Abstract
An indirect peroxidase technique was developed for determination of IgA antibodies to varicella zoster virus (VZV). The antigen consisted of acetone-fixed trypsinised VZV-infected cells. Rabbit antihuman IgA peroxidase conjugate was used to detect human IgA antibodies bound to viral antigen. In parallel IgG antibodies to VZV were determined by an immunoperoxidase antibody to membrane antigen (IPAMA) technique. Varicella zoster virus IgA antibodies were detected in all five varicella and seven zoster patients. No VZV IgA antibodies (less than 2) were detected in 45 healthy control sera. Neither were they found in paired sera of five patients with herpes simplex infection, five patients with human cytomegalovirus infection and two patients with Epstein-Barr virus infection. Application of immunoperoxidase IgA technique in serodiagnosis of primary and reactivated VZV infections is discussed.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arvin A. M., Koropchak C. M. Immunoglobulins M and G to varicella-zoster virus measured by solid-phase radioimmunoassay: antibody responses to varicella and herpes zoster infections. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Sep;12(3):367–374. doi: 10.1128/jcm.12.3.367-374.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
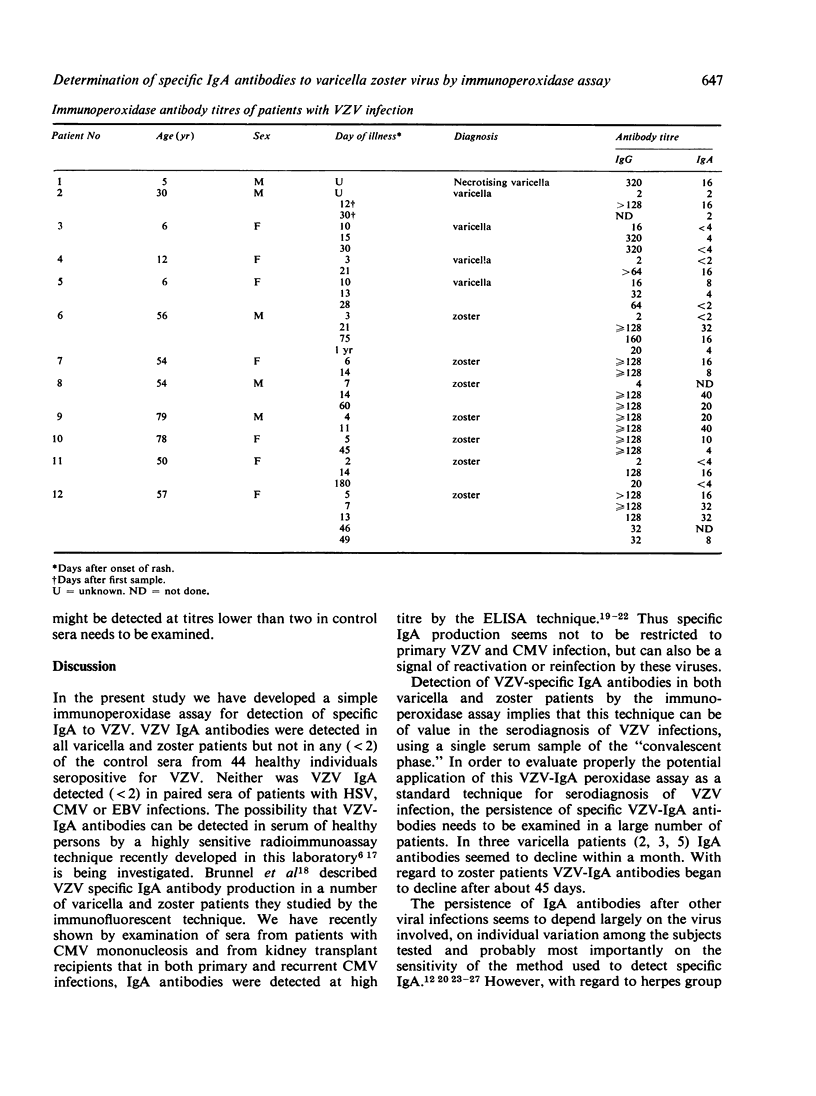
- Brunell P. A., Gershon A. A., Uduman S. A., Steinberg S. Varicella-Zoster Immunoglobulins during Varicella, Latency, and Zoster. J Infect Dis. 1975 Jul;132(1):49–54. doi: 10.1093/infdis/132.1.49. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell-Benzie A., Kangro H. O., Heath R. B. The development and evaluation of a solid-phase radioimmunoassay (RIA) procedure for the determination of susceptibility to varicella. J Virol Methods. 1981 Feb;2(3):149–158. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(81)90033-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dowling P., Menonna J., Cook S. Cytomegalovirus complement fixation antibody in Guillain-Barré syndrome. Neurology. 1977 Dec;27(12):1153–1156. doi: 10.1212/wnl.27.12.1153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein M. A. An assessment of the possible role of viruses in the aetiology of Burkitt's lymphoma. Prog Exp Tumor Res. 1978;21:72–99. doi: 10.1159/000400859. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman M. G., Leventon-Kriss S., Sarov I. Sensitive solid-phase radioimmunoassay for detection of human immunoglobulin G antibodies to varicella-zoster virus. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Jan;9(1):1–10. doi: 10.1128/jcm.9.1.1-10.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman M. G. Salivary IgA antibodies to mumps virus during and after mumps. J Infect Dis. 1981 Apr;143(4):617–617. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.4.617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerna G., Achilli G., Chambers R. W. Determination of neutralizing antibody and IgG antibody to varicella-zoster virus and of IgG antibody to membrane antigens by the immunoperoxidase technique. J Infect Dis. 1977 Jun;135(6):975–979. doi: 10.1093/infdis/135.6.975. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg R. D., Sarov I. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of antibodies to varicella zoster virus. Isr J Med Sci. 1980 Feb;16(2):111–117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham R. C., Jr, Karnovsky M. J. The early stages of absorption of injected horseradish peroxidase in the proximal tubules of mouse kidney: ultrastructural cytochemistry by a new technique. J Histochem Cytochem. 