Abstract
Inappropriate activation of the renin-angiotensin system (RAS) contributes to many CKDs. However, the role of the RAS in modulating AKI requires elucidation, particularly because stimulating type 1 angiotensin II (AT1) receptors in the kidney or circulating inflammatory cells can have opposing effects on the generation of inflammatory mediators that underpin the pathogenesis of AKI. For example, TNF-α is a fundamental driver of cisplatin nephrotoxicity, and generation of TNF-α is suppressed or enhanced by AT1 receptor signaling in T lymphocytes or the distal nephron, respectively. In this study, cell tracking experiments with CD4-Cre mT/mG reporter mice revealed robust infiltration of T lymphocytes into the kidney after cisplatin injection. Notably, knockout of AT1 receptors on T lymphocytes exacerbated the severity of cisplatin-induced AKI and enhanced the cisplatin-induced increase in TNF-α levels locally within the kidney and in the systemic circulation. In contrast, knockout of AT1 receptors on kidney epithelial cells ameliorated the severity of AKI and suppressed local and systemic TNF-α production induced by cisplatin. Finally, disrupting TNF-α production specifically within the renal tubular epithelium attenuated the AKI and the increase in circulating TNF-α levels induced by cisplatin. These results illustrate discrepant tissue–specific effects of RAS stimulation on cisplatin nephrotoxicity and raise the concern that inflammatory mediators produced by renal parenchymal cells may influence the function of remote organs by altering systemic cytokine levels. Our findings suggest selective inhibition of AT1 receptors within the nephron as a promising intervention for protecting patients from cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity.
Keywords: cisplatin, acute renal failure, angiotensin
Cisplatin is a chemotherapy agent widely used in the treatment of solid tumors. Although the range of therapeutic options for patients with these malignancies has expanded considerably in recent years, cisplatin remains one of the most frequently prescribed anticancer drugs and shows sufficient efficacy to warrant exploration for new indications in ongoing clinical trials.1 However, cisplatin has several side effects, including renal toxicity, which affects over one quarter of treated patients.2 Understanding the mechanisms of cisplatin nephrotoxicity should guide strategies to preserve the chemotherapeutic benefits of cisplatin while minimizing the risks of associated AKI.3,4 In this regard, TNF-α plays a central role in mediating cisplatin–induced renal damage.5,6
Our recent experiments have suggested that actions of the renin-angiotensin system (RAS) are tissue dependent in the setting of various CKDs.7–9 Despite the wide use of RAS inhibitors, including type 1 angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs), little evidence is available to direct the use of these medicines when a patient is at risk of developing AKI. During persistent hypertension, we found that inactivation of type 1 angiotensin II (AT1) receptors on T lymphocytes led to exaggerated generation of TNF through the induction of the Th1 transcription factor T-bet.8 Given the importance of TNF in instigating cisplatin nephrotoxicity, we posited that activation of AT1 receptor on T cells may limit cisplatin-induced AKI by constraining T cell elaboration of TNF. By contrast, in epithelial cells of the distal nephron that do not express high levels of T-bet, angiotensin II stimulates de novo TNF expression,10 prompting us to test whether activation of AT1 receptors in the distal nephron contributes to cisplatin nephrotoxicity. To our knowledge, these studies are the first to document opposing actions of AT1 receptors in hematopoietic and renal parenchymal cells in the pathogenesis of AKI. These data should guide the development of tissue–selective RAS blockade strategies for the prevention or treatment of AKI induced by cisplatin.
To examine whether T cells accumulate in the kidneys after administration of cisplatin, we used a CD4-Cre mT/mG reporter mouse line in which CD4+ and CD8+ T cells fluoresce green, but all other cell lineages fluoresce red. After intraperitoneal (ip) cisplatin injection, we noted infiltrating eGFP+ T cells scattered throughout the renal parenchyma (Figure 1B) peaking at 12 hours, consistent with previous findings by Liu et al.11
Figure 1.
