Abstract
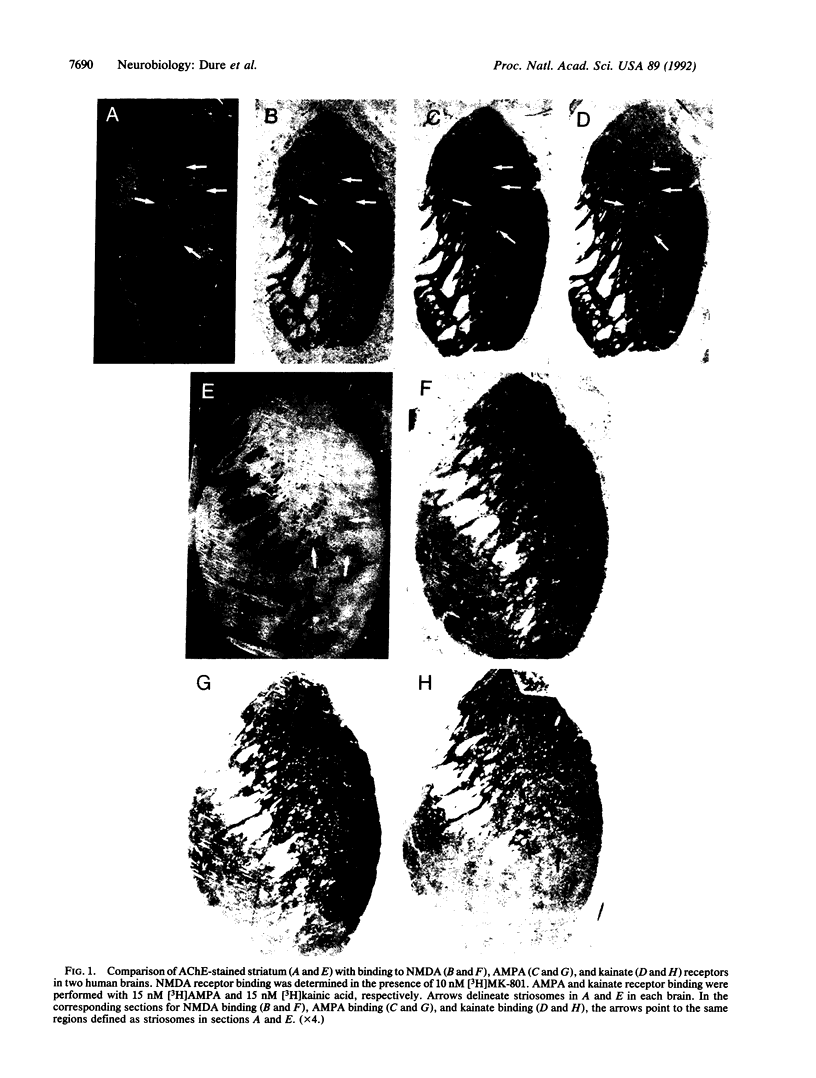
Division of the mammalian neostriatum into two intermingled compartments called striosomes and matrix has been established by analysis of enzyme activity, neuropeptide distribution, nucleic acid hybridization, and neurotransmitter receptor binding. Striosomes and matrix are distinct with respect to afferent and efferent connections, and these regions provide the potential for modulation and integration of information flow within basal ganglia circuitry. The primary neurotransmitters of corticostriatal afferents are excitatory amino acids, but to date no correlation of excitatory amino acid receptors and striatal compartments has been described. We examined binding to the three pharmacologically distinct ionotropic excitatory amino acid receptors, N-methyl-D-aspartate, alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methylisoxazole-4-propionic acid, and kainate, in human striatum using in vitro receptor autoradiography and compared the binding to striosomes and matrix histochemically defined by acetylcholinesterase activity. Our findings reveal increased binding to N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors and alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methylisoxazole-4-propionic acid receptors in matrix relative to striosomes and increased kainate receptor binding in striosomes relative to matrix. These results suggest that afferent input to the two striatal compartments may be mediated by pharmacologically distinct excitatory amino acid receptor subtypes.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albin R. L., Young A. B., Penney J. B. The functional anatomy of basal ganglia disorders. Trends Neurosci. 1989 Oct;12(10):366–375. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(89)90074-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alexander G. E., Crutcher M. D. Functional architecture of basal ganglia circuits: neural substrates of parallel processing. Trends Neurosci. 1990 Jul;13(7):266–271. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(90)90107-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alexander G. E., DeLong M. R., Strick P. L. Parallel organization of functionally segregated circuits linking basal ganglia and cortex. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1986;9:357–381. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.09.030186.002041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Auer R., Kalimo H., Olsson Y., Wieloch T. The dentate gyrus in hypoglycemia: pathology implicating excitotoxin-mediated neuronal necrosis. Acta Neuropathol. 1985;67(3-4):279–288. doi: 10.1007/BF00687813. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Besson M. J., Graybiel A. M., Nastuk M. A. [3H]SCH 23390 binding to D1 dopamine receptors in the basal ganglia of the cat and primate: delineation of striosomal compartments and pallidal and nigral subdivisions. Neuroscience. 1988 Jul;26(1):101–119. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(88)90130-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Besson M. J., Graybiel A. M., Quinn B. Co-expression of neuropeptides in the cat's striatum: an immunohistochemical study of substance P, dynorphin B and enkephalin. Neuroscience. 1990;39(1):33–58. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(90)90220-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolam J. P., Izzo P. N., Graybiel A. M. Cellular substrate of the histochemically defined striosome/matrix system of the caudate nucleus: a combined Golgi and immunocytochemical study in cat and ferret. Neuroscience. 1988 Mar;24(3):853–875. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(88)90073-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolam J. P., Smith Y. The GABA and substance P input to dopaminergic neurones in the substantia nigra of the rat. Brain Res. 1990 Oct 8;529(1-2):57–78. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(90)90811-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson M., Carlsson A. Interactions between glutamatergic and monoaminergic systems within the basal ganglia--implications for schizophrenia and Parkinson's disease. Trends Neurosci. 1990 Jul;13(7):272–276. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(90)90108-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapman A. G., Dürmuller N., Lees G. J., Meldrum B. S. Excitotoxicity of NMDA and kainic acid is modulated by nigrostriatal dopaminergic fibres. Neurosci Lett. 1989 Dec 15;107(1-3):256–260. