Abstract
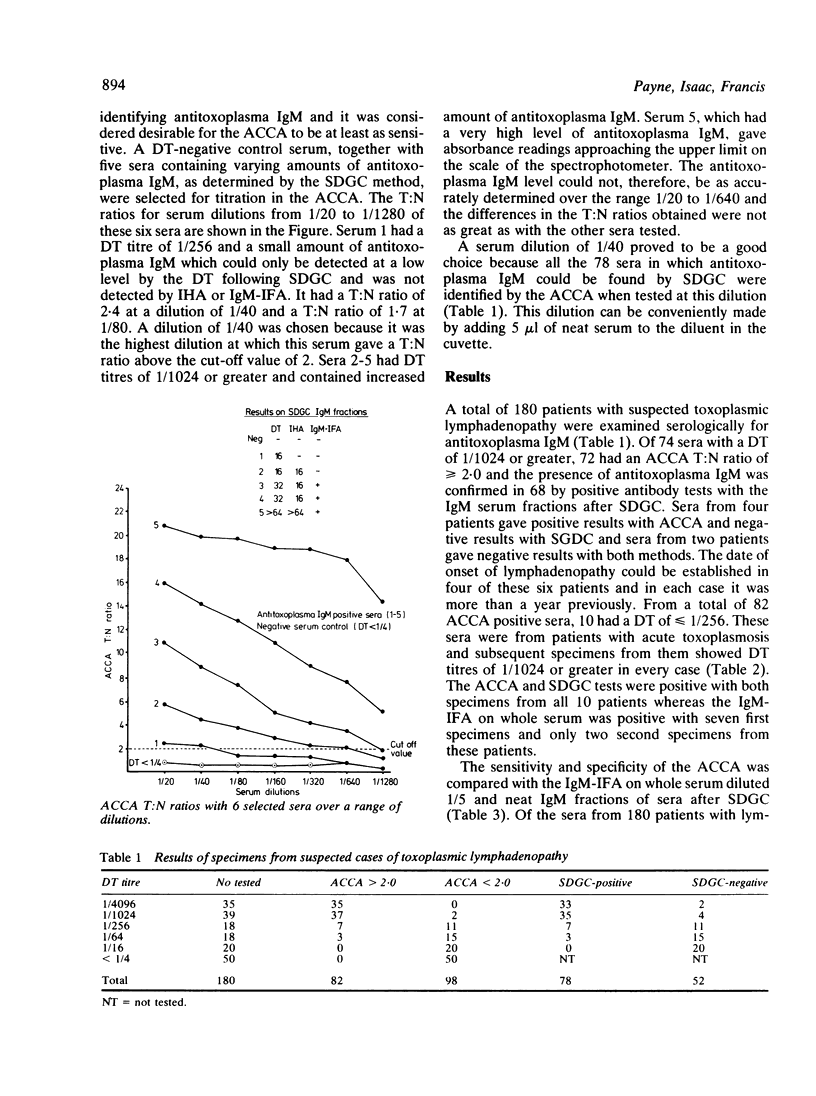
Sera from 180 patients with suspected toxoplasmic lymphadenopathy were examined for antitoxoplasma IgM by an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), using antibody class capture (ACCA). Of 82 positive ACCA results, 78 were confirmed by testing the IgM fractions of the sera, obtained by sucrose density gradient centrifugation (SDGC). The four positive results which could not be confirmed were all from patients with at least a year's history of lymphadenopathy. Sera from 10 patients with low Sabin Feldman dye test (DT) titers gave positive ACCA results and subsequent specimens from them showed a rise in antibody concentration, confirming the diagnosis of acute toxoplasmosis. The antitoxoplasma IgM immunofluorescent antibody test (IgM-IFA) on whole serum was relatively insensitive and gave false-positive results with sera containing rheumatoid factor (RF) and antinuclear factor (ANF). There were no false-positive ACCA results with such sera, probably because the conjugates were prepared from F(ab')2 fragments of antitoxoplasma serum. The ACCA proved to be sensitive, specific and easily automated enabling examination of large numbers of specimens.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Araujo F. G., Barnett E. V., Gentry L. O., Remington J. S. False-positive anti-Toxoplasma fluorescent-antibody tests in patients with antinuclear antibodies. Appl Microbiol. 1971 Sep;22(3):270–275. doi: 10.1128/am.22.3.270-275.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camargo M. E., Leser P. G., Rocca A. Rheumatoid factors as a cause for false positive IgM anti-toxoplasma fluorescent tests. A technique for specific results. Rev Inst Med Trop Sao Paulo. 1972 Sep-Oct;14(5):310–313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caul E. O., Hobbs S. J., Roberts P. C., Clarke S. K. Evaluation of a simplified sucrose gradient method for the detection of rubella-specific IgM in routine diagnostic practice. J Med Virol. 1978;2(2):153–163. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890020210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen I. R., Norins L. C., Julian A. J. Competition between, and effectiveness of, IgG and IgM antibodies in indirect fluorescent antibody and other tests. J Immunol. 1967 Jan;98(1):143–149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duermeyer W., van der Veen J. Specific detection of IgM-antibodies by ELISA, applied in hepatitis-A. Lancet. 1978 Sep 23;2(8091):684–685. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)92802-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta J. D., Peterson V., Stout M., Murphy A. M. Single-sample diagnosis of recent rubella by fractionation of antibody on Sephadex G-200 column. J Clin Pathol. 1971 Sep;24(6):547–550. doi: 10.1136/jcp.24.6.547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naot Y., Barnett E. V., Remington J. S. Method for avoiding false-positive results occurring in immunoglobulin M enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays due to presence of both rheumatoid factor and antinuclear antibodies. J Clin Microbiol. 1981 Jul;14(1):73–78. doi: 10.1128/jcm.14.1.73-78.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naot Y., Luft B. J., Remington J. S. False-positive serological tests in heart transplant recipients. Lancet. 1981 Sep 12;2(8246):590–591. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)90986-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naot Y., Remington J. S. An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of IgM antibodies to Toxoplasma gondii: use for diagnosis of acute acquired toxoplasmosis. J Infect Dis. 1980 Nov;142(5):757–766. doi: 10.1093/infdis/142.5.757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remington J. S., Miller M. J., Brownlee I. IgM antibodies in acute toxoplasmosis. II. Prevalence and significance in acquired cases. J Lab Clin Med. 1968 May;71(5):855–866. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossi G., Choi T. K., Nisonoff A. Crystals of fragment Fab': preparation from pepsin digests of human IgG myeloma proteins. Nature. 1969 Aug 23;223(5208):837–838. doi: 10.1038/223837a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sabin A. B., Feldman H. A. Dyes as Microchemical Indicators of a New Immunity Phenomenon Affecting a Protozoon Parasite (Toxoplasma). Science. 1948 Dec 10;108(2815):660–663. doi: 10.1126/science.108.2815.660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