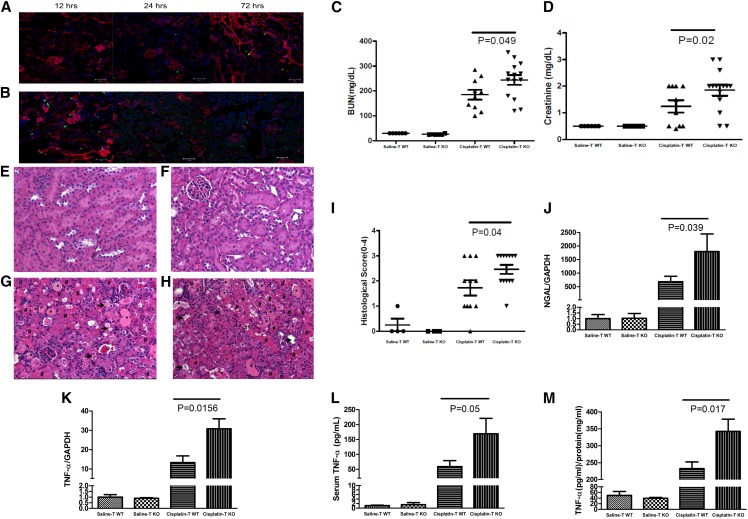
Stimulation of AT1A receptors on T lymphocytes attenuates cisplatin-induced AKI. (A and B) Representative images of kidney sections from CD4-Cre+ mT/mG mice at 12, 24, or 72 hours after (A) saline or (B) cisplatin injection. (C–M) Renal function and injury parameters in WT (TWT) mice and CD4-Cre+ Agtr1afl/fl (TKO) mice at 72 hours after saline or cisplatin treatment. (C) BUN and (D) sCr (n=6 for saline and n≥10 for cisplatin). (E–H) Representative images of kidney sections from saline– and cisplatin–treated (E and G) TWT and (F and H) TKO mice, respectively. *Tubular dilation (mild injury); #lysed tubules (severe injury with cell death); →, loss of brush border (mild injury). (I) Semiquantitative scoring of renal pathology. (J and K) Renal mRNA expression of (J) NGAL and (K) TNF-α. (L) Serum and (M) whole–kidney TNF-α protein content. GAPDH, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase.
We then tested whether abrogating AT1 receptor signals selectively within T lymphocytes influences the development of cisplatin-induced AKI. Wild-type (WT) mice and mice genetically deficient of the dominant murine AT1 receptor isoform (AT1A) solely within T cells (TKO; Supplemental Figure 1) had similar levels of BUN and serum creatinine (sCr) after saline treatment, indicating that the T cell AT1 receptor does not affect baseline renal function (Figure 1, C and D). At 72 hours after cisplatin administration, BUN levels in WT mice increased markedly from 30±0 to 185±20 mg/dl, whereas sCr increased from 0.5±0 to 1.2±0.2 mg/dl. This degree of renal function decline is consistent with prior studies using the cisplatin model of AKI.5 However, cisplatin–treated TKO mice had even higher levels of BUN (244±20 mg/dl; P=0.05) and sCr (1.9±0.2 mg/dl; P=0.02), suggesting that AT1 receptor stimulation on T cells attenuates the severity of cisplatin–induced renal dysfunction.
To evaluate if the T cell AT1 receptor has similar effects on renal pathology, we used our previously reported histologic scoring system12 to analyze hematoxylin and eosin (H&E)–stained kidney sections. No kidney injury was detected in saline–treated WT and TKO mice (Figure 1, E, F, and I). Both TKO and WT mice had evidence of kidney injury at 72 hours after cisplatin treatment. However, TKO mice had more severe kidney pathology than WT controls (2.46±0.18 versus 1.73±0.30 arbitrary units; P=0.04), confirming that the AT1 receptor on T cells acts to constrain renal damage in cisplatin nephrotoxicity (Figure 1, G–I).
Neutrophil gelatinase–associated lipocalin (NGAL) is a widely used marker for AKI. Compared with saline, cisplatin treatment resulted in massive upregulation in NGAL mRNA expression as measured by real-time PCR in kidney tissues from WT mice (P=0.04). Kidney tissues from cisplatin–treated TKO mice had approximately threefold higher levels of NGAL mRNA expression compared with cisplatin-treated WTs (P=0.04) (Figure 1J). Because TNF is a fundamental driver of cisplatin-induced AKI, we profiled the expression of TNF in the kidney and systemic circulation. Compared with WTs, cisplatin–treated TKO mice had higher levels of TNF mRNA (P=0.02) (Figure 1K) and protein (343±36 versus 233±20 pg/mg tissue protein; P=0.02) (Figure 1M) in the kidney and higher circulating TNF levels (169±52 versus 59±20 pg/ml; P=0.05) (Figure 1L). Thus, activation of the T cell AT1 receptor suppresses generation of TNF within the kidney and reduces the degree of kidney injury during cisplatin nephrotoxicity.
Although our findings confirm the importance of CD4+ T lymphocytes in mediating cisplatin-induced AKI,11 these experiments are the first, to our knowledge, to document a protective effect of the T cell AT1 receptor in the setting of AKI and highlight a potential danger of treating patients who require cisplatin chemotherapy with an ARB. Although we cannot exclude a TNF-independent contribution to the exaggerated renal injury in the TKOs, the actions of AT1 receptors on T cells to limit TNF production are consistent with our previous findings in the setting of hypertensive kidney damage and can accrue from both an effect on T-bet–mediated T cell differentiation and a reduction in T cell-renal tubular cell interactions caused by effects of the T cell AT1 receptor on chemokine generation.8
Angiotensin II upregulates TNF production in the distal nephron.10 Therefore, to evaluate the contribution of AT1 receptor activation in the distal nephron to TNF generation and AKI after cisplatin treatment, we generated Ksp-Cre Agtr1aflox/flox mice (KKO) lacking AT1A receptors solely in the distal nephron. We observed the distribution pattern of our gene targeting strategy in the cisplatin model by subjecting Ksp-Cre mT/mG reporter mice to our cisplatin model. After saline or cisplatin injection, green fluorescent protein emanated from the distal nephron, including the loop of Henle (Figure 2, A and B), a major source of kidney-derived TNF.10
Figure 2.
