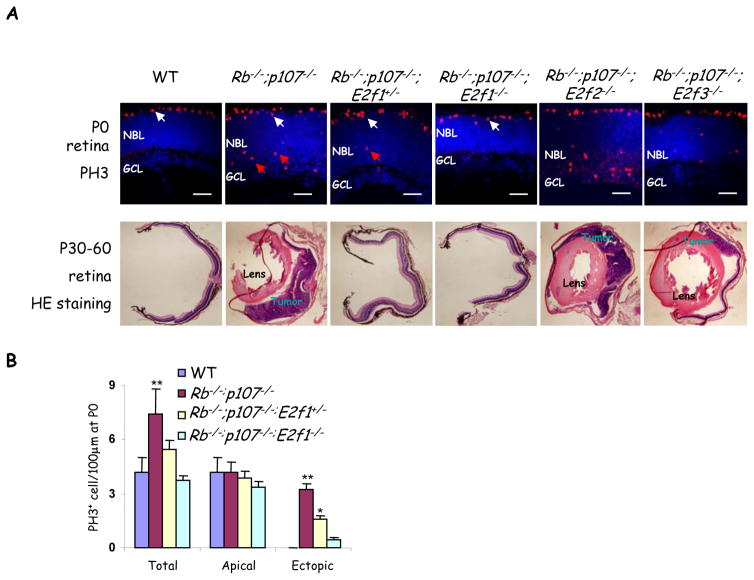
Figure 5. Heterozygosity for E2f1 is sufficient to block retinoblastoma.
(A) P0 and adult (P30–P60) retinal sections of the indicated genotypes were stained for mitotic cells (PH3, red) and nuclei (DAPI, blue), or H&E (lower panels). Apical mitoses (white arrows) represent normal progenitors while ectopic mitoses (red arrows) represent abnormally dividing differentiating neurons that are abundant in the Rb/p107 null retina, and reduced or virtually absent when one or two E2f1 alleles are removed, respectively. Scale bar, 50μm. The lens or tumors in adult H&E sections are indicated. For quantification of tumor frequency see Table 2. (B) Quantification of mitoses in indicated genotypes. Data are mean ± SD and asterisks indicate significant difference from WT (* P<0.05, ** P<0.01. Students t-test For simplicity “Rb−/−” represents αCre;Rbf/f in (A & B). NBL: neuroblastic layer, GCL: ganglion cell layer.