Abstract
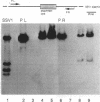
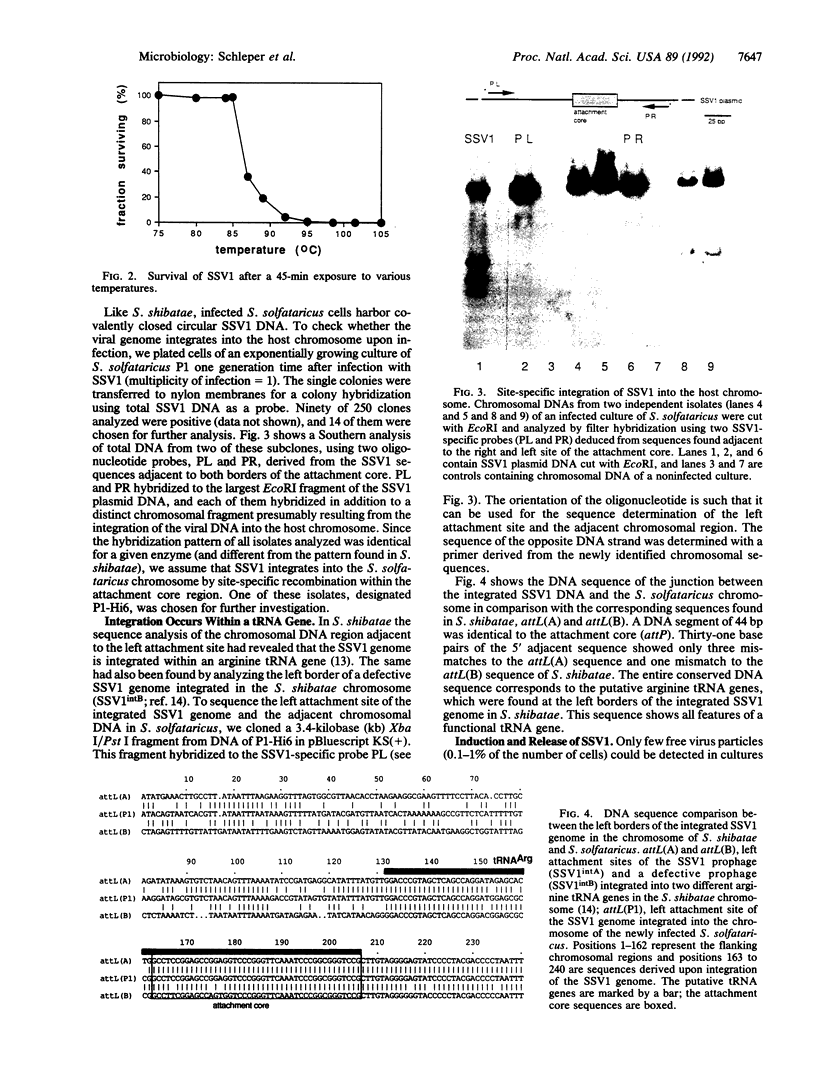
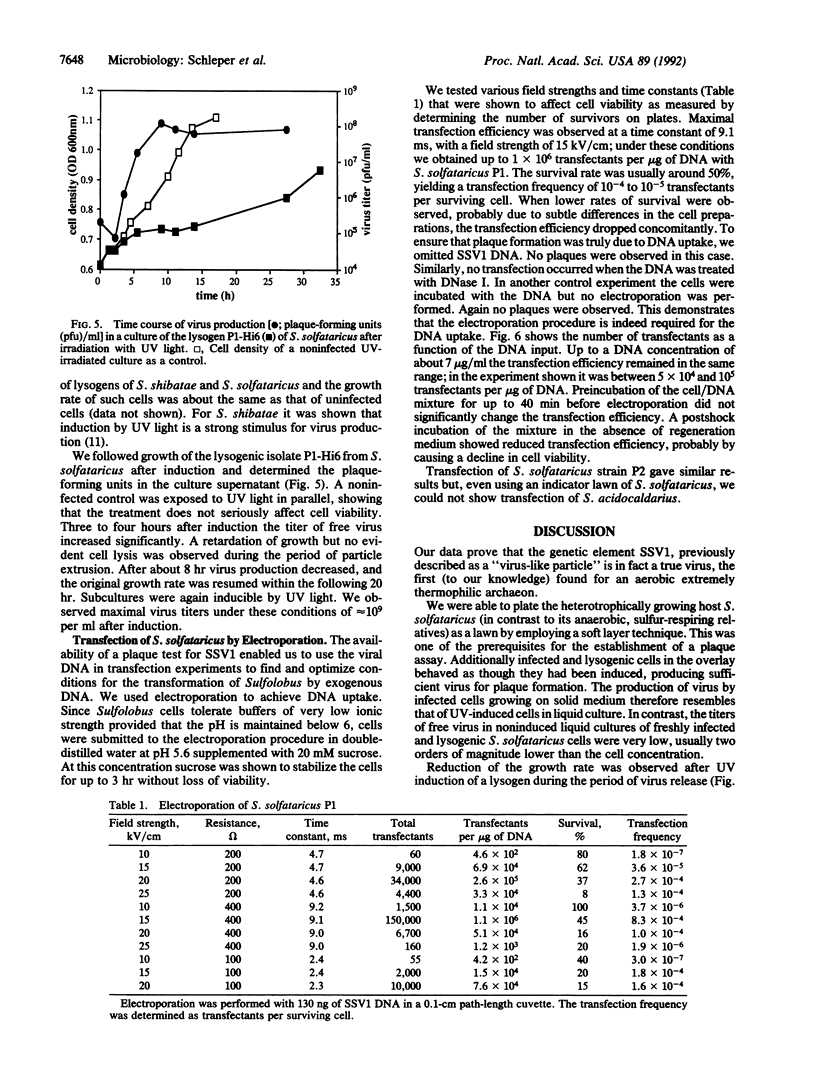
The lemon-shaped "virus-like" particle SSV1 produced by the thermophilic archaeon Sulfolobus shibatae has not previously been observed to infect any host. Using a plaque assay suitable for the extreme growth conditions of this archaeon, we have shown infection of Sulfolobus solfataricus by SSV1. Upon infection, the viral genome was always found integrated into a tRNA gene of the host chromosome, a situation similar to that in S. shibatae, proving that site-specific integration is involved in establishing the lysogenic state. As in S. shibatae, UV-irradiation of lysogenized S. solfataricus led to virus production apparently not accompanied by cell lysis. We have also demonstrated the efficient uptake of exogenous DNA and its expression in Sulfolobus by transfecting S. solfataricus with SSV1 DNA by electroporation. Transfection efficiencies of up to 10(6) transfectants per microgram of DNA were obtained.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bertani G., Baresi L. Genetic transformation in the methanogen Methanococcus voltae PS. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jun;169(6):2730–2738. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.6.2730-2738.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blaseio U., Pfeifer F. Transformation of Halobacterium halobium: development of vectors and investigation of gas vesicle synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(17):6772–6776. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.17.6772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brock T. D., Brock K. M., Belly R. T., Weiss R. L. Sulfolobus: a new genus of sulfur-oxidizing bacteria living at low pH and high temperature. Arch Mikrobiol. 1972;84(1):54–68. doi: 10.1007/BF00408082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cline S. W., Doolittle W. F. Efficient transfection of the archaebacterium Halobacterium halobium. J Bacteriol. 1987 Mar;169(3):1341–1344. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.3.1341-1344.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cline S. W., Schalkwyk L. C., Doolittle W. F. Transformation of the archaebacterium Halobacterium volcanii with genomic DNA. J Bacteriol. 1989 Sep;171(9):4987–4991. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.9.4987-4991.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gernhardt P., Possot O., Foglino M., Sibold L., Klein A. Construction of an integration vector for use in the archaebacterium Methanococcus voltae and expression of a eubacterial resistance gene. Mol Gen Genet. 1990 Apr;221(2):273–279. doi: 10.1007/BF00261731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grogan D. W. Phenotypic characterization of the archaebacterial genus Sulfolobus: comparison of five wild-type strains. J Bacteriol. 1989 Dec;171(12):6710–6719. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.12.6710-6719.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grogan D. W. Selectable mutant phenotypes of the extremely thermophilic archaebacterium Sulfolobus acidocaldarius. J Bacteriol. 1991 Dec;173(23):7725–7727. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.23.7725-7727.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grogan D., Palm P., Zillig W. Isolate B12, which harbours a virus-like element, represents a new species of the archaebacterial genus Sulfolobus, Sulfolobus shibatae, sp. nov. Arch Microbiol. 1990;154(6):594–599. doi: 10.1007/BF00248842. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gropp F., Palm P., Zillig W. Expression and regulation of Halobacterium halobium phage phi H genes. Can J Microbiol. 1989 Jan;35(1):182–188. doi: 10.1139/m89-028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes M. L., Dyall-Smith M. L. A plasmid vector with a selectable marker for halophilic archaebacteria. J Bacteriol. 1990 Feb;172(2):756–761. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.2.756-761.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ken R., Hackett N. R. Halobacterium halobium strains lysogenic for phage phi H contain a protein resembling coliphage repressors. J Bacteriol. 1991 Feb;173(3):955–960. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.3.955-960.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondo S., Yamagishi A., Oshima T. Positive selection for uracil auxotrophs of the sulfur-dependent thermophilic archaebacterium Sulfolobus acidocaldarius by use of 5-fluoroorotic acid. J Bacteriol. 1991 Dec;173(23):7698–7700. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.23.7698-7700.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lam W. L., Doolittle W. F. Shuttle vectors for the archaebacterium Halobacterium volcanii. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5478–5482. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5478. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M. H., Pascopella L., Jacobs W. R., Jr, Hatfull G. F. Site-specific integration of mycobacteriophage L5: integration-proficient vectors for Mycobacterium smegmatis, Mycobacterium tuberculosis, and bacille Calmette-Guérin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 15;88(8):3111–3115. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.8.3111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin A., Yeats S., Janekovic D., Reiter W. D., Aicher W., Zillig W. SAV 1, a temperate u.v.-inducible DNA virus-like particle from the archaebacterium Sulfolobus acidocaldarius isolate B12. EMBO J. 1984 Sep;3(9):2165–2168. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02107.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meile L., Abendschein P., Leisinger T. Transduction in the archaebacterium Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum Marburg. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jun;172(6):3507–3508. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.6.3507-3508.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Micheletti P. A., Sment K. A., Konisky J. Isolation of a coenzyme M-auxotrophic mutant and transformation by electroporation in Methanococcus voltae. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jun;173(11):3414–3418. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.11.3414-3418.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neumann H., Schwass V., Eckerskorn C., Zillig W. Identification and characterization of the genes encoding three structural proteins of the Thermoproteus tenax virus TTV1. Mol Gen Genet. 1989 May;217(1):105–110. doi: 10.1007/BF00330948. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palm P., Schleper C., Grampp B., Yeats S., McWilliam P., Reiter W. D., Zillig W. Complete nucleotide sequence of the virus SSV1 of the archaebacterium Sulfolobus shibatae. Virology. 1991 Nov;185(1):242–250. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90771-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierson L. S., 3rd, Kahn M. L. Integration of satellite bacteriophage P4 in Escherichia coli. DNA sequences of the phage and host regions involved in site-specific recombination. J Mol Biol. 1987 Aug 5;196(3):487–496. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90026-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prangishvili D. A., Vashakidze R. P., Chelidze M. G., Gabriadze IYu A restriction endonuclease SuaI from the thermoacidophilic archaebacterium Sulfolobus acidocaldarius. FEBS Lett. 1985 Nov 11;192(1):57–60. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80042-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiter W D, Palm P, Yeats S, Zillig W. Gene expression in archaebacteria: physical mapping of constitutive and UV-inducible transcripts from the Sulfolobus virus-like particle SSV1. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Sep;209(2):270–275. doi: 10.1007/BF00329653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiter W. D., Hüdepohl U., Zillig W. Mutational analysis of an archaebacterial promoter: essential role of a TATA box for transcription efficiency and start-site selection in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(24):9509–9513. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.9509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiter W. D., Palm P. Identification and characterization of a defective SSV1 genome integrated into a tRNA gene in the archaebacterium Sulfolobus sp. B12. Mol Gen Genet. 1990 Mar;221(1):65–71. doi: 10.1007/BF00280369. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiter W. D., Palm P., Yeats S. Transfer RNA genes frequently serve as integration sites for prokaryotic genetic elements. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Mar 11;17(5):1907–1914. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.5.1907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiter W. D., Palm P., Zillig W. Analysis of transcription in the archaebacterium Sulfolobus indicates that archaebacterial promoters are homologous to eukaryotic pol II promoters. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jan 11;16(1):1–19. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiter W. D., Palm P., Zillig W. Transcription termination in the archaebacterium Sulfolobus: signal structures and linkage to transcription initiation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Mar 25;16(6):2445–2459. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.6.2445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiter W. D., Zillig W., Palm P. Archaebacterial viruses. Adv Virus Res. 1988;34:143–188. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60517-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnabel H., Zillig W., Pfäffle M., Schnabel R., Michel H., Delius H. Halobacterium halobium phage øH. EMBO J. 1982;1(1):87–92. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01129.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R., Kandler O., Wheelis M. L. Towards a natural system of organisms: proposal for the domains Archaea, Bacteria, and Eucarya. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(12):4576–4579. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worrell V. E., Nagle D. P., Jr, McCarthy D., Eisenbraun A. Genetic transformation system in the archaebacterium Methanobacterium thermoautotrophicum Marburg. J Bacteriol. 1988 Feb;170(2):653–656. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.2.653-656.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeats S., McWilliam P., Zillig W. A plasmid in the archaebacterium Sulfolobus acidocaldarius. EMBO J. 1982;1(9):1035–1038. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01292.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]