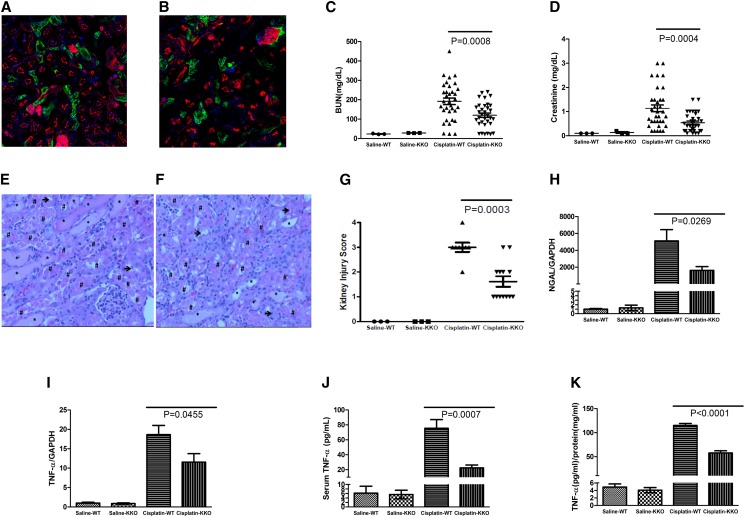
AT1A receptor activation on kidney epithelial cells exaggerates cisplatin nephrotoxicity. (A and B) Representative images of kidney sections from KSP-Cre+ mT/mG mice 72 hours after (A) saline or (B) cisplatin injection. (C) BUN and (D) sCr in saline– or cisplatin–treated WT and KKO mice (n=3 for saline and n≥33 for cisplatin). (E–G) Kidney pathology in cisplatin-treated mice. Representative images of kidney sections from cisplatin-treated (E) WT and (F) KKO mice. *Tubular dilation (mild injury); #lysed tubules (severe injury with cell death); →loss of brush border (mild injury). (G) WT and KKO kidney pathology scores (n=3 for saline and n≥12 for cisplatin). (H and I) Renal mRNA expression of (H) NGAL and (I) TNF-α. (J) Serum and (K) kidney TNF-α protein content (n=3 for saline and n≥7 for cisplatin). GAPDH, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase.
Because WT and KKO mice had similar levels of BUN or sCr after saline injection, AT1 receptors on epithelial cells of the distal nephron do not seem to affect renal function at baseline. Seventy-two hours after cisplatin treatment, BUN levels in WT mice increased dramatically from 24±1 to 192±17 mg/dl, whereas sCr increased from 0.1±0 to 1.1±0.1 mg/dl (Figure 2, C and D). In contrast to the TKO cohort above, cisplatin–treated KKO mice had approximately 30% lower BUN levels than WTs (120.2±11.33 mg/dl; P<0.001) and a 50% decrement in sCr (0.5±0.1 mg/dl; P<0.001). Thus, AT1 receptor stimulation on kidney epithelial cells makes a striking contribution to renal dysfunction during cisplatin nephropathy.
To determine if the AT1 receptor on kidney epithelial cells influences disruptions in renal architecture after cisplatin, we again analyzed HE–stained kidney sections from the experimental groups (Figure 2, E–G). KKO mice had about 50% less kidney injury than WT controls at 72 hours after cisplatin treatment (1.6±0.2 versus 3.0±0.2; P=0.003), confirming that AT1 receptors on kidney epithelial cells accentuate kidney damage in cisplatin-induced AKI.
As in the earlier experiment, cisplatin treatment induced robust NGAL mRNA expression in the kidneys of WT mice compared with saline-treated controls (P<0.03) (Figure 2H). Compared with cisplatin-treated WTs, kidney tissues from KKO mice had an approximately 70% reduction in mRNA expression of NGAL (P=0.03) (Figure 2H). Because angiotensin II has the capacity to induce renal production of TNF, we again measured expression of TNF in the kidney and systemic circulation in our experimental groups. Compared with WTs, cisplatin–treated KKO mice had lower levels of renal TNF mRNA (P=0.05) (Figure 2I) and protein (58±5 versus 115±4 pg/mg tissue protein; P<0.001) (Figure 2K) and reduced serum TNF levels (22±4 versus 75±12 pg/ml; P<0.001) (Figure 2J). These data indicate that AT1 receptor stimulation on kidney epithelial cells provokes generation of TNF during cisplatin nephropathy sufficiently to alter TNF levels in the systemic circulation.
