Abstract
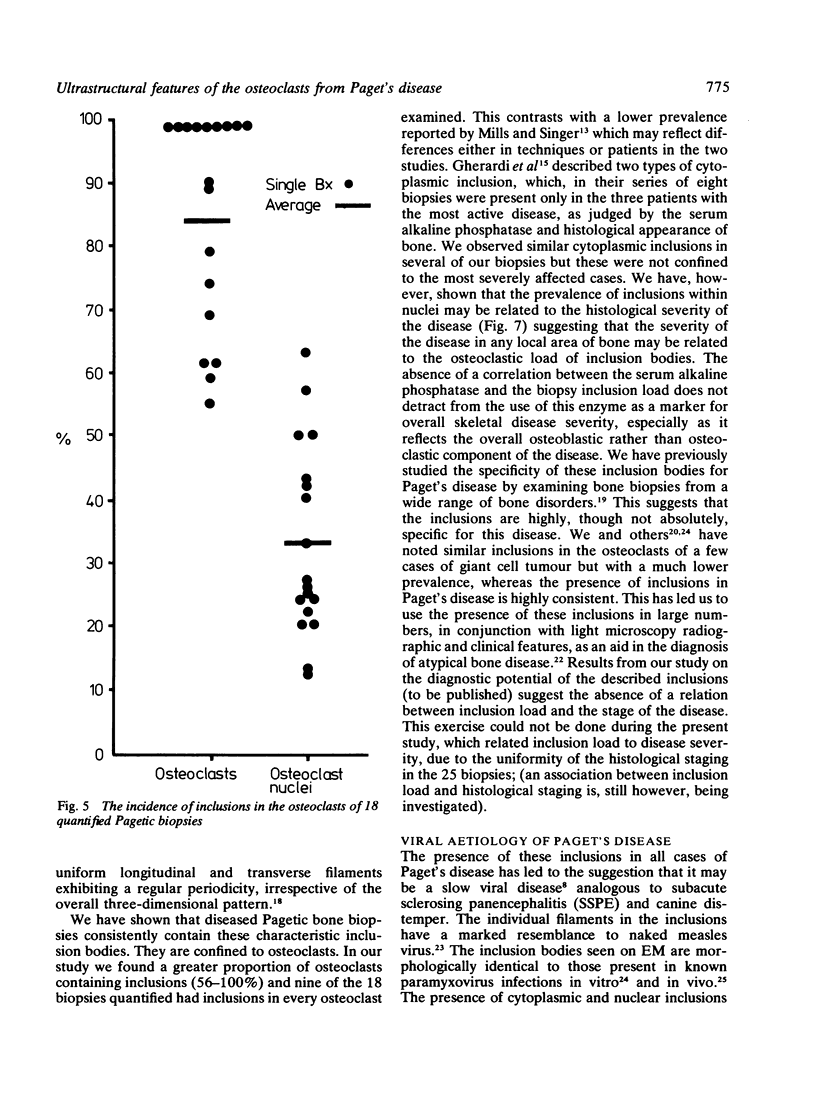
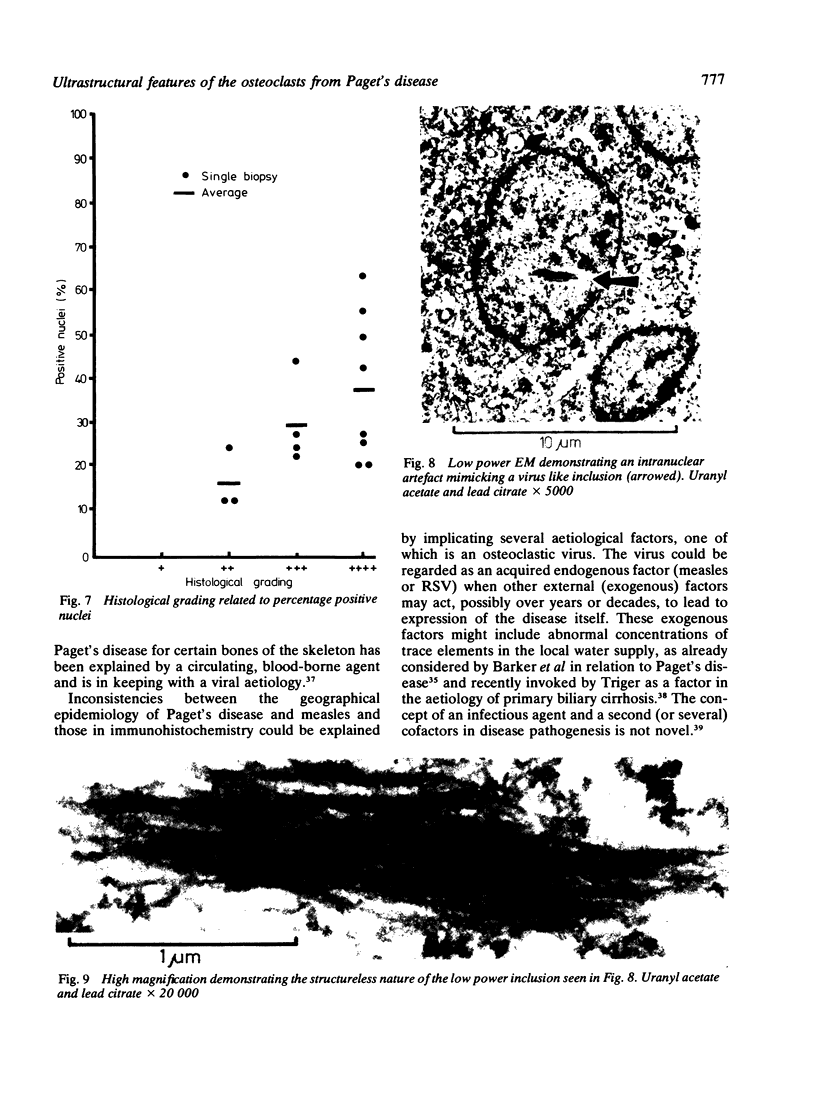
The ultrastructure of the osteocytes, osteoblasts, osteoclasts, haemopoietic and other connective tissue cells was examined in 27 biopsies from 22 patients with Paget's disease of bone. Electron microscopy showed characteristic nuclear and cytoplasmic inclusions in the osteoclasts of all of the 25 biopsies exhibiting histological evidence of Paget's disease. Such inclusions were absent from all the other types examined. The intranuclear inclusions consisted of stacked rows or complex whorls of tubular filaments with an individual filament diameter of 12-15 nm, often arranged in a paracrystalline array. The frequency of occurrence of inclusions in the osteoclasts and their individual nuclei measured quantitatively in 18 of the biopsies was related to the histological severity of the disease process. The similarity of the observed inclusions to those of paramyxovirus inclusion bodies (particularly measles) support the hypothesis that Paget's disease is a slow virus infection.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barker D. J., Chamberlain A. T., Guyer P. B., Gardner M. J. Paget's disease of bone: the Lancashire focus. Br Med J. 1980 Apr 26;280(6222):1105–1107. doi: 10.1136/bmj.280.6222.1105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COLLINS D. H. Paget's disease of bone; incidence and subclinical forms. Lancet. 1956 Jul 14;271(6933):51–57. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(56)90422-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen T. T., Watanabe I., Zeman W., Mealey J., Jr Subacute sclerosing panencephalitis: propagation of measles virus from brain biopsy in tissue culture. Science. 1969 Mar 14;163(3872):1193–1194. doi: 10.1126/science.163.3872.1193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gherardi G., Lo Cascio V., Bonucci E. Fine structure of nuclei and cytoplasm of osteoclasts in Paget's disease of bone. Histopathology. 1980 Jan;4(1):63–74. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.1980.tb02898.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutensohn N., Cole P. Childhood social environment and Hodgkin's disease. N Engl J Med. 1981 Jan 15;304(3):135–140. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198101153040302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harmon T. P., Morton K. S. Osteogenic sarcoma in four siblings. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1966 Aug;48(3):493–498. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heyderman E. Immunoperoxidase technique in histopathology: applications, methods, and controls. J Clin Pathol. 