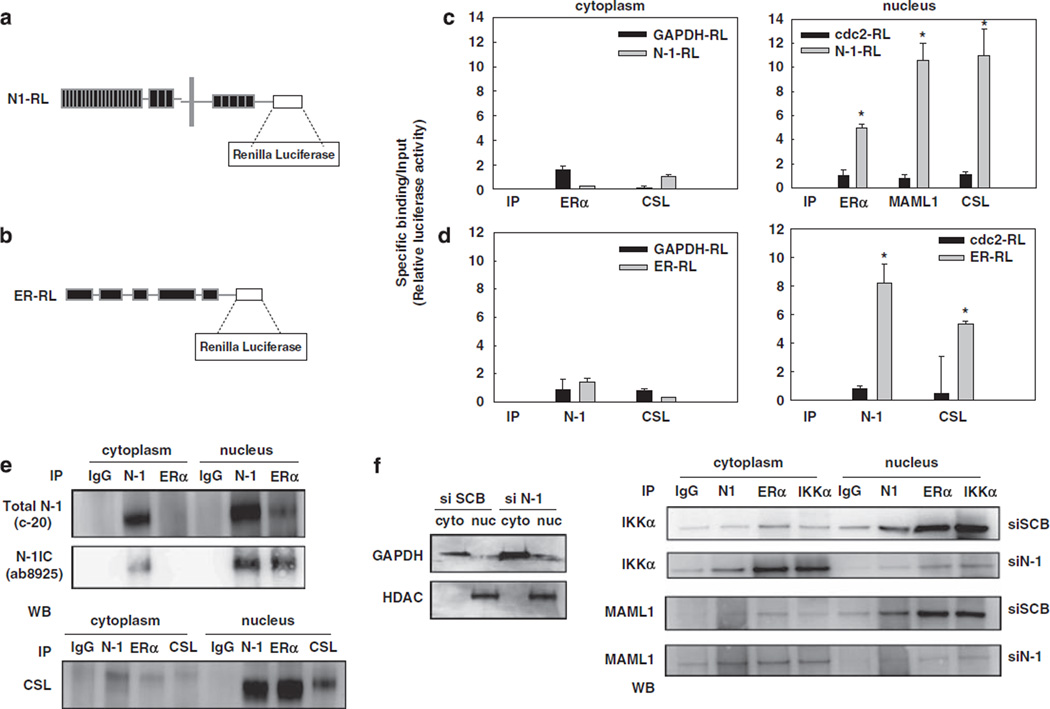
Figure 5.
The Notch-1 and ERα transcriptional complexes interact in chromatin-enriched nuclear extracts. (a, b) Schematics for the constructs of N1-RL (a) and ERα-RL (b). (c) MCF-7 cells were transfected with N1-RL or the negative controls GAPDH-RL (for cytoplasmic proteins) and Cdc2-RL (for nuclear proteins). Cells were harvested after 3 days E2 starvation and nuclear extraction was performed. Cytoplasmic or nuclear extracts were immunoprecipitated with ERα, CSL and MAML1 antibodies. (d) MCF-7 cells were transfected with ERα-RL or negative controls. Cells were harvested after 3 days E2 starvation and nuclear extraction was performed. Cytoplasm lysates or nuclear extracts were immunoprecipitated with Notch-1 and CSL antibodies; *P ⩽ 0.001. (e) Standard IP-western blot was performed on cytoplasmic or nuclear extracts from MCF-7 cells grown in charcoal-stripped medium for 3 days with antibodies to Notch-1, ERα, and CSL. (f) MCF-7 cells were grown in charcoal-stripped medium for a total of 3 days. Cells were transfected with Notch-1 siRNA or scrambled control, and harvested 48 h after transfection. The efficiency of nuclear extraction was verified by western blotting (left). IP–western blot was performed with antibodies to Notch-1, ERα and IKKα. A 10-µl volume of eluted material from each IP was analysed by western blotting for IKKα or MAML1. ChIP, chromatin immunoprecipitation; ERα, estrogen receptor-α; ERα-RL, Renilla luciferase-tagged ERα; GAPDH, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; N1-RL, Renilla luciferase-tagged Notch-1; siRNA, short interfering RNA.