Cisplatin damages the kidney by activating apoptosis and necroptosis signaling cascades13 but also, by activating the innate and adaptive immune systems. Although RAS activation has been implicated in both regulating cell death and provoking inflammatory responses, we and others have struggled to reconcile the proinflammatory effects of global RAS activation with our more recent findings that AT1 receptor activation directly on immune cells limits their production of inflammatory cytokines.9,14–16 These experiments directly confront this paradox in the context of AKI by revealing that AT1 receptors on renal tubular cells rather than on immune cells upregulate TNF, even at the systemic level, and thereby, incite an inflammatory response that is, in turn, tempered by activation of AT1 receptors on T lymphocytes. The cell-specific responses of inflammatory signaling cascades to angiotensin receptor stimulation can be explained by the expression of transcription factors, such as T-bet, which is prominent within T cells but not within renal tubular cells.17
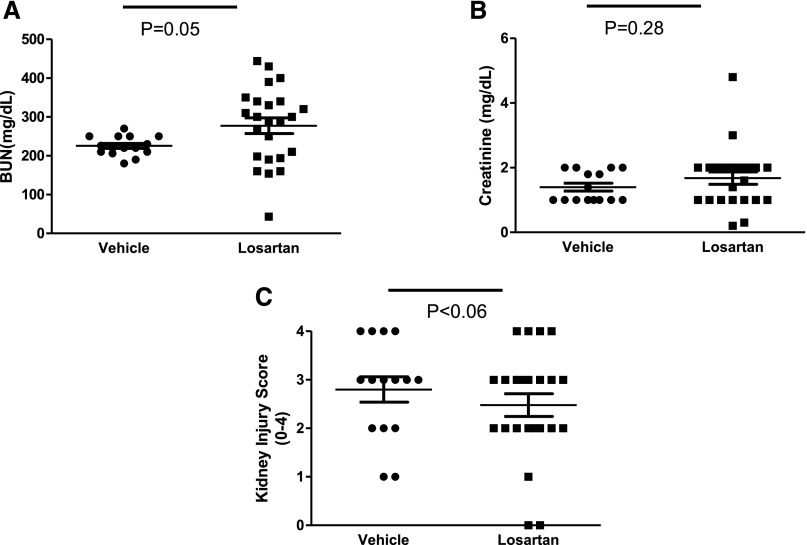
To determine the net effect of global AT1 receptor blockade on the severity of cisplatin nephrotoxicity, we treated WT mice with losartan or vehicle during cisplatin AKI. BUN levels were nonsignificantly higher in losartan-treated animals compared with vehicle-treated controls, whereas losartan therapy had no measurable effect on sCr levels (Figure 3, A and B) or renal mRNA expression of TNF after cisplatin (1.00±0.23 versus 0.96±0.28 arbitrary units). By contrast, losartan had a nonsignificant protective effect on renal pathology at 72 hours after cisplatin injection (Figure 3C). This failure of the ARB to significantly alter the course of cisplatin nephrotoxicity is consistent with prior reports18 and further illustrates the competing actions of AT1 receptors on T cells versus those in the kidney to influence AKI pathogenesis, leading to a net neutral effect of global ARB therapy.
Figure 3.
The effects of AT1 receptor blockade on cisplatin nephrotoxicity. (A) BUN, (B) sCr, and (C) kidney pathology scores in vehicle– or losartan–treated WT mice at 72 hours after cisplatin injection (n≥15).