1966 Apr;14(4):291–302. doi: 10.1177/14.4.291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOPE-SIMPSON R. E. THE NATURE OF HERPES ZOSTER: A LONG-TERM STUDY AND A NEW HYPOTHESIS. Proc R Soc Med. 1965 Jan;58:9–20. doi: 10.1177/003591576505800106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hacham M., Leventon-Kriss S., Sarov I. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of virus-specific IgM antibodies to varicella-zoster virus. Intervirology. 1980;13(4):214–222. doi: 10.1159/000149128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haikin H., Leventon-Kriss S., Sarov I. Antibody to varicella-zoster virus-induced membrane antigen: immunoperoxidase assay with air-dried target cells. J Infect Dis. 1979 Oct;140(4):601–604. doi: 10.1093/infdis/140.4.601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haikin H., Sarov I. Immunoperoxidase antibody to human cytomegalovirus-induced membrane antigen assay in the absence of interfering immunoglobulin G receptors. Intervirology. 1980;14(3-4):155–159. doi: 10.1159/000149177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halonen P., Bennich H., Torfason E., Karlsson T., Ziola B., Matikainen M. T., Hjertsson E., Wesslen T. Solid-phase radioimmunoassay of serum immunoglobulin A antibodies to respiratory syncytial virus and adenovirus. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Aug;10(2):192–197. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.2.192-197.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halonen P., Meurman O., Matikainen M. T., Torfason E., Bennich H. IgA antibody response in acute rubella determined by solid-phase radioimmunoassay. J Hyg (Lond) 1979 Aug;83(1):69–75. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400025833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henle G., Henle W. Epstein-Barr virus-specific IgA serum antibodies as an outstanding feature of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 1976 Jan 15;17(1):1–7. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910170102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hornsleth A., Leerhoy J., Grauballe P., Spanggaard H. Persistence of rubellavirus-specific immunoglobulin M and immunoglobulin A antibodies: investigation of successive serum samples with lowered immunoglobulin G concentration. Infect Immun. 1975 Apr;11(4):804–808. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.4.804-808.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahane S., Dvilansky A., Estok L., Nathan I., Zolotov Z., Sarov I. Detection of anti-platelet antibodies in patients with idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP) and in patients with rubella and herpes group viral infections. Clin Exp Immunol. 1981 Apr;44(1):49–56. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalimo K. O., Marttila R. J., Granfors K., Viljanen M. K. Solid-phase radioimmunoassay of human immunoglobulin M and immunoglobulin G antibodies against herpes simplex virus type 1 capsid, envelope, and excreted antigens. Infect Immun. 1977 Mar;15(3):883–889. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.3.883-889.