1979 Oct;32(10):971–978. doi: 10.1136/jcp.32.10.971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higenbottam T., Clark T. J. Influence of breath holding at total lung capacity on maximal expiratory flow measurements. Clin Sci (Lond) 1981 Jan;60(1):11–15. doi: 10.1042/cs0600011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horta-Barbosa L., Fuccillo D. A., Sever J. L., Zeman W. Subacute sclerosing panencephalitis: isolation of measles virus from a brain biopsy. Nature. 1969 Mar 8;221(5184):974–974. doi: 10.1038/221974a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen A. B., Spjut H. J., Smith M. N., Rapp F. Intracellular branched tubular structures in osteosarcoma. An ultrastructural and serological study. Cancer. 1971 Jun;27(6):1440–1448. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197106)27:6<1440::aid-cncr2820270626>3.0.co;2-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KALLMAN F., ADAMS J. M., WILLIAMS R. C., IMAGAWA D. T. Fine structure of cellular inclusions in measles virus infections. J Biophys Biochem Cytol. 1959 Dec;6:379–382. doi: 10.1083/jcb.6.3.379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiessling W. R., Hall W. W., Yung L. L., ter Meulen V. Measles-virus-specific immunoglobulin-M response in subacute sclerosing panencephalitis. Lancet. 1977 Feb 12;1(8007):324–327. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(77)91132-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Charpentier Y., Le Charpentier M., Forest M., Daudet-Monsac M., Lavenu-Vacher M. C., Louvel A., Sedel L., Abelanet R. Inclusions intranucléaires dans une tumeur osseuse à cellules géantes. Mise en évidence au microscope électronique. Nouv Presse Med. 1977 Jan 29;6(4):259–262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macgregor J. D., MacDonald J., Ingram E. A., McDonnell M., Marshall B. Epidemic measles in Shetland during 1977 and 1978. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1981 Feb 7;282(6262):434–436. doi: 10.1136/bmj.282.6262.434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills B. G., Singer F. R. Nuclear inclusions in Paget's disease of bone. Science. 1976 Oct 8;194(4261):201–202. doi: 10.1126/science.959849. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills B. G., Singer F. R., Weiner L. P., Holst P. A. Cell cultures from bone affected by Paget's disease. Arthritis Rheum. 1980 Oct;23(10):1115–1120. doi: 10.1002/art.1780231007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morton D. L., Malmgren R. A. Human osteosarcomas: immunologic evidence suggesting an associated infectious agent. Science. 1968 Dec 13;162(3859):1279–1281. doi: 10.1126/science.162.3859.1279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakai T., Shand F. L., Howatson A. F. Development of measles virus in vitro. Virology. 