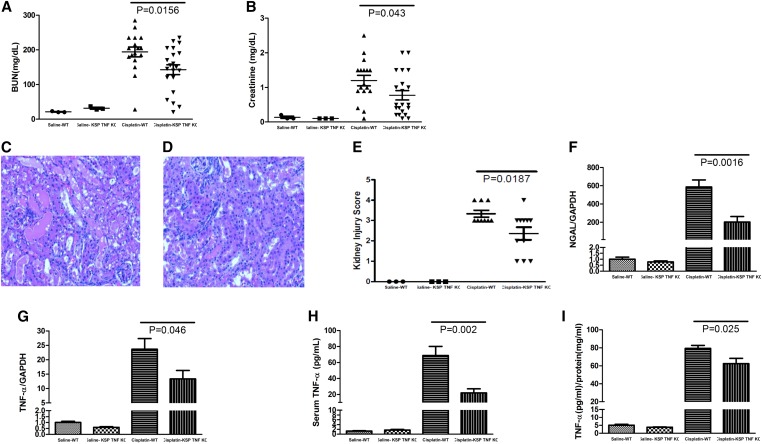
To directly test whether kidney epithelial cell–derived TNF contributed to the differences in AKI severity noted between the WT and KKO mice, we intercrossed Ksp-Cre mice with mice harboring a floxed TNF gene locus, yielding mice with deficiency of TNF solely in the renal epithelium (TNF KKO) and their WT littermates. WT mice and TNF KKO mice had similar BUN and sCr levels after saline treatment, suggesting that TNF generated by kidney epithelial cells does not affect renal function at baseline. As in earlier experiments, by 72 hours after cisplatin administration, the BUN in the WT mice increased markedly from 21±1 to 194±14 mg/dl, whereas sCr increased from 0.13±0.06 to 1.20±0.15 mg/dl (Figure 4, A and B). However, cisplatin–treated TNF KKO mice had significantly lower levels of BUN (143±14 mg/dl; P=0.02) and sCr (0.78±0.13 mg/dl; P=0.04). We then examined whether TNF from kidney epithelial cells influences the severity of renal pathology in our model. TNF KKO mice had approximately 50% less kidney damage than WT controls at 72 hours after cisplatin treatment (Figure 4, C–E) (P=0.02). Moreover, by real-time PCR, kidney tissues from TNF KKO mice had approximately 70% less mRNA expression of the kidney injury marker NGAL compared with WTs (P=0.002). Thus, TNF generated by kidney epithelial cells accounts for a substantial component of cisplatin-induced AKI.
Figure 4.
Role of TNF-α generated by the renal epithelium in the development of cisplatin–induced renal damage. (A and B) Kidney function in cisplatin–treated WT and TNF KKO (Ksp TNF KO) mice as measured by (A) BUN and (B) sCr. (C–E) Renal pathology in cisplatin-treated animals. Representative images of kidney sections from cisplatin–treated (C) WT and (D) TNF KKO mice with (E) a summary of renal injury scores (n=3 for saline and n≥17 for cisplatin). (F and G) Renal mRNA expression of (F) NGAL and (G) TNF-α (n=3 for saline and n≥9 for cisplatin). (H) Serum and (I) kidney TNF-α protein content (n=3 for saline and n=8 for cisplatin). GAPDH, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase.
We then profiled renal and systemic TNF levels in the TNF KKO and WT cohorts (Figure 4, G–I). Cisplatin–treated TNF KKO mice had significantly less TNF expression than the WTs in the kidney at both the mRNA (P=0.05) and protein levels (62.4±5.9 versus 79.3±3.4 pg TNF/mg tissue protein; P=0.03). These data show that the distal nephron is an important source of TNF in the injured kidney but that other cell lineages also contribute nontrivial amounts of TNF in this setting. Abrogating TNF production in the distal nephron also had a profound effect on serum TNF levels (22.0±5.1 versus 68.7±11.4 pg/ml; P=0.002). These data confirm the importance of TNF produced in the distal nephron to determining local TNF levels within the kidney and within the circulation during cisplatin nephrotoxicity.
Finally, to assess the extent to which AT1 receptor activation in the kidney potentiates cisplatin-induced AKI by stimulating TNF generation, we administered losartan to cisplatin–treated WT and TNF KKO animals. In the presence of an ARB, WT and TNF KKO animals had similar BUN and sCr levels at 72 hours after cisplatin (Supplemental Figure 2). These data suggest that AT1 receptor stimulation in the renal epithelium drives cisplatin nephrotoxicity largely through the induction of TNF in the kidney.
Thus, RAS activation within kidney epithelial cells mediates cisplatin-induced AKI by triggering local TNF production to such a degree that systemic TNF levels escalate. Although the alterations in systemic TNF levels could accrue directly from enhanced generation in the distal nephron, the dramatic effects of TNF deletion in the nephron on systemic TNF levels would suggest additional secondary effects related to either downstream immune activation or reduced TNF clearance with worsening renal parenchymal injury. Our findings corroborate the elegant murine chimera study from Zhang et al.6 showing that TNF produced by nonhematopoietic cells is responsible for cisplatin nephrotoxicity. To our knowledge, however, these experiments provide the first direct evidence that the renal tubular epithelium triggers its own demise during cisplatin therapy via the local generation of TNF. Because our strategy has targeted the distal nephron, future experiments will need to identify the roles of TNF generated in other nephron segments to modulate AKI and CKD progression, particularly because the proximal tubule is a major target of cisplatin toxicity.