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(89)90827-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesselet M. F., Graybiel A. M. Striatal neurons expressing somatostatin-like immunoreactivity: evidence for a peptidergic interneuronal system in the cat. Neuroscience. 1986 Mar;17(3):547–571. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(86)90030-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi D. W., Rothman S. M. The role of glutamate neurotoxicity in hypoxic-ischemic neuronal death. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1990;13:171–182. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.13.030190.001131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiFiglia M. Excitotoxic injury of the neostriatum: a model for Huntington's disease. Trends Neurosci. 1990 Jul;13(7):286–289. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(90)90111-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donnan G. A., Kaczmarczyk S. J., Paxinos G., Chilco P. J., Kalnins R. M., Woodhouse D. G., Mendelsohn F. A. Distribution of catecholamine uptake sites in human brain as determined by quantitative [3H] mazindol autoradiography. J Comp Neurol. 1991 Feb 15;304(3):419–434. doi: 10.1002/cne.903040307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dure L. S., 4th, Young A. B., Penney J. B. Excitatory amino acid binding sites in the caudate nucleus and frontal cortex of Huntington's disease. Ann Neurol. 1991 Dec;30(6):785–793. doi: 10.1002/ana.410300607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egebjerg J., Bettler B., Hermans-Borgmeyer I., Heinemann S. Cloning of a cDNA for a glutamate receptor subunit activated by kainate but not AMPA. Nature. 1991 Jun 27;351(6329):745–748. doi: 10.1038/351745a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faden A. I., Demediuk P., Panter S. S., Vink R. The role of excitatory amino acids and NMDA receptors in traumatic brain injury. Science. 1989 May 19;244(4906):798–800. doi: 10.1126/science.2567056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faull R. L., Dragunow M., Villiger J. W. The distribution of neurotensin receptors and acetylcholinesterase in the human caudate nucleus: evidence for the existence of a third neurochemical compartment. Brain Res. 1989 May 29;488(1-2):381–386. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(89)90735-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faull R. L., Villiger J. W. Heterogeneous distribution of benzodiazepine receptors in the human striatum: a quantitative autoradiographic study comparing the pattern of receptor labelling with the distribution of acetylcholinesterase staining. Brain Res. 1986 Aug 27;381(1):153–158. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(86)90704-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrante R. J., Kowall N. W. Tyrosine hydroxylase-like immunoreactivity is distributed in the matrix compartment of normal human and Huntington's disease striatum. Brain Res. 1987 Jul 21;416(1):141–146. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(87)91506-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geneser-Jensen F. A., Blackstad T. W. Distribution of acetyl cholinesterase in the hippocampal region of the guinea pig. I. Entorhinal area, parasubiculum, and presubiculum. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1971;114(4):460–481. doi: 10.1007/BF00325634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerfen C. R., Baimbridge K. G., Miller J. J. The neostriatal mosaic: compartmental distribution of calcium-binding protein and parvalbumin in the basal ganglia of the rat and monkey. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8780–8784. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8780. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerfen C. R., Baimbridge K. G., Thibault J. The neostriatal mosaic: III. Biochemical and developmental dissociation of patch-matrix mesostriatal systems. J Neurosci. 1987 Dec;7(12):3935–3944. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.07-12-03935.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerfen C. R. The neostriatal mosaic. I. Compartmental organization of projections from the striatum to the substantia nigra in the rat. J Comp Neurol. 1985 Jun 22;236(4):454–476. doi: 10.1002/cne.902360404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerfen C. R. The neostriatal mosaic: compartmentalization of corticostriatal input and striatonigral output systems. Nature. 1984 Oct 4;311(5985):461–464. doi: 10.1038/311461a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerfen C. R. The neostriatal mosaic: striatal patch-matrix organization is related to cortical lamination. Science. 