Abstract
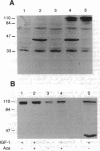
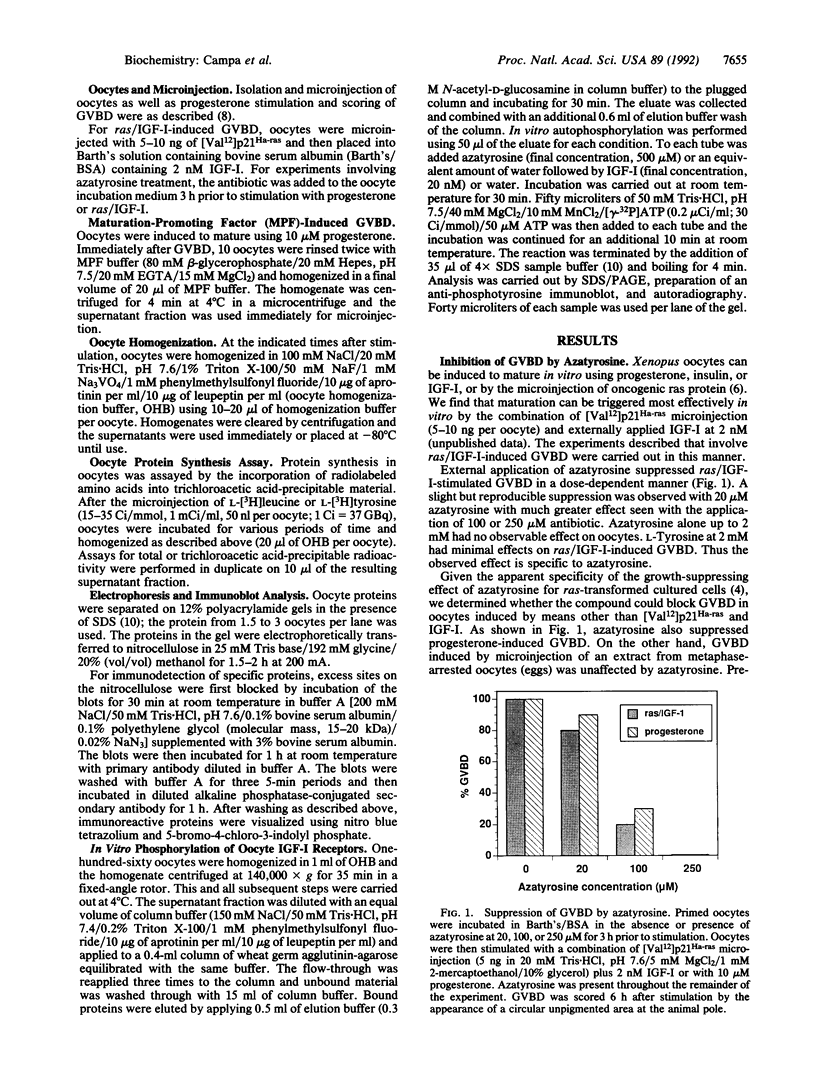
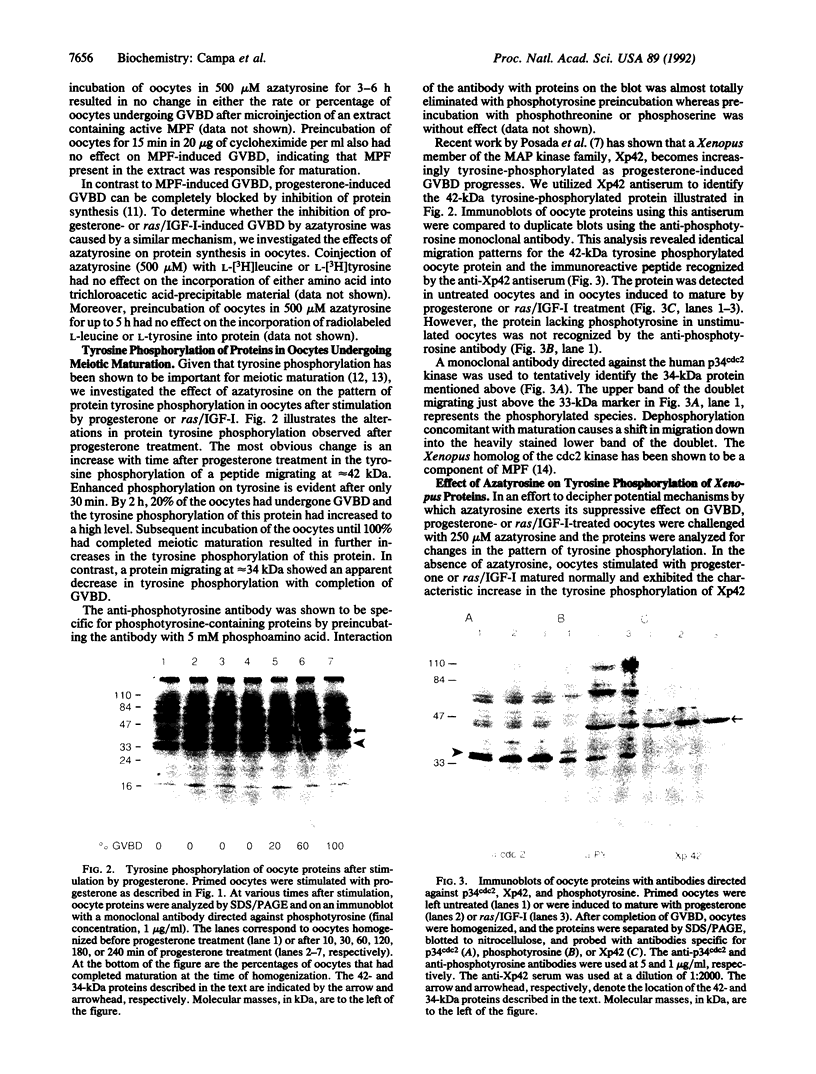
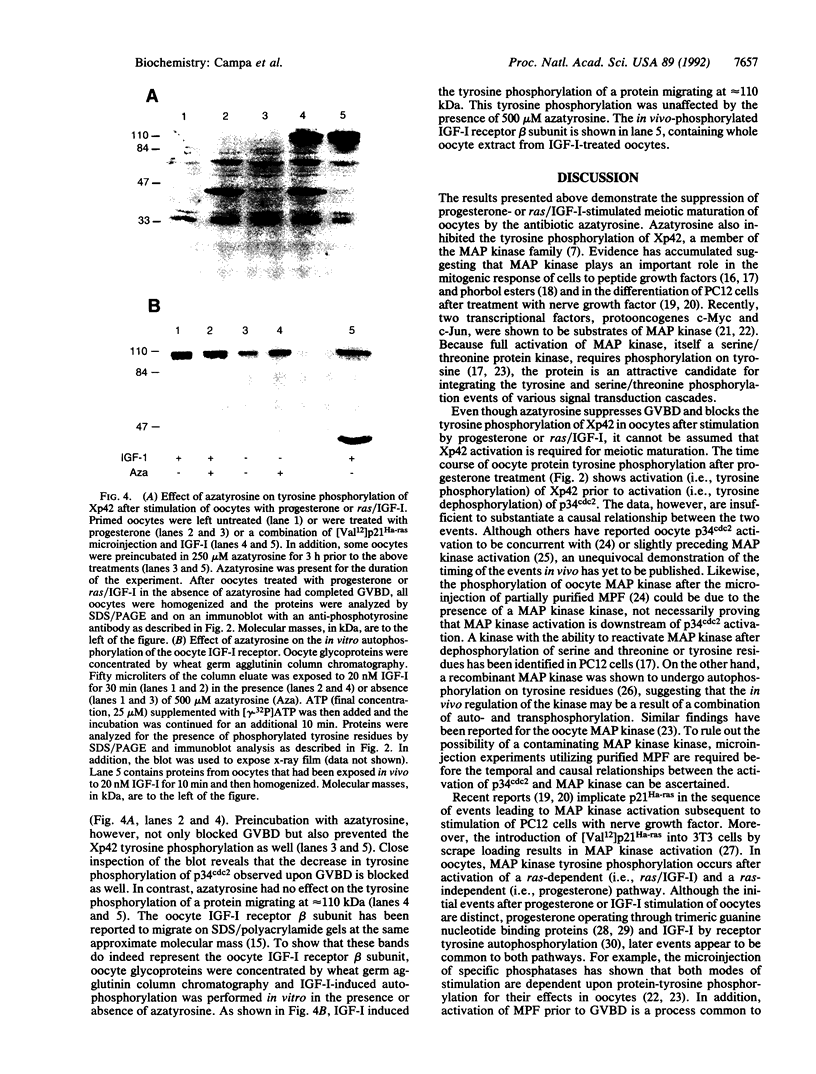
The antibiotic azatyrosine [DL-3-(5-hydroxy-2-pyridyl)alanine] suppressed meiotic maturation in oocytes induced by progesterone or the combination of [Val12]p21Ha-ras microinjection and insulin-like growth factor I. The suppression was dose-dependent in the range of 20-250 microM azatyrosine. In addition, azatyrosine blocked the tyrosine phosphorylation of Xp42, a member of the mitogen-activated protein kinase family, after progesterone or [Val12]p21Ha-ras/insulin-like growth factor I stimulation. Activation of maturation-promoting factor, as shown by a decrease in the tyrosine phosphorylation of the Xenopus homolog of p34cdc2, was also suppressed by azatyrosine. Azatyrosine had no effect in vivo or in vitro on the growth factor-induced autophosphorylation of the oocyte insulin-like growth factor I receptor. Azatyrosine has been shown by others [Shindo-Okada, N., Makabe, O., Nagahara, H. & Nishimura, S. (1989) Mol. Carcinog. 2, 159-167] to inhibit the growth of ras-transformed cells without affecting that of nontransformed cells. In oocytes, the antibiotic exerts an inhibitory action on both a ras-dependent and a ras-independent pathway. Lack of an effect of azatyrosine on germinal vesicle breakdown induced by the microinjection of an extract from mature oocytes, however, suggests that azatryosine is acting upstream of maturation-promoting factor activation.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allende C. C., Hinrichs M. V., Santos E., Allende J. E. Oncogenic ras protein induces meiotic maturation of amphibian oocytes in the presence of protein synthesis inhibitors. FEBS Lett. 1988 Jul 18;234(2):426–430. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80130-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Almoguera C., Shibata D., Forrester K., Martin J., Arnheim N., Perucho M. Most human carcinomas of the exocrine pancreas contain mutant c-K-ras genes. Cell. 1988 May 20;53(4):549–554. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90571-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alvarez E., Northwood I. C., Gonzalez F. A., Latour D. A., Seth A., Abate C., Curran T., Davis R. J. Pro-Leu-Ser/Thr-Pro is a consensus primary sequence for substrate protein phosphorylation. Characterization of the phosphorylation of c-myc and c-jun proteins by an epidermal growth factor receptor threonine 669 protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 15;266(23):15277–15285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett C. B., Schroetke R. M., Van der Hoorn F. A., Nordeen S. K., Maller J. L. Ha-rasVal-12,Thr-59 activates S6 kinase and p34cdc2 kinase in Xenopus oocytes: evidence for c-mosxe-dependent and -independent pathways. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jan;10(1):310–315. