Abstract
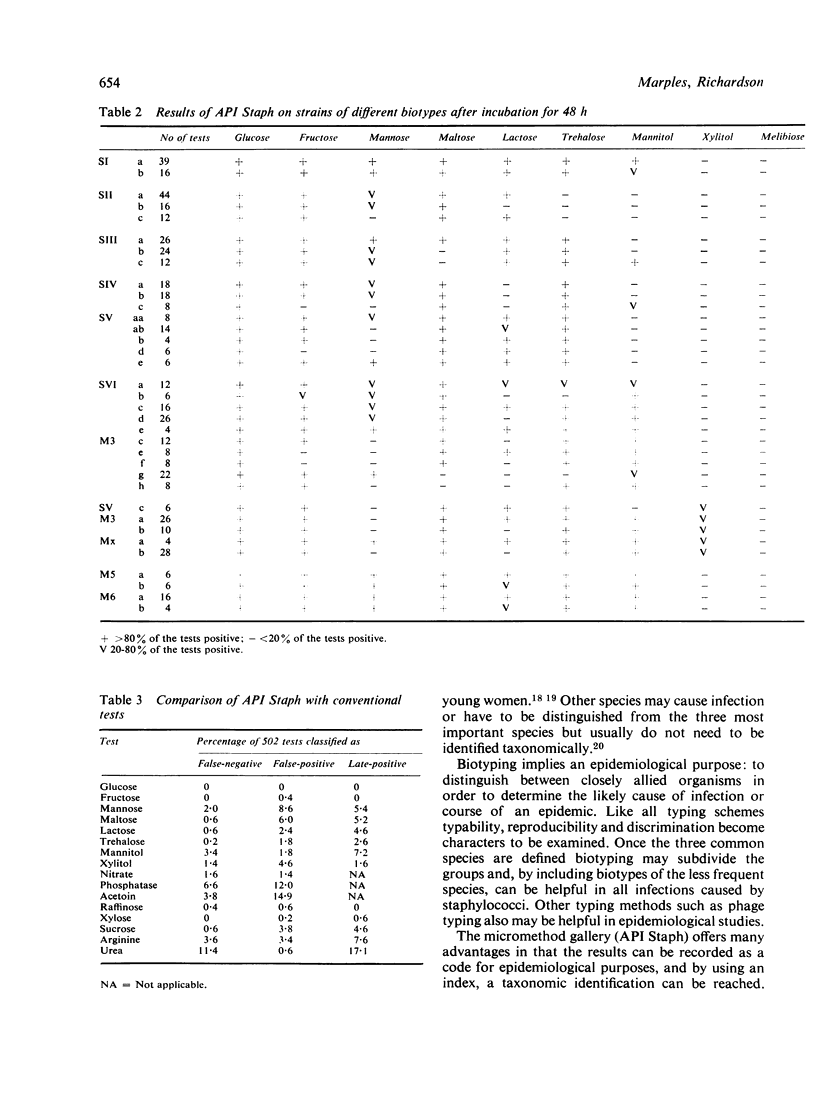
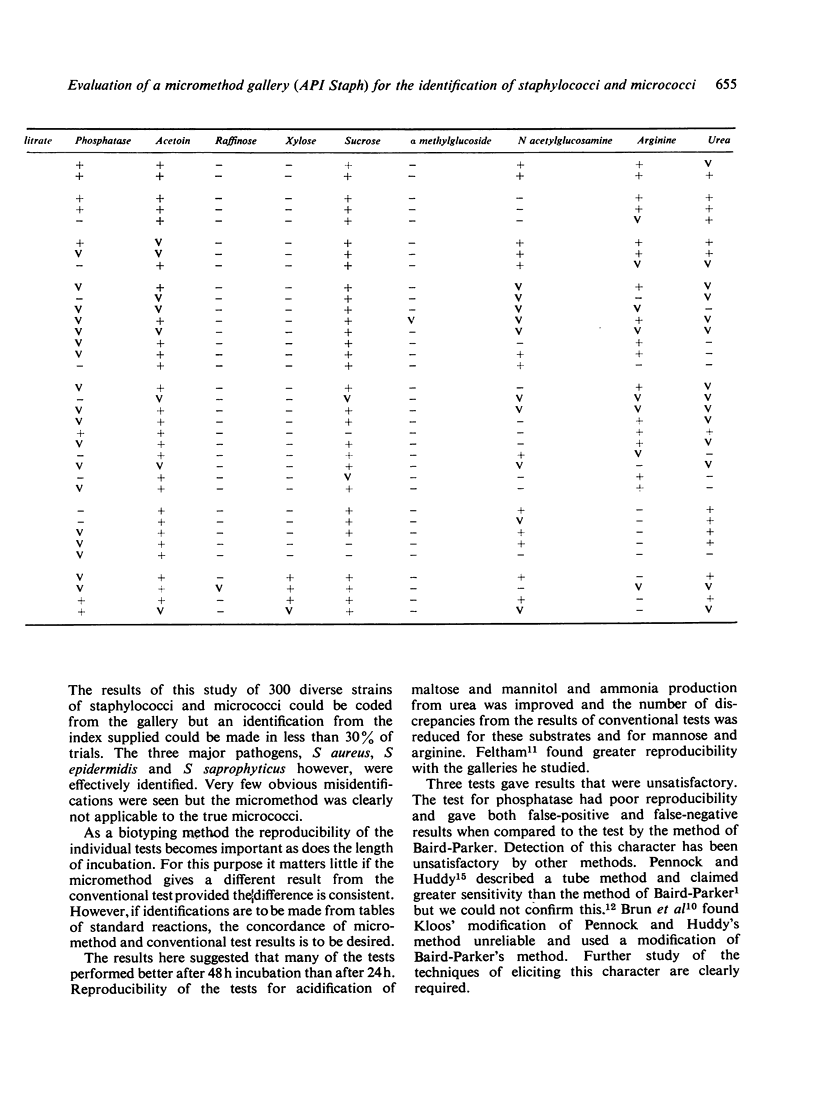
A collection of 300 well-characterised strains of staphylococci and micrococci was examined by a commercially available gallery micromethod (API Staph). The results were compared with biotyping by conventional methods. The gallery micromethod broadly agreed with the biotyping scheme used but gave an identification from the index supplied in less than 30% of the trials. Reproducibility was better after 48 h incubation than after 24 h but was poor for the tests for phosphatase and acetoin. When compared with the results of conventional tests, the tests for acetoin, phosphatase and urea were unsatisfactory.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BAIRD-PARKER A. C. A classification of micrococci and staphylococci based on physiological and biochemical tests. J Gen Microbiol. 1963 Mar;30:409–427. doi: 10.1099/00221287-30-3-409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baird-Parker A. C. The basis for the present classification of staphylococci and micrococci. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1974 Jul 31;236(0):7–14. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1974.tb41478.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brun Y., Fleurette J., Forey F. Micromethod for biochemical identification of coagulase-negative staphylococci. J Clin Microbiol. 1978 Nov;8(5):503–508. doi: 10.1128/jcm.8.5.503-508.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feltham R. K. A taxonomic study of the Micrococcaceae. J Appl Bacteriol. 1979 Oct;47(2):243–254. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1979.tb01751.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kloos W. E., Schleifer K. H. Simplified scheme for routine identification of human Staphylococcus species. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 Jan;1(1):82–88. doi: 10.1128/jcm.1.1.82-88.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maskell R. Importance of coagulase-negative staphylococci as pathogens in the urinary tract. Lancet. 1974 Jun 8;1(7867):1155–1158. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)90634-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell R. G. Classification of Staphylococcus albus strains isolated from the urinary tract. J Clin Pathol. 1968 Jan;21(1):93–96. doi: 10.1136/jcp.21.1.93. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelzer K., Pulvere G., Jeljaszweicz J., Pillich J. Modification of Baird-Parker's classification system of Staphylococcus albus. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1973;158(4):249–257. doi: 10.1007/BF02121411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pennock C. A., Huddy R. B. Phosphatase reaction of coagulase-negative staphylococci and micrococci. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1967 Apr;93(2):685–688. doi: 10.1002/path.1700930231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