1989 Oct 20;246(4928):385–388. doi: 10.1126/science.2799392. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerfen C. R., Young W. S., 3rd Distribution of striatonigral and striatopallidal peptidergic neurons in both patch and matrix compartments: an in situ hybridization histochemistry and fluorescent retrograde tracing study. Brain Res. 1988 Sep 13;460(1):161–167. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(88)91217-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giménez-Amaya J. M., Graybiel A. M. Compartmental origins of the striatopallidal projection in the primate. Neuroscience. 1990;34(1):111–126. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(90)90306-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giménez-Amaya J. M., Graybiel A. M. Modular organization of projection neurons in the matrix compartment of the primate striatum. J Neurosci. 1991 Mar;11(3):779–791. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.11-03-00779.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goto S., Hirano A., Rojas-Corona R. R. An immunohistochemical investigation of the human neostriatum in Huntington's disease. Ann Neurol. 1989 Mar;25(3):298–304. doi: 10.1002/ana.410250315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goto S., Hirano A. Synaptophysin expression in the striatum in Huntington's disease. Acta Neuropathol. 1990;80(1):88–91. doi: 10.1007/BF00294227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graybiel A. M. Correspondence between the dopamine islands and striosomes of the mammalian striatum. Neuroscience. 1984 Dec;13(4):1157–1187. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(84)90293-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graybiel A. M., Moratalla R. Dopamine uptake sites in the striatum are distributed differentially in striosome and matrix compartments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(22):9020–9024. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.22.9020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graybiel A. M., Pickel V. M., Joh T. H., Reis D. J., Ragsdale C. W., Jr Direct demonstration of a correspondence between the dopamine islands and acetylcholinesterase patches in the developing striatum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5871–5875. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graybiel A. M., Ragsdale C. W., Jr Clumping of acetylcholinesterase activity in the developing striatum of the human fetus and young infant. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Feb;77(2):1214–1218. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.2.1214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graybiel A. M., Ragsdale C. W., Jr Histochemically distinct compartments in the striatum of human, monkeys, and cat demonstrated by acetylthiocholinesterase staining. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5723–5726. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graybiel A. M., Ragsdale C. W., Jr, Yoneoka E. S., Elde R. P. An immunohistochemical study of enkephalins and other neuropeptides in the striatum of the cat with evidence that the opiate peptides are arranged to form mosaic patterns in register with the striosomal compartments visible by acetylcholinesterase staining. Neuroscience. 1981;6(3):377–397. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(81)90131-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenamyre J. T., Olson J. M., Penney J. B., Jr, Young A. B. Autoradiographic characterization of N-methyl-D-aspartate-, quisqualate- and kainate-sensitive glutamate binding sites. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1985 Apr;233(1):254–263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenamyre J. T. The role of glutamate in neurotransmission and in neurologic disease. Arch Neurol. 1986 Oct;43(10):1058–1063. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1986.00520100062016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenamyre J. T., Young A. B. Excitatory amino acids and Alzheimer's disease. Neurobiol Aging. 1989 Sep-Oct;10(5):593–602. doi: 10.1016/0197-4580(89)90143-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenamyre J. T., Young A. B., Penney J. B. Quantitative autoradiographic distribution of L-[3H]glutamate-binding sites in rat central nervous system. J Neurosci. 1984 Aug;4(8):2133–2144. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.04-08-02133.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groves P. M., Martone M., Young S. J., Armstrong D. M. Three-dimensional pattern of enkephalin-like immunoreactivity in the caudate nucleus of the cat. J Neurosci. 