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.1.310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birchmeier C., Broek D., Wigler M. ras proteins can induce meiosis in Xenopus oocytes. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):615–621. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90233-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantley L. C., Auger K. R., Carpenter C., Duckworth B., Graziani A., Kapeller R., Soltoff S. Oncogenes and signal transduction. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):281–302. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90639-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casillas A., Hanekom C., Williams K., Katz R., Nel A. E. Stimulation of B-cells via the membrane immunoglobulin receptor or with phorbol myristate 13-acetate induces tyrosine phosphorylation and activation of a 42-kDa microtubule-associated protein-2 kinase. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 5;266(28):19088–19094. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung D. L., Brandt-Rauf P., Murphy R. B., Nishimura S., Yamaizumi Z., Weinstein I. B., Pincus M. R. A peptide from the GAP-binding domain of the ras-p21 protein as well as azatyrosine block ras-induced maturation of Xenopus oocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1991 Dec 31;181(3):1378–1384. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(91)92091-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cicirelli M. F., Tonks N. K., Diltz C. D., Weiel J. E., Fischer E. H., Krebs E. G. Microinjection of a protein-tyrosine-phosphatase inhibits insulin action in Xenopus oocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(14):5514–5518. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.14.5514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunphy W. G., Brizuela L., Beach D., Newport J. The Xenopus cdc2 protein is a component of MPF, a cytoplasmic regulator of mitosis. Cell. 1988 Jul 29;54(3):423–431. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90205-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrell J. E., Jr, Wu M., Gerhart J. C., Martin G. S. Cell cycle tyrosine phosphorylation of p34cdc2 and a microtubule-associated protein kinase homolog in Xenopus oocytes and eggs. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;11(4):1965–1971. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.4.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotoh Y., Nishida E., Matsuda S., Shiina N., Kosako H., Shiokawa K., Akiyama T., Ohta K., Sakai H. In vitro effects on microtubule dynamics of purified Xenopus M phase-activated MAP kinase. Nature. 1991 Jan 17;349(6306):251–254. doi: 10.1038/349251a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gómez N., Cohen P. Dissection of the protein kinase cascade by which nerve growth factor activates MAP kinases. Nature. 