Although several experimental strategies have been proposed to ameliorate cisplatin nephrotoxicity, clinical practice only includes supportive measures.19 Previous interventions failed, because the renoprotective strategy either interfered with the chemotherapeutic efficacy of cisplatin or invoked a separate set of prohibitive side effects, such as immunosuppression in the case of global TNF blockade. Immunosuppression is particularly problematic given the immunocompromised state of many patients with malignancy receiving chemotherapy. Intervening with angiotensin receptor blockade is attractive in this population because of ARB’s track record of safety in broad patient populations and some emerging data suggesting that ARBs may retard the progression of some tumors by regulating immune cell-epithelial cell interactions.20
The use of RAS inhibition in the prevention or treatment of AKI is controversial.21,22 Although some experiments have suggested a protective effect of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition or ARB therapy early during ischemic-reperfusion kidney injury, outcomes with these agents have not been uniformly favorable.23–26 One concern with these treatments is the risk of hemodynamic insult related to an acute lowering of glomerular filtration pressure. These studies, therefore, parse the mechanisms underpinning the mixed effects of global RAS inhibition during cisplatin-induced AKI by defining the distinct roles of AT1 receptors on T cells and kidney epithelial cells in this setting and documenting the critical contribution of TNF in the distal nephron to cisplatin nephrotoxicity. We submit that tissue-specific actions of AT1 receptors in other forms of AKI warrant investigation to aid in the development of adjuvant therapies that avoid off–target proinflammatory actions of global angiotensin receptor blockade and allow cell-specific targeting of the RAS as pertinent technologies emerge. Our results suggest that such an optimized ARB strategy may hold promise as a novel intervention for cisplatin-induced AKI.
Concise Methods
Animals
In this study, 129/SvEv floxed Agtr1a mice27 were crossed with 129/SvEv CD4-Cre mice28 to generate TKO mice and WT Cre− Agtr1afl/fl littermates (further detail in Supplemental Material); 129/SvEv floxed Agtr1a mice were similarly crossed with 129/SvEv Ksp-Cre mice29 to generate KKO mice and WT littermates (Ksp-Cre− Agtr1afl/fl). Finally, floxed TNFa mice30 backcrossed six generations onto the 129/SvEv strain were bred with 129/SvEv Ksp-Cre mice to generate TNF KKO mice and WT littermates (Ksp-Cre− TNFafl/fl). Genotyping was performed to detect the presence of both flox and Cre as previously described.8 Additional verification was performed on purified immune cell populations and other solid organs as shown in Supplemental Figure 1. To map the distributional pattern of Cre recombinase expression in disease, mT/mG mice from The Jackson Laboratory (Bar Harbor, ME) were crossed with the CD4-Cre or Ksp-Cre recombinase transgenic lines; mT/mG mice normally express red fluorescent protein in all tissues. When Cre is present, the mT cassette is deleted, triggering expression of the membrane-targeted eGFP. Mice were bred and maintained in the Association for Assessment and Accreditation of Laboratory Animal Care–accredited animal facilities at the Durham Veterans Affairs Medical Center according to National Institutes of Health guidelines. All of the animal studies were approved by the Durham Veterans Affairs Medical Center Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee and conducted in accordance with the National Institutes of Health Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. Animals had free access to standard rodent chow and water. Female 12-week-old mice and littermate controls were used for experiments.
Cisplatin–Induced Kidney Injury Model
Experimental mice were injected ip with a single dose of 30 mg/kg cisplatin or equal volume of saline to induce kidney injury or serve as control animals as described previously.12 Mice were euthanized after 72 hours if not otherwise specified. Blood samples and kidney tissues were obtained for additional analysis. In some experiments, losartan at 20 mg/kg (gift from Merck GmbH, Darmstadt, Germany) or saline vehicle was injected ip at 20 mg/kg daily as described.31
Assessment of Renal Function
sCr and BUN levels were determined by using Automated Blood Chemical Analyzer Vitro 350 (Orthoclinical Diagnostic Inc., Rochester, NY).
Histologic Analyses
Kidney tissues were first fixed with 10% formalin solution and embedded with paraffin. HE staining was performed on 5-μm sections. All of the tissues were examined by experienced pathologists masked to the experimental groups. The kidney sections were graded on the basis of a previously established scoring system.12 Briefly, the percentages of tubules with cell lysis, loss of brush border, and cast formation were recorded on the basis of a scale from zero to four (0, no damage; 1, <25%; 2, 25%–50%; 3, 50%–75%; and 4, >75%). An overall histologic score for each kidney was obtained by adding the individual injury component scores.
Renal mRNA Expression
Total RNA was isolated by using an RNeasy Mini Kit per the manufacturer’s instructions (Qiagen, Germantown, MD). Gene expression levels of TNF-α and NGAL were determined by real–time RT-PCR as previously described.9
Cytokine ELISA
Serum or kidney samples were obtained during euthanasia. Kidney samples were homogenized in a cell lysis buffer with protease inhibitor (Roche, Basel, Switzerland). Total protein concentration was first determined using a bicinchoninic acid Kit. Cytokines were then quantified in the supernatants by using an ELISA Kit from Invitrogen (Carlsbad, CA) according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
Statistical Analyses
The values within a group are expressed as means±SEMs. For comparisons between groups, statistical significance was assessed using ANOVA followed by an unpaired t test for normally distributed data and a Mann–Whitney test for non–normally distributed data. For comparisons within groups, variables were analyzed by a paired t test.