1988 Mar;8(3):892–900. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.08-03-00892.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haber S. N. Neurotransmitters in the human and nonhuman primate basal ganglia. Hum Neurobiol. 1986;5(3):159–168. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herkenham M., Pert C. B. Mosaic distribution of opiate receptors, parafascicular projections and acetylcholinesterase in rat striatum. Nature. 1981 Jun 4;291(5814):415–418. doi: 10.1038/291415a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch E., Graybiel A. M., Agid Y. A. Melanized dopaminergic neurons are differentially susceptible to degeneration in Parkinson's disease. Nature. 1988 Jul 28;334(6180):345–348. doi: 10.1038/334345a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansen K. L., Faull R. L., Dragunow M. NMDA and kainic acid receptors have a complementary distribution to AMPA receptors in the human cerebellum. Brain Res. 1990 Nov 5;532(1-2):351–354. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(90)91783-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiménez-Castellanos J., Graybiel A. M. Compartmental origins of striatal efferent projections in the cat. Neuroscience. 1989;32(2):297–321. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(89)90080-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston J. G., Gerfen C. R., Haber S. N., van der Kooy D. Mechanisms of striatal pattern formation: conservation of mammalian compartmentalization. Brain Res Dev Brain Res. 1990 Dec 1;57(1):93–102. doi: 10.1016/0165-3806(90)90189-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawaguchi Y., Wilson C. J., Emson P. C. Projection subtypes of rat neostriatal matrix cells revealed by intracellular injection of biocytin. J Neurosci. 1990 Oct;10(10):3421–3438. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.10-10-03421.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langer L. F., Graybiel A. M. Distinct nigrostriatal projection systems innervate striosomes and matrix in the primate striatum. Brain Res. 1989 Oct 2;498(2):344–350. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(89)91114-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- London E. D., Coyle J. T. Specific binding of [3H]kainic acid to receptor sites in rat brain. Mol Pharmacol. 1979 May;15(3):492–505. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loopuijt L. D. Distribution of dopamine D-2 receptors in the rat striatal complex and its comparison with acetylcholinesterase. Brain Res Bull. 1989 May;22(5):805–817. doi: 10.1016/0361-9230(89)90023-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowenstein P. R., Joyce J. N., Coyle J. T., Marshall J. F. Striosomal organization of cholinergic and dopaminergic uptake sites and cholinergic M1 receptors in the adult human striatum: a quantitative receptor autoradiographic study. Brain Res. 1990 Feb 26;510(1):122–126. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(90)90736-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowenstein P. R., Slesinger P. A., Singer H. S., Walker L. C., Casanova M. F., Raskin L. S., Price D. L., Coyle J. T. Compartment-specific changes in the density of choline and dopamine uptake sites and muscarinic and dopaminergic receptors during the development of the baboon striatum: a quantitative receptor autoradiographic study. J Comp Neurol. 1989 Oct 15;288(3):428–446. doi: 10.1002/cne.902880306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malach R., Graybiel A. M. Mosaic architecture of the somatic sensory-recipient sector of the cat's striatum. J Neurosci. 1986 Dec;6(12):3436–3458. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.06-12-03436.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masu M., Tanabe Y., Tsuchida K., Shigemoto R., Nakanishi S. Sequence and expression of a metabotropic glutamate receptor. Nature. 1991 Feb 28;349(6312):760–765. doi: 10.1038/349760a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller L. P., Lyeth B. G., Jenkins L. W., Oleniak L., Panchision D., Hamm R. J., Phillips L. L., Dixon C. E., Clifton G. L., Hayes R. L. Excitatory amino acid receptor subtype binding following traumatic brain injury. Brain Res. 1990 Aug 27;526(1):103–107. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(90)90254-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monaghan D. T., Bridges R. J., Cotman C. W. The excitatory amino acid receptors: their classes, pharmacology, and distinct properties in the function of the central nervous system. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1989;29:365–402. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.29.040189.002053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moriyoshi K., Masu M., Ishii T., Shigemoto R., Mizuno N., Nakanishi S. Molecular cloning and characterization of the rat NMDA receptor. Nature. 1991 Nov 7;354(6348):31–37. doi: 10.1038/354031a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murrin L. C., Zeng W. Y. Dopamine D1 receptor development in the rat striatum: early localization in striosomes. Brain Res. 1989 Feb 20;480(1-2):170–177. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(89)91579-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen E. O., Drejer J., Cha J. H., Young A. B., Honoré T. Autoradiographic characterization and localization of quisqualate binding sites in rat brain using the antagonist [3H]6-cyano-7-nitroquinoxaline-2,3-dione: comparison with (R,S)-[3H]alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid binding sites. J Neurochem. 1990 Feb;54(2):686–695. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1990.tb01925.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palacios J. M., Niehoff D. L., Kuhar M. J. Receptor autoradiography with tritium-sensitive film: potential for computerized densitometry. Neurosci Lett. 1981 Sep 1;25(2):101–105. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(81)90315-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penny G. R., Wilson C. J., Kitai S. T. Relationship of the axonal and dendritic geometry of spiny projection neurons to the compartmental organization of the neostriatum. J Comp Neurol. 1988 Mar 8;269(2):275–289. doi: 10.1002/cne.902690211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry T. L., Hansen S. What excitotoxin kills striatal neurons in Huntington's disease? Clues from neurochemical studies. Neurology. 1990 Jan;40(1):20–24. doi: 10.1212/wnl.40.1.20. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petit F., Glowinski J. Stimulatory effect of substance P on the spontaneous release of newly synthesized [3H]dopamine from rat striatal slices: a tetrodotoxin-sensitive process. Neuropharmacology. 1986 Sep;25(9):1015–1021. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(86)90196-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plaitakis A. Glutamate dysfunction and selective motor neuron degeneration in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: a hypothesis. Ann Neurol. 1990 Jul;28(1):3–8. doi: 10.1002/ana.410280103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quirion R., Gaudreau P., Martel J. C., St-Pierre S., Zamir N. Possible interactions between dynorphin and dopaminergic systems in rat basal ganglia and substantia nigra. Brain Res. 1985 Apr 8;331(2):358–362. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(85)91563-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ragsdale C. W., Jr, Graybiel A. M. A simple ordering of neocortical areas established by the compartmental organization of their striatal projections. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(16):6196–6199. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.16.6196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ragsdale C. W., Jr, Graybiel A. M. The fronto-striatal projection in the cat and monkey and its relationship to inhomogeneities established by acetylcholinesterase histochemistry. Brain Res. 1981 Mar 16;208(2):259–266. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)90556-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rainbow T. C., Wieczorek C. M., Halpain S. Quantitative autoradiography of binding sites for [3H]AMPA, a structural analogue of glutamic acid. Brain Res. 1984 Aug 20;309(1):173–177. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)91025-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reid M., Herrera-Marschitz M., Hökfelt T., Terenius L., Ungerstedt U. Differential modulation of striatal dopamine release by intranigral injection of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), dynorphin A and substance P. Eur J Pharmacol. 1988 Mar 15;147(3):411–420. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(88)90176-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiner A., Albin R. L., Anderson K. D., D'Amato C. J., Penney J. B., Young A. B. Differential loss of striatal projection neurons in Huntington disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(15):5733–5737. