Abstract
Reactivation of latent virus is believed to result from a signal transduction event that induces immediate-early (IE) gene transcription. Evidence is presented that the major IE promoter (MIEP) of human cytomegalovirus (hCMV) is activated by physiological levels of retinoic acid (RA) in human embryonal carcinoma cells. Mutagenesis experiments localized in the MIEP enhancer, a retinoic acid-responsive element composed of a direct repeat separated by five nucleotides. Protein-DNA binding experiments revealed that this element functions as a specific target site for the direct interaction of nuclear receptor proteins for RA. These findings implicate the biologically active derivative of vitamin A (RA) as a potential modulator of hCMV pathogenesis in infants and immunocompromised adults.
Full text
PDF
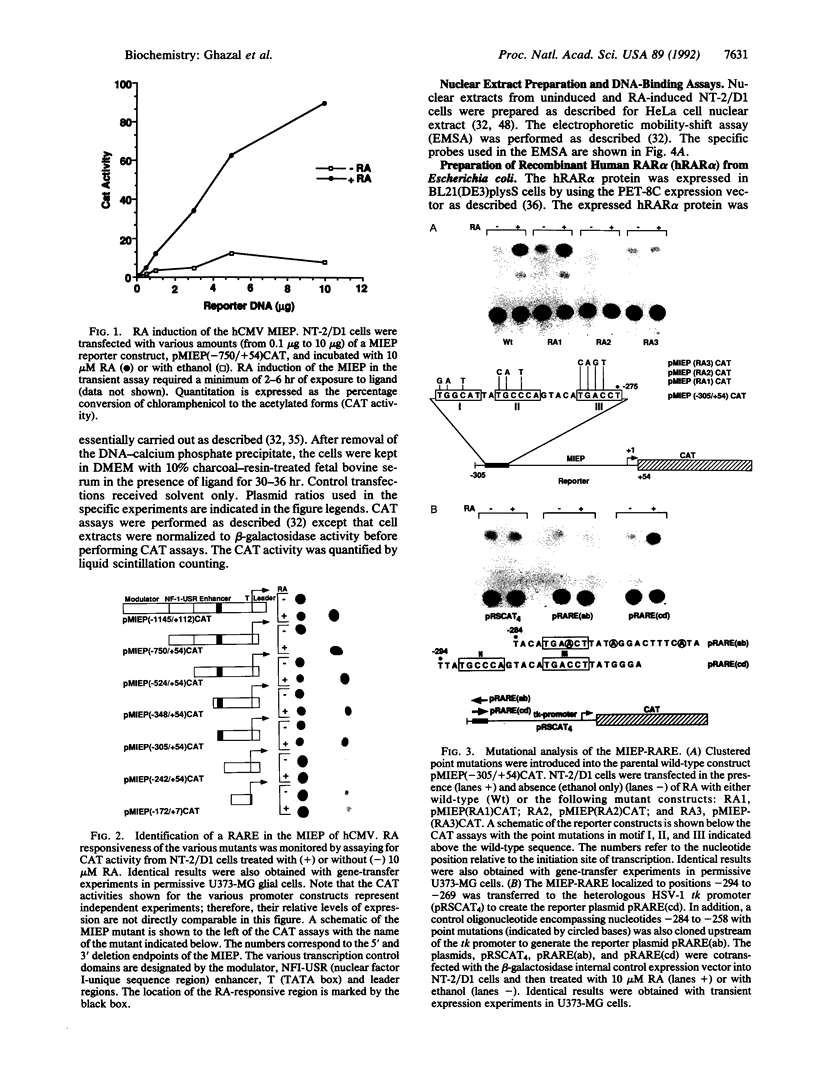

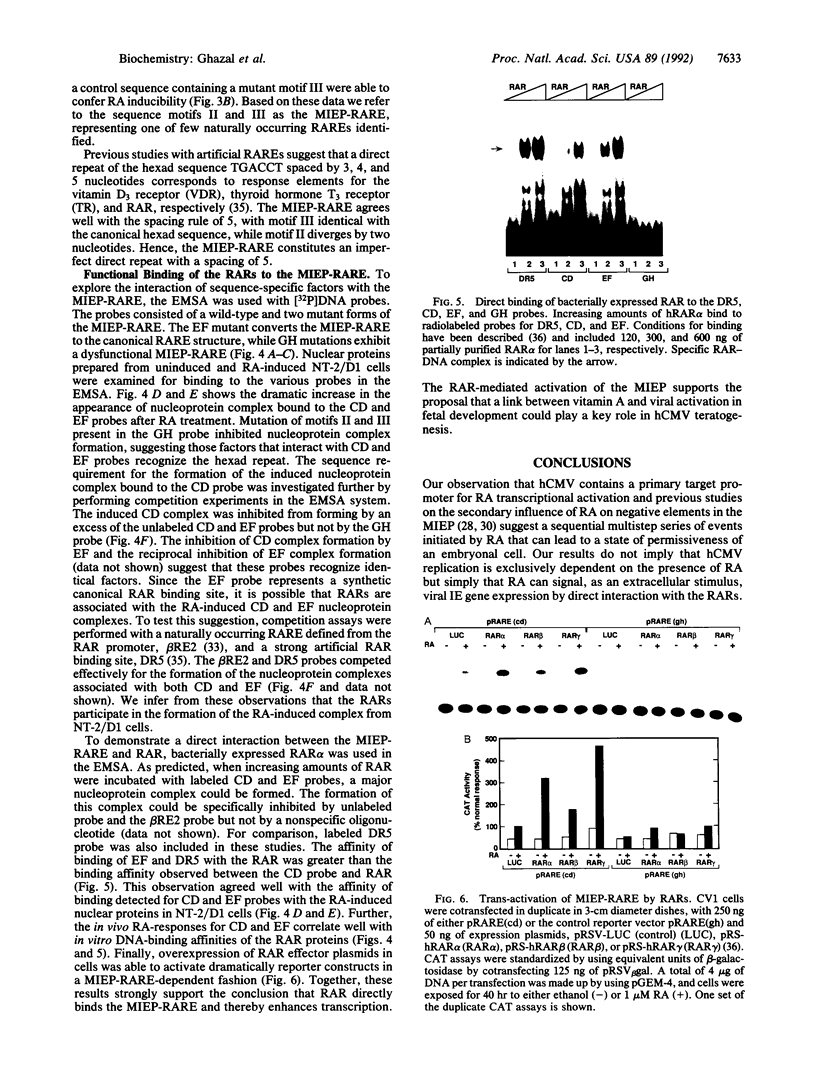

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrews P. W., Damjanov I., Simon D., Banting G. S., Carlin C., Dracopoli N. C., Føgh J. Pluripotent embryonal carcinoma clones derived from the human teratocarcinoma cell line Tera-2. Differentiation in vivo and in vitro. Lab Invest. 1984 Feb;50(2):147–162. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews P. W., Gönczöl E., Plotkin S. A., Dignazio M., Oosterhuis J. W. Differentiation of TERA-2 human embryonal carcinoma cells into neurons and HCMV permissive cells. Induction by agents other than retinoic acid. Differentiation. 1986;31(2):119–126. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1986.tb00392.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews P. W. Retinoic acid induces neuronal differentiation of a cloned human embryonal carcinoma cell line in vitro. Dev Biol. 1984 Jun;103(2):285–293. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(84)90316-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CROME L., FRANCE N. E. Microgyria and cytomegalic inclusion disease in infancy. J Clin Pathol. 1959 Sep;12:427–434. doi: 10.1136/jcp.12.5.427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CROME L. Microgyria. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1952 Jul;64(3):479–495. doi: 10.1002/path.1700640308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIEZEL P. B. Mikrogyrie infolge cerebraler Speicheldrüsenvirusinfektion im Rhamen einer generalisierten Cytomegalie bei einem Säugling, Zugleich ein Beitrag zur Theorie der Windungsbildung. Virchows Arch Pathol Anat Physiol Klin Med. 1954;325(1):109–130. doi: 10.1007/BF00954506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duester G., Shean M. L., McBride M. S., Stewart M. J. Retinoic acid response element in the human alcohol dehydrogenase gene ADH3: implications for regulation of retinoic acid synthesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;11(3):1638–1646. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.3.1638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. M. The steroid and thyroid hormone receptor superfamily. Science. 1988 May 13;240(4854):889–895. doi: 10.1126/science.3283939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman W. R., Lerner C. W., Mines J. A., Lash R. S., Nadel A. J., Starr M. B., Tapper M. L. A prospective study of the ophthalmologic findings in the acquired immune deficiency syndrome. Am J Ophthalmol. 1984 Feb;97(2):133–142. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9394(14)76082-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghazal P., Lubon H., Fleckenstein B., Hennighausen L. Binding of transcription factors and creation of a large nucleoprotein complex on the human cytomegalovirus enhancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(11):3658–3662. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.11.3658. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghazal P., Nelson J. A. Enhancement of RNA polymerase II initiation complexes by a novel DNA control domain downstream from the cap site of the cytomegalovirus major immediate-early promoter. J Virol. 1991 May;65(5):2299–2307. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.5.2299-2307.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giguere V., Ong E. S., Segui P., Evans R. M. Identification of a receptor for the morphogen retinoic acid. Nature. 1987 Dec 17;330(6149):624–629. doi: 10.1038/330624a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green S., Chambon P. Nuclear receptors enhance our understanding of transcription regulation. Trends Genet. 1988 Nov;4(11):309–314. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(88)90108-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gönczöl E., Andrews P. W., Plotkin S. A. Cytomegalovirus replicates in differentiated but not in undifferentiated human embryonal carcinoma cells. Science. 1984 Apr 13;224(4645):159–161. doi: 10.1126/science.6322309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAYMAKER W., GIRDANY B. R., STEPHENS J., LILLIE R. D., FETTERMAN G. H. Cerebral involvement with advanced periventricular calcification in generalized cytomegalic inclusion disease in the newborn; a clinicopathological report of a case diagnosed during life. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1954 Oct;13(4):562–586. doi: 10.1093/jnen/13.4.562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanshaw J. B. Congenital and acquired cytomegalovirus infection. Pediatr Clin North Am. 1966 May;13(2):279–293. doi: 10.1016/s0031-3955(16)31838-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishikawa T., Umesono K., Mangelsdorf D. J., Aburatani H., Stanger B. Z., Shibasaki Y., Imawari M., Evans R. M., Takaku F. A functional retinoic acid receptor encoded by the gene on human chromosome 12. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Jun;4(6):837–844. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-6-837. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaFemina R., Hayward G. S. Constitutive and retinoic acid-inducible expression of cytomegalovirus immediate-early genes in human teratocarcinoma cells. J Virol. 1986 May;58(2):434–440. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.2.434-440.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lammer E. J., Chen D. T., Hoar R. M., Agnish N. D., Benke P. J., Braun J. T., Curry C. J., Fernhoff P. M., Grix A. W., Jr, Lott I. T. Retinoic acid embryopathy. N Engl J Med. 1985 Oct 3;313(14):837–841. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198510033131401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langman J., Welch G. W. Excess vitamin A and development of the cerebral cortex. J Comp Neurol. 1967 Sep;131(1):15–26. doi: 10.1002/cne.901310103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucas P. C., O'Brien R. M., Mitchell J. A., Davis C. M., Imai E., Forman B. M., Samuels H. H., Granner D. K. A retinoic acid response element is part of a pleiotropic domain in the phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 15;88(6):2184–2188. