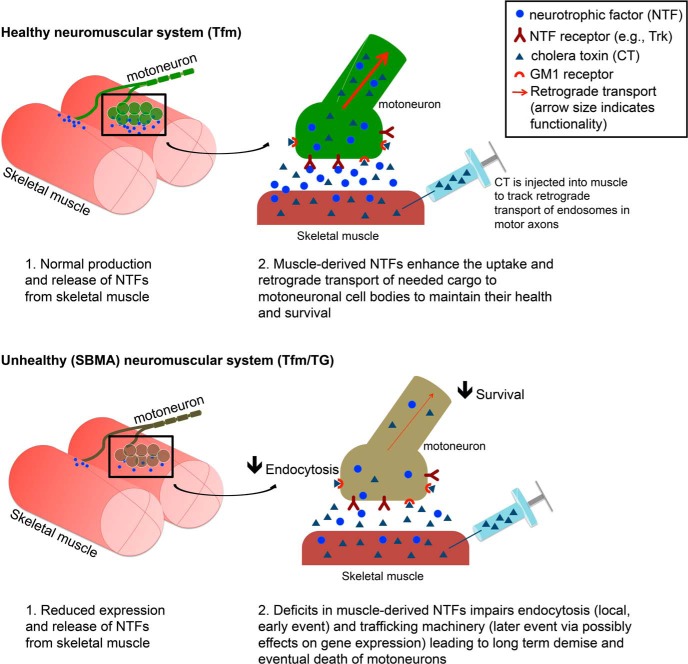
Figure 4.
Proposed model of the non-cell-autonomous influence of muscle on motoneuronal axonal transport. In the healthy neuromuscular system, neurotrophic factors produced and released from skeletal muscle support motoneuronal health and survival. SBMA skeletal muscle is deficient in neurotrophic factors, which may lead to reduced endocytosis in motoneurons, which may manifest as reduced retrograde transport of cholera toxin and reduced endosomal flux, as observed in the present study. Therapies aimed at increasing muscle-derived neurotrophic factors may remedy defective axonal transport and ameliorate disease symptoms.