Abstract
Saccharomyces cerevisiae translation initiation factor eIF-4A, an RNA helicase of the Asp-Glu-Ala-Asp (DEAD) box protein family, was mutated in the putative ATP binding site and expressed in Escherichia coli. Mutant proteins with alanine at position 66 replaced by glycine [eIF-4A(A66G)] or valine [eIF-4A(A66V)] were purified from Escherichia coli extracts and analyzed in vitro for activity in ATP crosslinking, ATP hydrolysis, RNA helicase, and translation assays. The results show that in vitro ATP hydrolysis activity, RNA helicase activity, and translation activity of eIF-4A correlate with in vivo activity of the factor. Whereas eIF-4A(A66G) showed wild-type activity in all assays, eIF-4A(A66V) was active in ATP crosslinking but inactive in ATP hydrolysis and RNA helicase assays. In vitro translation was supported by wild-type eIF-4A and eIF-4A(A66G) but not by eIF-4A(A66V). The results show that, for their translation, the majority of mRNAs from Saccharomyces cerevisiae including an mRNA with the initiator AUG positioned 8 nucleotides downstream of the cap structure require eIF-4A that is able to hydrolyze ATP.
Full text
PDF

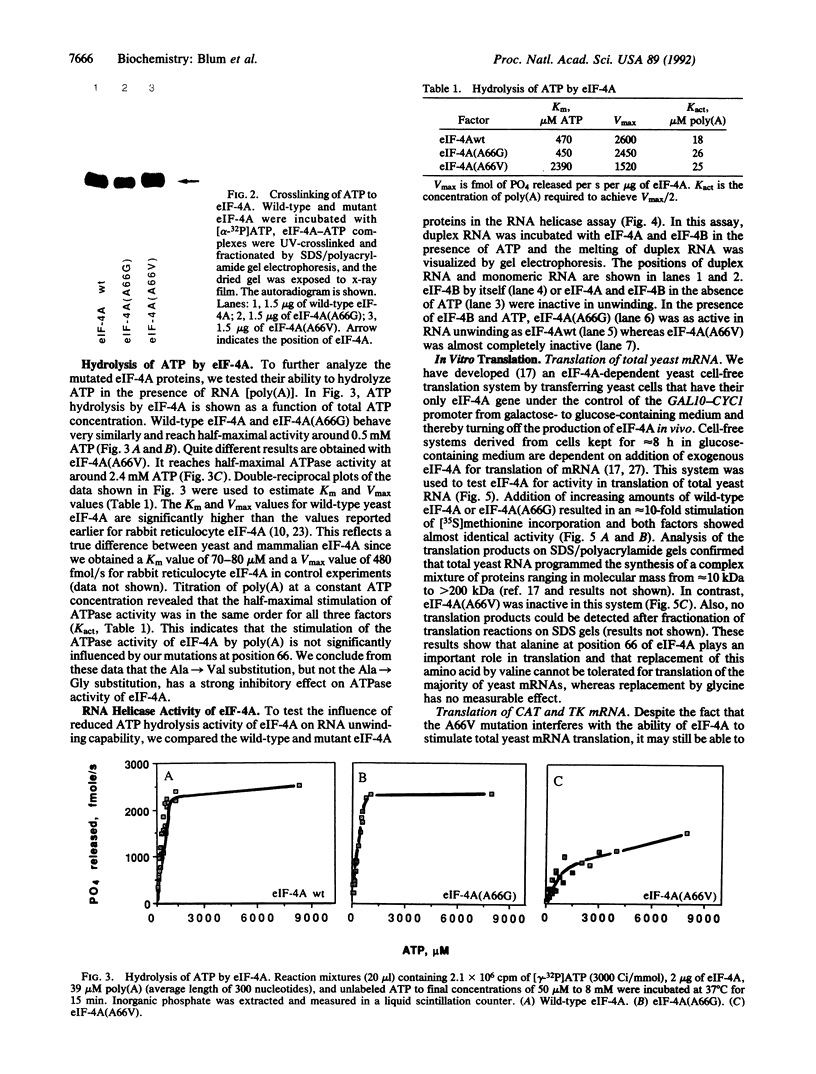


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abramson R. D., Dever T. E., Merrick W. C. Biochemical evidence supporting a mechanism for cap-independent and internal initiation of eukaryotic mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1988 May 5;263(13):6016–6019. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altmann M., Blum S., Wilson T. M., Trachsel H. The 5'-leader sequence of tobacco mosaic virus RNA mediates initiation-factor-4E-independent, but still initiation-factor-4A-dependent translation in yeast extracts. Gene. 1990 Jul 2;91(1):127–129. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90173-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altmann M., Edery I., Sonenberg N., Trachsel H. Purification and characterization of protein synthesis initiation factor eIF-4E from the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochemistry. 1985 Oct 22;24(22):6085–6089. doi: 10.1021/bi00343a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altmann M., Edery I., Trachsel H., Sonenberg N. Site-directed mutagenesis of the tryptophan residues in yeast eukaryotic initiation factor 4E. Effects on cap binding activity. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 25;263(33):17229–17232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson C. W., Baum P. R., Gesteland R. F. Processing of adenovirus 2-induced proteins. J Virol. 1973 Aug;12(2):241–252. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.2.241-252.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blum S., Mueller M., Schmid S. R., Linder P., Trachsel H. Translation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: initiation factor 4A-dependent cell-free system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(16):6043–6046. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.16.6043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grifo J. A., Abramson R. D., Satler C. A., Merrick W. C. RNA-stimulated ATPase activity of eukaryotic initiation factors. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 10;259(13):8648–8654. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaramillo M., Browning K., Dever T. E., Blum S., Trachsel H., Merrick W. C., Ravel J. M., Sonenberg N. Translation initiation factors that function as RNA helicases from mammals, plants and yeast. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Aug 27;1050(1-3):134–139. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(90)90154-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Role of ATP in binding and migration of 40S ribosomal subunits. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(2 Pt 2):459–467. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90356-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. The scanning model for translation: an update. J Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;108(2):229–241. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.2.229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linder P., Lasko P. F., Ashburner M., Leroy P., Nielsen P. J., Nishi K., Schnier J., Slonimski P. P. Birth of the D-E-A-D box. Nature. 1989 Jan 12;337(6203):121–122. doi: 10.1038/337121a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linder P., Prat A. Baker's yeast, the new work horse in protein synthesis studies: analyzing eukaryotic translation initiation. Bioessays. 1990 Nov;12(11):519–526. doi: 10.1002/bies.950121103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linder P., Slonimski P. P. An essential yeast protein, encoded by duplicated genes TIF1 and TIF2 and homologous to the mammalian translation initiation factor eIF-4A, can suppress a mitochondrial missense mutation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2286–2290. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milburn S. C., Hershey J. W., Davies M. V., Kelleher K., Kaufman R. J. Cloning and expression of eukaryotic initiation factor 4B cDNA: sequence determination identifies a common RNA recognition motif. EMBO J. 1990 Sep;9(9):2783–2790. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07466.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moldave K. Eukaryotic protein synthesis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:1109–1149. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.005333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller P. P., Trachsel H. Translation and regulation of translation in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Jul 31;191(2):257–261. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb19118.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen P. J., McMaster G. K., Trachsel H. Cloning of eukaryotic protein synthesis initiation factor genes: isolation and characterization of cDNA clones encoding factor eIF-4A. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Oct 11;13(19):6867–6880. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.19.6867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen P. J., Trachsel H. The mouse protein synthesis initiation factor 4A gene family includes two related functional genes which are differentially expressed. EMBO J. 1988 Jul;7(7):2097–2105. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03049.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishi K., Morel-Deville F., Hershey J. W., Leighton T., Schnier J. An eIF-4A-like protein is a suppressor of an Escherichia coli mutant defective in 50S ribosomal subunit assembly. Nature. 1988 Dec 1;336(6198):496–498. doi: 10.1038/336496a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pain V. M. Initiation of protein synthesis in mammalian cells. Biochem J. 1986 May 1;235(3):625–637. doi: 10.1042/bj2350625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelletier J., Sonenberg N. The involvement of mRNA secondary structure in protein synthesis. Biochem Cell Biol. 1987 Jun;65(6):576–581. doi: 10.1139/o87-074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhoads R. E. Cap recognition and the entry of mRNA into the protein synthesis initiation cycle. Trends Biochem Sci. 1988 Feb;13(2):52–56. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(88)90028-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozen F., Edery I., Meerovitch K., Dever T. E., Merrick W. C., Sonenberg N. Bidirectional RNA helicase activity of eucaryotic translation initiation factors 4A and 4F. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Mar;10(3):1134–1144. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.3.1134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozen F., Pelletier J., Trachsel H., Sonenberg N. A lysine substitution in the ATP-binding site of eucaryotic initiation factor 4A abrogates nucleotide-binding activity. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Sep;9(9):4061–4063. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.9.4061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar G., Edery I., Sonenberg N. Photoaffinity labeling of the cap-binding protein complex with ATP/dATP. Differential labeling of free eukaryotic initiation factor 4A and the eukaryotic initiation factor 4A component of the cap-binding protein complex with [alpha-32P]ATP/dATP. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 5;260(25):13831–13837. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid S. R., Linder P. D-E-A-D protein family of putative RNA helicases. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Feb;6(3):283–291. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01470.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid S. R., Linder P. Translation initiation factor 4A from Saccharomyces cerevisiae: analysis of residues conserved in the D-E-A-D family of RNA helicases. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jul;11(7):3463–3471. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.7.3463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Séraphin B., Simon M., Boulet A., Faye G. Mitochondrial splicing requires a protein from a novel helicase family. Nature. 1989 Jan 5;337(6202):84–87. doi: 10.1038/337084a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. E., Saraste M., Runswick M. J., Gay N. J. Distantly related sequences in the alpha- and beta-subunits of ATP synthase, myosin, kinases and other ATP-requiring enzymes and a common nucleotide binding fold. EMBO J. 1982;1(8):945–951. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01276.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]