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.6.2184. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangelsdorf D. J., Ong E. S., Dyck J. A., Evans R. M. Nuclear receptor that identifies a novel retinoic acid response pathway. Nature. 1990 May 17;345(6272):224–229. doi: 10.1038/345224a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangelsdorf D. J., Umesono K., Kliewer S. A., Borgmeyer U., Ong E. S., Evans R. M. A direct repeat in the cellular retinol-binding protein type II gene confers differential regulation by RXR and RAR. Cell. 1991 Aug 9;66(3):555–561. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90018-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marques Dias M. J., Harmant-van Rijckevorsel G., Landrieu P., Lyon G. Prenatal cytomegalovirus disease and cerebral microgyria: evidence for perfusion failure, not disturbance of histogenesis, as the major cause of fetal cytomegalovirus encephalopathy. Neuropediatrics. 1984 Feb;15(1):18–24. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1052334. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muñoz-Cánoves P., Vik D. P., Tack B. F. Mapping of a retinoic acid-responsive element in the promoter region of the complement factor H gene. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 25;265(33):20065–20068. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myerson D., Hackman R. C., Nelson J. A., Ward D. C., McDougall J. K. Widespread presence of histologically occult cytomegalovirus. Hum Pathol. 1984 May;15(5):430–439. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(84)80076-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson J. A., Gnann J. W., Jr, Ghazal P. Regulation and tissue-specific expression of human cytomegalovirus. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1990;154:75–100. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-74980-3_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson J. A., Groudine M. Transcriptional regulation of the human cytomegalovirus major immediate-early gene is associated with induction of DNase I-hypersensitive sites. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Feb;6(2):452–461. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.2.452. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson J. A., Reynolds-Kohler C., Smith B. A. Negative and positive regulation by a short segment in the 5'-flanking region of the human cytomegalovirus major immediate-early gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Nov;7(11):4125–4129. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.11.4125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palestine A. G., Rodrigues M. M., Macher A. M., Chan C. C., Lane H. C., Fauci A. S., Masur H., Longo D., Reichert C. M., Steis R. Ophthalmic involvement in acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Ophthalmology. 1984 Sep;91(9):1092–1099. doi: 10.1016/s0161-6420(84)34201-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pass R. F., Stagno S., Myers G. J., Alford C. A. Outcome of symptomatic congenital cytomegalovirus infection: results of long-term longitudinal follow-up. Pediatrics. 1980 Nov;66(5):758–762. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petkovich M., Brand N. J., Krust A., Chambon P. A human retinoic acid receptor which belongs to the family of nuclear receptors. Nature. 