1991 Sep 12;353(6340):170–173. doi: 10.1038/353170a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hainaut P., Kowalski A., Giorgetti S., Baron V., Van Obberghen E. Insulin and insulin-like-growth-factor-I (IGF-I) receptors in Xenopus laevis oocytes. Comparison with insulin receptors from liver and muscle. Biochem J. 1991 Feb 1;273(Pt 3):673–678. doi: 10.1042/bj2730673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaleko M., Rutter W. J., Miller A. D. Overexpression of the human insulinlike growth factor I receptor promotes ligand-dependent neoplastic transformation. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;10(2):464–473. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.2.464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korn L. J., Siebel C. W., McCormick F., Roth R. A. Ras p21 as a potential mediator of insulin action in Xenopus oocytes. Science. 1987 May 15;236(4803):840–843. doi: 10.1126/science.3554510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M. G., Nurse P. Complementation used to clone a human homologue of the fission yeast cell cycle control gene cdc2. Nature. 1987 May 7;327(6117):31–35. doi: 10.1038/327031a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leevers S. J., Marshall C. J. Activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase, ERK2, by p21ras oncoprotein. EMBO J. 1992 Feb;11(2):569–574. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05088.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan D. O., Ho L., Korn L. J., Roth R. A. Insulin action is blocked by a monoclonal antibody that inhibits the insulin receptor kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(2):328–332. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.2.328. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukhopadhyay T., Tainsky M., Cavender A. C., Roth J. A. Specific inhibition of K-ras expression and tumorigenicity of lung cancer cells by antisense RNA. Cancer Res. 1991 Mar 15;51(6):1744–1748. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Posada J., Cooper J. A. Requirements for phosphorylation of MAP kinase during meiosis in Xenopus oocytes. Science. 1992 Jan 10;255(5041):212–215. doi: 10.1126/science.1313186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Posada J., Sanghera J., Pelech S., Aebersold R., Cooper J. A. Tyrosine phosphorylation and activation of homologous protein kinases during oocyte maturation and mitogenic activation of fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 May;11(5):2517–2528. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.5.2517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pulverer B. J., Kyriakis J. M., Avruch J., Nikolakaki E., Woodgett J. R. Phosphorylation of c-jun mediated by MAP kinases. Nature. 1991 Oct 17;353(6345):670–674. doi: 10.1038/353670a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray L. B., Sturgill T. W. Rapid stimulation by insulin of a serine/threonine kinase in 3T3-L1 adipocytes that phosphorylates microtubule-associated protein 2 in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(6):1502–1506. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.6.1502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodenhuis S., Slebos R. J. The ras oncogenes in human lung cancer. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1990 Dec;142(6 Pt 2):S27–S30. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/142.6_Pt_2.S27. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadler S. E., Maller J. L., Cooper D. M. Progesterone inhibition of Xenopus oocyte adenylate cyclase is not mediated via the Bordetella pertussis toxin substrate. Mol Pharmacol. 1984 Nov;26(3):526–531. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadler S. E., Maller J. L. Inhibition of Xenopus oocyte adenylate cyclase by progesterone: a novel mechanism of action. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Protein Phosphorylation Res. 1985;19:179–194. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shindo-Okada N., Makabe O., Nagahara H., Nishimura S. Permanent conversion of mouse and human cells transformed by activated ras or raf genes to apparently normal cells by treatment with the antibiotic azatyrosine. Mol Carcinog. 1989;2(3):159–167. doi: 10.1002/mc.2940020309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas S. M., DeMarco M., D'Arcangelo G., Halegoua S., Brugge J. S. Ras is essential for nerve growth factor- and phorbol ester-induced tyrosine phosphorylation of MAP kinases. Cell. 1992 Mar 20;68(6):1031–1040. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90075-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonks N. K., Cicirelli M. F., Diltz C. D., Krebs E. G., Fischer E. H. Effect of microinjection of a low-Mr human placenta protein tyrosine phosphatase on induction of meiotic cell division in Xenopus oocytes. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;10(2):458–463. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.2.458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood K. W., Sarnecki C., Roberts T. M., Blenis J. ras mediates nerve growth factor receptor modulation of three signal-transducing protein kinases: MAP kinase, Raf-1, and RSK. Cell. 1992 Mar 20;68(6):1041–1050. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90076-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu J., Rossomando A. J., Her J. H., Del Vecchio R., Weber M. J., Sturgill T. W. Autophosphorylation in vitro of recombinant 42-kilodalton mitogen-activated protein kinase on tyrosine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 1;88(21):9508–9512. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.21.9508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K., Lapetina E. G., Moxham C. P. Insulin like growth factor-I induces limited association of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase to its receptor. Endocrinology. 1992 Mar;130(3):1490–1498. doi: 10.1210/endo.130.3.1311242. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]