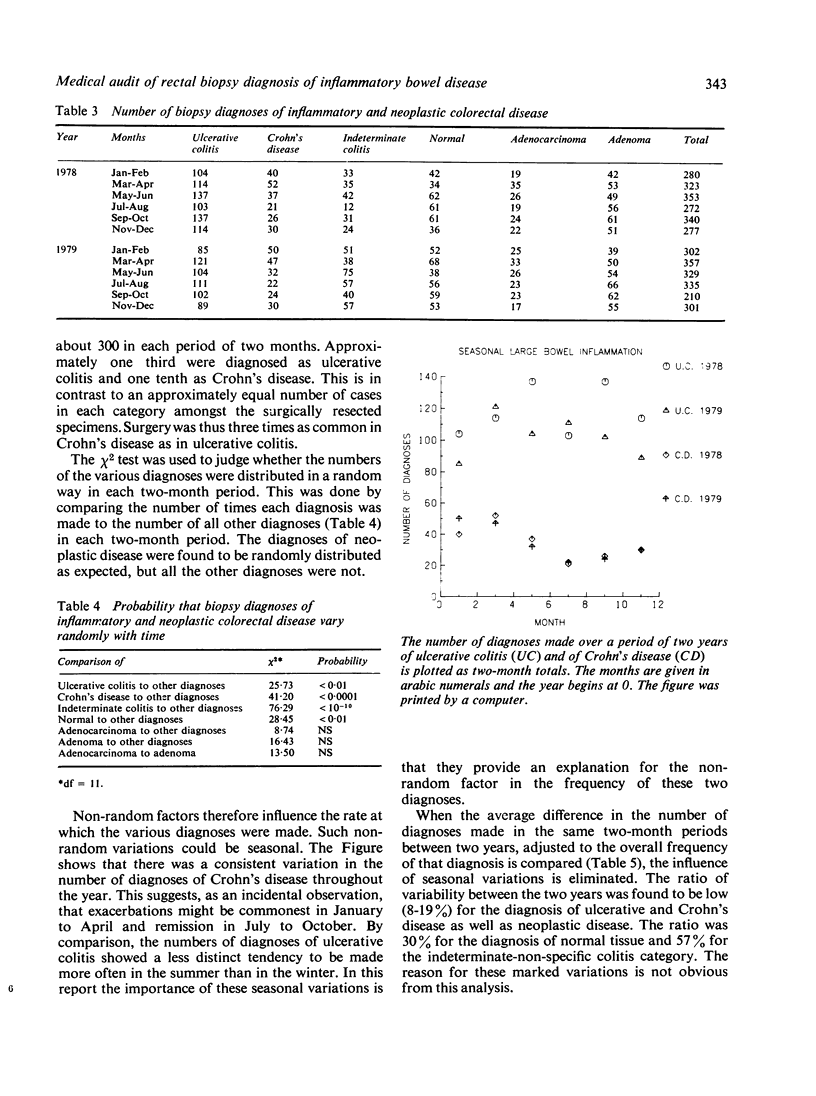
The records of the rectal biopsy diagnoses of ulcerative colitis and Crohn's disease in the Department of Pathology, St Mark's Hospital, London, were reviewed. The biopsy diagnoses were compared to subsequent resection diagnoses on the same patients, and annual and seasonal variations in the frequency of these and related diagnoses were studied. The accuracy rate for the biopsy diagnosis of ulcerative colitis was about 70% and for Crohn's disease about 40% each time a biopsy was read. The low figure for the accuracy rate for Crohn's disease could be attributed to sampling error inherent in the diagnosis of a disease which is essentially patchy, showing discontinuous pathology. Also, many patients with Crohn's disease have a normal rectum which is biopsied to demonstrate the distinction from ulcerative colitis. In practical terms therefore a 40% accuracy rate in Crohn's disease is probably adequate. The rate of "false-positive" diagnoses was about 5%. There was a seasonal variation in the frequency of these two diagnoses, but no variation attributable to changes in observers, as pathology trainees in the Department change regularly. The frequency of diagnoses of non-specific inflammation and of normal colon did show such non-random variations.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Morson B. C. Pathology of inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterol Jpn. 1980 Apr;15(2):184–187. doi: 10.1007/BF02774935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner K. E., Hutton R. C. Cost-benefit and cost-effectiveness analysis in health care. Growth and composition of the literature. Med Care. 1980 Nov;18(11):1069–1084. doi: 10.1097/00005650-198011000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



