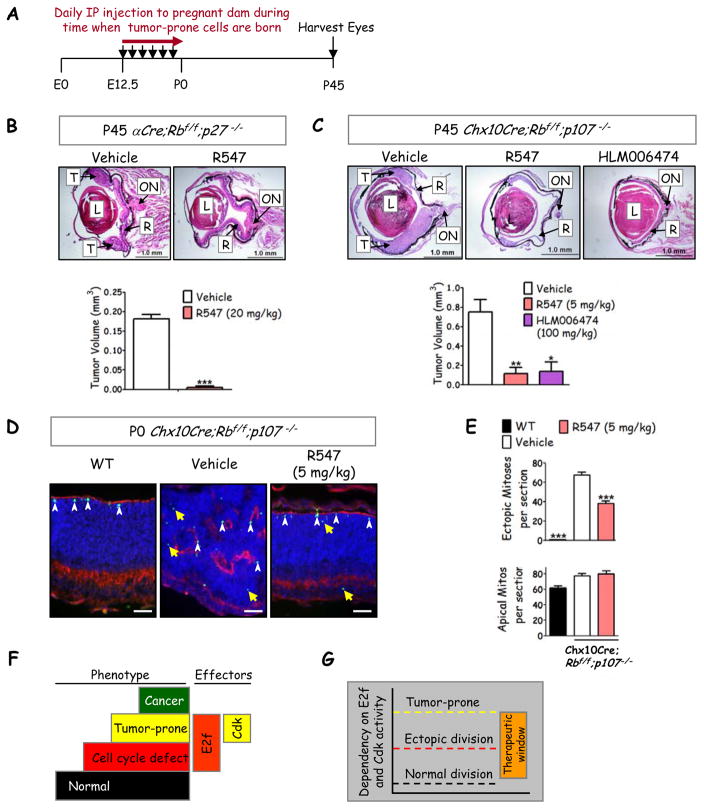
Figure 6. Chemoprevention of retinoblastoma through brief Cdk or E2f inhibition.
(A) Summary of chemoprevention strategy. (B) H&E stain of P45 retina in αCre;Rb f/f;p27−/− mice treated with either vehicle (n=8) or pan-Cdk inhibitor R547 (n=10) with quantification of tumor volume (bottom panel). (C) H&E stain of P45 retina in Chx10Cre;Rbf/f;p107−/− mice treated with vehicle (n=10), R547 (n=8), or E2f inhibitor HLM006474 (n=4) with tumor volume quantified (lower panel). (B,C) T: Tumor, R: retina, L: lens, ON: optic nerve (scale bar, 1 mm). (D) P0 retina of Chx10Cre;Rb f/f;p107−/− mice treated with vehicle or R547 were stained with PH3 (green) and the F-actin marker, phalloidin (red). Yellow arrows indicate ectopic PH3+ cells and white arrowheads represent apical mitotic progenitors (scale bar, 50 μm). (E) Quantification of ectopic (upper panel) or apical (lower panel) mitoses per section shows that the drug inhibits abnormal but not normal division. *= p<0.05; ** = p<0.01; *** = p<0.0001 compared to vehicle using an unpaired Student’s t-test (B) or One-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni multiple comparisons posthoc test (C, F). Data represented as mean ± SEM (n represented per eye, n ≥ 4 for each condition). (F) Model summarizing critical molecular steps to the tumor-prone state. In the mouse retina Rb loss activates E2f1 and triggers ectopic division (red step), but additional genetic events are required to activate Cdk2 and thus create tumor susceptibility (yellow step). Sporadic mutations permit progression to cancer (green step). (G) The data suggest distinct dependence on E2f and Cdk activity for normal division, ectopic division and tumor susceptibility, and thus expose a therapeutic window of dual axes activity which can be exploited to block transformation.