Disclosures
None.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by funding from National Institutes of Health Grants DK098382-02 (to S.B.G.) and DK087893-01 (to S.D.C.); Department of Veterans Affairs, Veterans Health Administration, Office of Research and Development, Biomedical Laboratory Research and Development Grants BX000893-01A2 and IK2BX002240; the Edna and Fred L. Mandel Center for Hypertension and Atherosclerosis Research; a Grant-in-Aid and Postdoctoral Fellowship 12POST11910012 from the American Heart Association; and Russian Science Foundation Grant 14-50-00060 (to S.A.N.). The George M. O’Brien Kidney Research Core Center under Grant P30DK079328 at the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center provided the Ksp-Cre mouse line.
Footnotes
Published online ahead of print. Publication date available at www.jasn.org.
This article contains supplemental material online at http://jasn.asnjournals.org/lookup/suppl/doi:10.1681/ASN.2015060683/-/DCSupplemental.
References
- 1.Kelland L: The resurgence of platinum-based cancer chemotherapy. Nat Rev Cancer 7: 573–584, 2007 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Dasari S, Tchounwou PB: Cisplatin in cancer therapy: Molecular mechanisms of action. Eur J Pharmacol 740: 364–378, 2014 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Pabla N, Dong Z: Curtailing side effects in chemotherapy: A tale of PKCδ in cisplatin treatment. Oncotarget 3: 107–111, 2012 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Bao H, Ge Y, Wang Z, Zhuang S, Dworkin L, Peng A, Gong R: Delayed administration of a single dose of lithium promotes recovery from AKI. J Am Soc Nephrol 25: 488–500, 2014 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Ramesh G, Reeves WB: TNF-alpha mediates chemokine and cytokine expression and renal injury in cisplatin nephrotoxicity. J Clin Invest 110: 835–842, 2002 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Zhang B, Ramesh G, Norbury CC, Reeves WB: Cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity is mediated by tumor necrosis factor-alpha produced by renal parenchymal cells. Kidney Int 72: 37–44, 2007 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Crowley SD, Gurley SB, Oliverio MI, Pazmino AK, Griffiths R, Flannery PJ, Spurney RF, Kim HS, Smithies O, Le TH, Coffman TM: Distinct roles for the kidney and systemic tissues in blood pressure regulation by the renin-angiotensin system. J Clin Invest 115: 1092–1099, 2005 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Zhang JD, Patel MB, Song YS, Griffiths R, Burchette J, Ruiz P, Sparks MA, Yan M, Howell DN, Gomez JA, Spurney RF, Coffman TM, Crowley SD: A novel role for type 1 angiotensin receptors on T lymphocytes to limit target organ damage in hypertension. Circ Res 110: 1604–1617, 2012 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Zhang JD, Patel MB, Griffiths R, Dolber PC, Ruiz P, Sparks MA, Stegbauer J, Jin H, Gomez JA, Buckley AF, Lefler WS, Chen D, Crowley SD: Type 1 angiotensin receptors on macrophages ameliorate IL-1 receptor-mediated kidney fibrosis. J Clin Invest 124: 2198–2203, 2014 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Ferreri NR, Escalante BA, Zhao Y, An SJ, McGiff JC: Angiotensin II induces TNF production by the thick ascending limb: Functional implications. Am J Physiol 274: F148–F155, 1998 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Liu M, Chien CC, Burne-Taney M, Molls RR, Racusen LC, Colvin RB, Rabb H: A pathophysiologic role for T lymphocytes in murine acute cisplatin nephrotoxicity. J Am Soc Nephrol 17: 765–774, 2006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Zhang D, Liu Y, Wei Q, Huo Y, Liu K, Liu F, Dong Z: Tubular p53 regulates multiple genes to mediate AKI. J Am Soc Nephrol 25: 2278–2289, 2014 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Xu Y, Ma H, Shao J, Wu J, Zhou L, Zhang Z, Wang Y, Huang Z, Ren J, Liu S, Chen X, Han J: A role for tubular necroptosis in cisplatin-induced AKI. J Am Soc Nephrol 26: 2647–2658, 2015 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Muller DN, Shagdarsuren E, Park JK, Dechend R, Mervaala E, Hampich F, Fiebeler A, Ju X, Finckenberg P, Theuer J, Viedt C, Kreuzer J, Heidecke H, Haller H, Zenke M, Luft FC: Immunosuppressive treatment protects against angiotensin II-induced renal damage. Am J Pathol 161: 1679–1693, 2002 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Muller DN, Dechend R, Mervaala EMA, Park J-K, Schmidt F, Fiebeler A, Theuer J, Breu V, Ganten D, Haller H, Luft FC: NF-kappaB inhibition ameliorates angiotensin II-induced inflammatory damage in rats. Hypertension 35: 193–201, 2000 