1987 Dec 3;330(6147):444–450. doi: 10.1038/330444a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosa F. W. Teratogenicity of isotretinoin. Lancet. 1983 Aug 27;2(8348):513–513. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)90538-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shelbourn S. L., Kothari S. K., Sissons J. G., Sinclair J. H. Repression of human cytomegalovirus gene expression associated with a novel immediate early regulatory region binding factor. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Nov 25;17(22):9165–9171. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.22.9165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shenefelt R. E. Morphogenesis of malformations in hamsters caused by retinoic acid: relation to dose and stage at treatment. Teratology. 1972 Feb;5(1):103–118. doi: 10.1002/tera.1420050115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith W. C., Nakshatri H., Leroy P., Rees J., Chambon P. A retinoic acid response element is present in the mouse cellular retinol binding protein I (mCRBPI) promoter. EMBO J. 1991 Aug;10(8):2223–2230. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07758.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sucov H. M., Murakami K. K., Evans R. M. Characterization of an autoregulated response element in the mouse retinoic acid receptor type beta gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(14):5392–5396. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.14.5392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umesono K., Murakami K. K., Thompson C. C., Evans R. M. Direct repeats as selective response elements for the thyroid hormone, retinoic acid, and vitamin D3 receptors. Cell. 1991 Jun 28;65(7):1255–1266. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90020-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasios G., Mader S., Gold J. D., Leid M., Lutz Y., Gaub M. P., Chambon P., Gudas L. The late retinoic acid induction of laminin B1 gene transcription involves RAR binding to the responsive element. EMBO J. 1991 May;10(5):1149–1158. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08055.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WELLER T. H., HANSHAW J. B. Virologic and clinical observations on cytomegalic inclusion disease. N Engl J Med. 1962 Jun 14;266:1233–1244. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196206142662401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILSON J. G., ROTH C. B., WARKANY J. An analysis of the syndrome of malformations induced by maternal vitamin A deficiency. Effects of restoration of vitamin A at various times during gestation. Am J Anat. 1953 Mar;92(2):189–217. doi: 10.1002/aja.1000920202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weller T. H. Pathogenesis of human cytomegalovirus-associated diseases. Historical perspective. Transplant Proc. 1991 Jun;23(3 Suppl 3):5-6, discussion 6-7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yow M. D. Congenital cytomegalovirus disease: a NOW problem. J Infect Dis. 1989 Feb;159(2):163–167. doi: 10.1093/infdis/159.2.163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Thé H., Vivanco-Ruiz M. M., Tiollais P., Stunnenberg H., Dejean A. Identification of a retinoic acid responsive element in the retinoic acid receptor beta gene. Nature. 1990 Jan 11;343(6254):177–180. doi: 10.1038/343177a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]