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leventon-Kriss S., Yoffe R., Rannon L., Modan M. Seroepidemiologic aspects of varicella zoster virus infections in an Israeli Jewish population. Isr J Med Sci. 1978 Jul;14(7):766–770. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy E., Sarov I. Determination of IgA antibodies to human cytomegalovirus by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). J Med Virol. 1980;6(3):249–257. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890060308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lycke E., Norrby R., Roos B. E. A serological study on mentally ill patients with particular reference to the prevalence of herpes virus infections. Br J Psychiatry. 1974 Mar;124(0):273–279. doi: 10.1192/bjp.124.3.273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikoskelainen J., Neel E. U., Stevens D. A. Epstein-Barr virus-specific serum immunoglobulin A as an acute-phase antibody in infectious mononucleosis. J Clin Microbiol. 1979 Jul;10(1):75–79. doi: 10.1128/jcm.10.1.75-79.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rawls W. E., Bacchetti S., Graham F. L. Relation of Herpes simplex viruses to human malignancies. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1977;77:71–95. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-66740-4_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross C. A., McDaid R. Specific IgM antibody in serum of patients with herpes zoster infections. Br Med J. 1972 Dec 2;4(5839):522–523. doi: 10.1136/bmj.4.5839.522. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarov I., Siqueira-Linhares M., Chardonnet Y., Levy E., Aymard M., Bosshard S., Nord E., Revillard J. P. Detection of specific IgA antibodies in serum of kidney transplant patients with recurrent cytomegalovirus infection. Intervirology. 1981;15(4):228–234. doi: 10.1159/000149236. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt N. J., Forghani B., Lennette E. H. Type specificity of complement-requiring and immunoglobulin M neutralizing antibody in initial herpes simplex virus infections of humans. Infect Immun. 1975 Oct;12(4):728–732. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.4.728-732.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt N. J., Lennette E. H. Neutralizing antibody responses to varicella-zoster virus. Infect Immun. 1975 Sep;12(3):606–613. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.3.606-613.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shemer Y., Leventon-Kriss S., Sarov I. Isolation and polypeptide characterization of varicella-zoster virus. Virology. 1980 Oct 15;106(1):133–140. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90228-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tovi F., Sidi J., Haikin H., Sarov B., Sarov I. Viral infection and acute peripheral facial palsy. A study with herpes simplex and varicella zoster viruses. Isr J Med Sci. 1980 Aug;16(8):576–580. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vahlne A., Edström S., Arstila P., Beran M., Ejnell H., Nylén O., Lycke E. Bell's palsy and herpes simplex virus. Arch Otolaryngol. 1981 Feb;107(2):79–81. doi: 10.1001/archotol.1981.00790380009003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams V., Gershon A., Brunell P. A. Serologic response to varicella-zoster membrane antigens measured by direct immunofluorescence. J Infect Dis. 1974 Dec;130(6):669–672. doi: 10.1093/infdis/130.6.669. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]