1969 May;38(1):50–67. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90127-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen M. The origin of bone cells in the postnatal organism. Arthritis Rheum. 1980 Oct;23(10):1073–1080. doi: 10.1002/art.1780231002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oyanagi S., ter Meulen V., Katz M., Koprowski H. Comparison of subacute sclerosing panencephalitis and measles viruses: an electron microscope study. J Virol. 1971 Jan;7(1):176–187. doi: 10.1128/jvi.7.1.176-187.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYNOLDS E. S. The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1963 Apr;17:208–212. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.1.208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rebel A., Malkani K., Basle M., Bregeon C., Patezour A., Filmon R. Particularités ultrastructurales des ostéoclastes de la maladie de Paget. Rev Rhum Mal Osteoartic. 1974 Dec;41(12):767–771. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rebel A., Malkani K., Baslé M., Bregeon C. Is Paget's disease of bone a viral infection? Calcif Tissue Res. 1977 May;22 (Suppl):283–286. doi: 10.1007/BF02064080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rebel A., Malkani K., Baslé M., Bregeon C. Osteoclast ultrastructure in Paget's disease. Calcif Tissue Res. 1976 Apr 20;(2):187–199. doi: 10.1007/BF02546407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulz A., Delling G., Ringe J. D., Ziegler R. Morbus Paget des Knochens: Untersuchungen zur Ultrastruktur der Osteoclasten und ihrer Cytopathogenese. Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histol. 1977 Dec 8;376(4):309–328. doi: 10.1007/BF00432301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer F. R., Mills B. G. The etiology of Paget's disease of bone. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1977;(127):37–42. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Triger D. R. Primary biliary cirrhosis: an epidemiological study. Br Med J. 1980 Sep 20;281(6243):772–775. doi: 10.1136/bmj.281.6243.772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vianna N. J. Evidence for infectious component of Hodgkin's disease and related considerations. Cancer Res. 1976 Feb;36(2 Pt 2):663–666. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh R. A., Meyer A. T. Nuclear fragmentations and associated fibrils in giant cell tumor of bone. Lab Invest. 1970 Jan;22(1):63–72. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams C. P., Meachim G., Taylor W. H. Effect of calcitonin treatment on osteoclast counts in Paget's disease of bone. J Clin Pathol. 1978 Dec;31(12):1212–1217. doi: 10.1136/jcp.31.12.1212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]