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Crowley SD, Song YS, Sprung G, Griffiths R, Sparks M, Yan M, Burchette JL, Howell DN, Lin EE, Okeiyi B, Stegbauer J, Yang Y, Tharaux PL, Ruiz P: A role for angiotensin II type 1 receptors on bone marrow-derived cells in the pathogenesis of angiotensin II-dependent hypertension. Hypertension 55: 99–108, 2010 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Szabo SJ, Kim ST, Costa GL, Zhang X, Fathman CG, Glimcher LH: A novel transcription factor, T-bet, directs Th1 lineage commitment. Cell 100: 655–669, 2000 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Okui S, Yamamoto H, Li W, Gamachi N, Fujita Y, Kashiwamura S, Miura D, Takai S, Miyazaki M, Urade M, Okamura H, Ueda H: Cisplatin-induced acute renal failure in mice is mediated by chymase-activated angiotensin-aldosterone system and interleukin-18. Eur J Pharmacol 685: 149–155, 2012 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Perazella MA: Onco-nephrology: Renal toxicities of chemotherapeutic agents. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 7: 1713–1721, 2012 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Egami K, Murohara T, Shimada T, Sasaki K, Shintani S, Sugaya T, Ishii M, Akagi T, Ikeda H, Matsuishi T, Imaizumi T: Role of host angiotensin II type 1 receptor in tumor angiogenesis and growth. J Clin Invest 112: 67–75, 2003 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Cheungpasitporn W, Thongprayoon C, Srivali N, O’Corragain OA, Edmonds PJ, Ungprasert P, Kittanamongkolchai W, Erickson SB: Preoperative renin-angiotensin system inhibitors use linked to reduced acute kidney injury: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Nephrol Dial Transplant 30: 978–988, 2015 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Mangieri A: Renin-angiotensin system blockers in cardiac surgery. J Crit Care 30: 613–618, 2015 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Bedford M, Farmer CK, Irving J, Stevens PE: Acute kidney injury: An acceptable risk of treatment with renin-angiotensin system blockade in primary care? Can J Kidney Health Dis 2: 14, 2015 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 24.El-Sayed SM, Abd-Ellah MF, Attia SM: Protective effect of captopril against cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. Pak J Pharm Sci 21: 255–261, 2008 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Goyal SN, Bharti S, Bhatia J, Nag TC, Ray R, Arya DS: Telmisartan, a dual ARB/partial PPAR-γ agonist, protects myocardium from ischaemic reperfusion injury in experimental diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab 13: 533–541, 2011 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Seujange Y, Eiam-Ong S, Tirawatnapong T, Eiam-Ong S: Role of angiotensin II on dihydrofolate reductase, GTP-cyclohydrolase 1 and nitric oxide synthase expressions in renal ischemia-reperfusion. Am J Nephrol 28: 692–700, 2008 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Gurley SB, Riquier-Brison AD, Schnermann J, Sparks MA, Allen AM, Haase VH, Snouwaert JN, Le TH, McDonough AA, Koller BH, Coffman TM: AT1A angiotensin receptors in the renal proximal tubule regulate blood pressure. Cell Metab 13: 469–475, 2011 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Lee PP, Fitzpatrick DR, Beard C, Jessup HK, Lehar S, Makar KW, Pérez-Melgosa M, Sweetser MT, Schlissel MS, Nguyen S, Cherry SR, Tsai JH, Tucker SM, Weaver WM, Kelso A, Jaenisch R, Wilson CB: A critical role for Dnmt1 and DNA methylation in T cell development, function, and survival. Immunity 15: 763–774, 2001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Shao X, Somlo S, Igarashi P: Epithelial-specific Cre/lox recombination in the developing kidney and genitourinary tract. J Am Soc Nephrol 13: 1837–1846, 2002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Grivennikov SI, Tumanov AV, Liepinsh DJ, Kruglov AA, Marakusha BI, Shakhov AN, Murakami T, Drutskaya LN, Förster I, Clausen BE, Tessarollo L, Ryffel B, Kuprash DV, Nedospasov SA: Distinct and nonredundant in vivo functions of TNF produced by t cells and macrophages/neutrophils: Protective and deleterious effects. Immunity 22: 93–104, 2005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Li H, Armando I, Yu P, Escano C, Mueller SC, Asico L, Pascua A, Lu Q, Wang X, Villar VA, Jones JE, Wang Z, Periasamy A, Lau YS, Soares-da-Silva P, Creswell K, Guillemette G, Sibley DR, Eisner G, Gildea JJ, Felder RA, Jose PA: Dopamine 5 receptor mediates Ang II type 1 receptor degradation via a ubiquitin-proteasome pathway in mice and human cells. J Clin Invest 118: 2180–2189, 2008 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.