Abstract
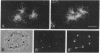
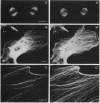
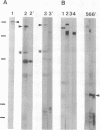
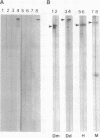
AX3, a monoclonal antibody raised against isolated microtubule-organizing centers of Dictyostelium discoideum, stains microtubule-containing structures in species ranging from Dictyostelium to human. On immunoblots, the AX3 antibody recognizes heat-stable proteins in the 260- to 280-kDa molecular-mass range in a number of different species. The AX3 antigens from HeLa and embryonic mouse fibroblast cells coprecipitate with microtubules in vitro, indicating that these antigens are, indeed, MAPs. The AX3 antigens are not immunologically related to the mammalian MAP-2 or MAP-4 but are related to the 205-kDa MAP of Drosophila. This report describes a structural-type MAP in Dictyostelium and a MAP that is detected in a wide variety of species. The Drosophila 205-kDa MAP had previously been proposed to represent a member of the MAP-4 class of proteins. From the results reported here, however, it is suggested that proteins recognized by AX3 monoclonal antibody, including the Drosophila 205-kDa MAP, represent a distinct class of MAPs that has been widely conserved through evolution.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aizawa H., Emori Y., Murofushi H., Kawasaki H., Sakai H., Suzuki K. Molecular cloning of a ubiquitously distributed microtubule-associated protein with Mr 190,000. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 15;265(23):13849–13855. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bulinski J. C., Borisy G. G. Immunofluorescence localization of HeLa cell microtubule-associated proteins on microtubules in vitro and in vivo. J Cell Biol. 1980 Dec;87(3 Pt 1):792–801. doi: 10.1083/jcb.87.3.792. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapin S. J., Bulinski J. C. Non-neuronal 210 x 10(3) Mr microtubule-associated protein (MAP4) contains a domain homologous to the microtubule-binding domains of neuronal MAP2 and tau. J Cell Sci. 1991 Jan;98(Pt 1):27–36. doi: 10.1242/jcs.98.1.27. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Lozanne A., Spudich J. A. Disruption of the Dictyostelium myosin heavy chain gene by homologous recombination. Science. 1987 May 29;236(4805):1086–1091. doi: 10.1126/science.3576222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein L. S., Laymon R. A., McIntosh J. R. A microtubule-associated protein in Drosophila melanogaster: identification, characterization, and isolation of coding sequences. J Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;102(6):2076–2087. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.6.2076. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irminger-Finger I., Laymon R. A., Goldstein L. S. Analysis of the primary sequence and microtubule-binding region of the Drosophila 205K MAP. J Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;111(6 Pt 1):2563–2572. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.6.2563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jung G., Hammer J. A., 3rd Generation and characterization of Dictyostelium cells deficient in a myosin I heavy chain isoform. J Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;110(6):1955–1964. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.6.1955. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilmartin J. V., Wright B., Milstein C. Rat monoclonal antitubulin antibodies derived by using a new nonsecreting rat cell line. J Cell Biol. 1982 Jun;93(3):576–582. doi: 10.1083/jcb.93.3.576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knecht D. A., Loomis W. F. Antisense RNA inactivation of myosin heavy chain gene expression in Dictyostelium discoideum. Science. 1987 May 29;236(4805):1081–1086. doi: 10.1126/science.3576221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotani S., Murofushi H., Maekawa S., Aizawa H., Sakai H. Isolation of rat liver microtubule-associated proteins. Evidence for a family of microtubule-associated proteins with molecular mass of around 200,000 which distribute widely among mammalian cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 15;263(11):5385–5389. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kotani S., Murofushi H., Maekawa S., Sato C., Sakai H. Characterization of microtubule-associated proteins isolated from bovine adrenal gland. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Apr 1;156(1):23–29. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09543.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maekawa T., Leslie R., Kuriyama R. Identification of a minus end-specific microtubule-associated protein located at the mitotic poles in cultured mammalian cells. Eur J Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;54(2):255–267. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matus A., Huber G., Bernhardt R. Neuronal microdifferentiation. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;48(Pt 2):775–782. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.048.01.079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olmsted J. B., Lyon H. D. A microtubule-associated protein specific to differentiated neuroblastoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1981 Apr 10;256(7):3507–3511. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olmsted J. B. Microtubule-associated proteins. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1986;2:421–457. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.02.110186.002225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olmsted J. B. Non-motor microtubule-associated proteins. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1991 Feb;3(1):52–58. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(91)90165-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parysek L. M., Asnes C. F., Olmsted J. B. MAP 4: occurrence in mouse tissues. J Cell Biol. 1984 Oct;99(4 Pt 1):1309–1315. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.4.1309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roos U. P. Probing the mechanisms of mitosis with Dictyostelium discoideum. Methods Cell Biol. 1987;28:261–279. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)61650-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sellitto C., Kimble M., Kuriyama R. Heterogeneity of microtubule organizing center components as revealed by monoclonal antibodies to mammalian centrosomes and to nucleus-associated bodies from dictyostelium. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton. 1992;22(1):7–24. doi: 10.1002/cm.970220103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weatherbee J. A., Luftig R. B., Weihing R. R. Purification and reconstitution of HeLa cell microtubules. Biochemistry. 1980 Aug 19;19(17):4116–4123. doi: 10.1021/bi00558a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weatherbee J. A., Sherline P., Mascardo R. N., Izant J. G., Luftig R. B., Weihing R. R. Microtubule-associated proteins of HeLa cells: heat stability of the 200,000 mol wt HeLa MAPs and detection of the presence of MAP-2 in HeLa cell extracts and cycled microtubules. J Cell Biol. 1982 Jan;92(1):155–163. doi: 10.1083/jcb.92.1.155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West R. R., Tenbarge K. M., Olmsted J. B. A model for microtubule-associated protein 4 structure. Domains defined by comparisons of human, mouse, and bovine sequences. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 15;266(32):21886–21896. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiche G. High-Mr microtubule-associated proteins: properties and functions. Biochem J. 1989 Apr 1;259(1):1–12. doi: 10.1042/bj2590001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiche G., Oberkanins C., Himmler A. Molecular structure and function of microtubule-associated proteins. Int Rev Cytol. 1991;124:217–273. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61528-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]