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.15.5733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiner A., Anderson K. D. The patterns of neurotransmitter and neuropeptide co-occurrence among striatal projection neurons: conclusions based on recent findings. Brain Res Brain Res Rev. 1990 Sep-Dec;15(3):251–265. doi: 10.1016/0165-0173(90)90003-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richfield E. K., Young A. B., Penney J. B. Comparative distribution of dopamine D-1 and D-2 receptors in the basal ganglia of turtles, pigeons, rats, cats, and monkeys. J Comp Neurol. 1987 Aug 15;262(3):446–463. doi: 10.1002/cne.902620308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakurai S. Y., Cha J. H., Penney J. B., Young A. B. Regional distribution and properties of [3H]MK-801 binding sites determined by quantitative autoradiography in rat brain. Neuroscience. 1991;40(2):533–543. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(91)90139-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seubert P., Lee K., Lynch G. Ischemia triggers NMDA receptor-linked cytoskeletal proteolysis in hippocampus. Brain Res. 1989 Jul 17;492(1-2):366–370. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(89)90921-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simasko S. M., Weiland G. A. Effect of neurotensin, substance P and TRH on the regulation of dopamine receptors in rat brain. Eur J Pharmacol. 1984 Nov 27;106(3):653–656. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(84)90074-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sommer B., Keinänen K., Verdoorn T. A., Wisden W., Burnashev N., Herb A., Köhler M., Takagi T., Sakmann B., Seeburg P. H. Flip and flop: a cell-specific functional switch in glutamate-operated channels of the CNS. Science. 1990 Sep 28;249(4976):1580–1585. doi: 10.1126/science.1699275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugimoto T., Itoh K., Yasui Y., Kamiya H., Uemura Y., Mizuno N. Changes of neurotensinlike immunoreactivity in the striatum of the cat after intrastriatal injection of kainic acid. J Comp Neurol. 1987 Sep 22;263(4):607–612. doi: 10.1002/cne.902630411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner B. H., Wilson J. S., McKenzie J. C., Richtand N. MPTP produces a pattern of nigrostriatal degeneration which coincides with the mosaic organization of the caudate nucleus. Brain Res. 1988 Nov 8;473(1):60–64. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(88)90315-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turski L., Klockgether T., Turski W. A., Schwarz M., Sontag K. H. Blockade of excitatory neurotransmission in the globus pallidus induces rigidity and akinesia in the rat: implications for excitatory neurotransmission in pathogenesis of Parkinson's diseases. Brain Res. 1990 Mar 26;512(1):125–131. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(90)91180-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werner P., Voigt M., Keinänen K., Wisden W., Seeburg P. H. Cloning of a putative high-affinity kainate receptor expressed predominantly in hippocampal CA3 cells. Nature. 1991 Jun 27;351(6329):742–744. doi: 10.1038/351742a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieloch T., Engelsen B., Westerberg E., Auer R. Lesions of the glutamatergic cortico-striatal projections in the rat ameliorate hypoglycemic brain damage in the striatum. Neurosci Lett. 1985 Jul 4;58(1):25–30. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(85)90323-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young A. B., Fagg G. E. Excitatory amino acid receptors in the brain: membrane binding and receptor autoradiographic approaches. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1990 Mar;11(3):126–133. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(90)90199-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young A. B., Greenamyre J. T., Hollingsworth Z., Albin R., D'Amato C., Shoulson I., Penney J. B. NMDA receptor losses in putamen from patients with Huntington's disease. Science. 1988 Aug 19;241(4868):981–983. doi: 10.1126/science.2841762. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zahm D. S., Eggerman K. W., Sprung R. F., Wesche D. E., Payne E. Postnatal development of striatal neurotensin immunoreactivity in relation to clusters of substance P immunoreactive neurons and the "dopamine islands" in the rat. J Comp Neurol. 1990 Jun 15;296(3):403–414. doi: 10.1002/cne.902960306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Kooy D. Developmental relationships between opiate receptors and dopamine in the formation of caudate-putamen patches. Brain Res. 1984 Jun;316(2):300–303. doi: 10.1016/0165-3806(84)90318-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]