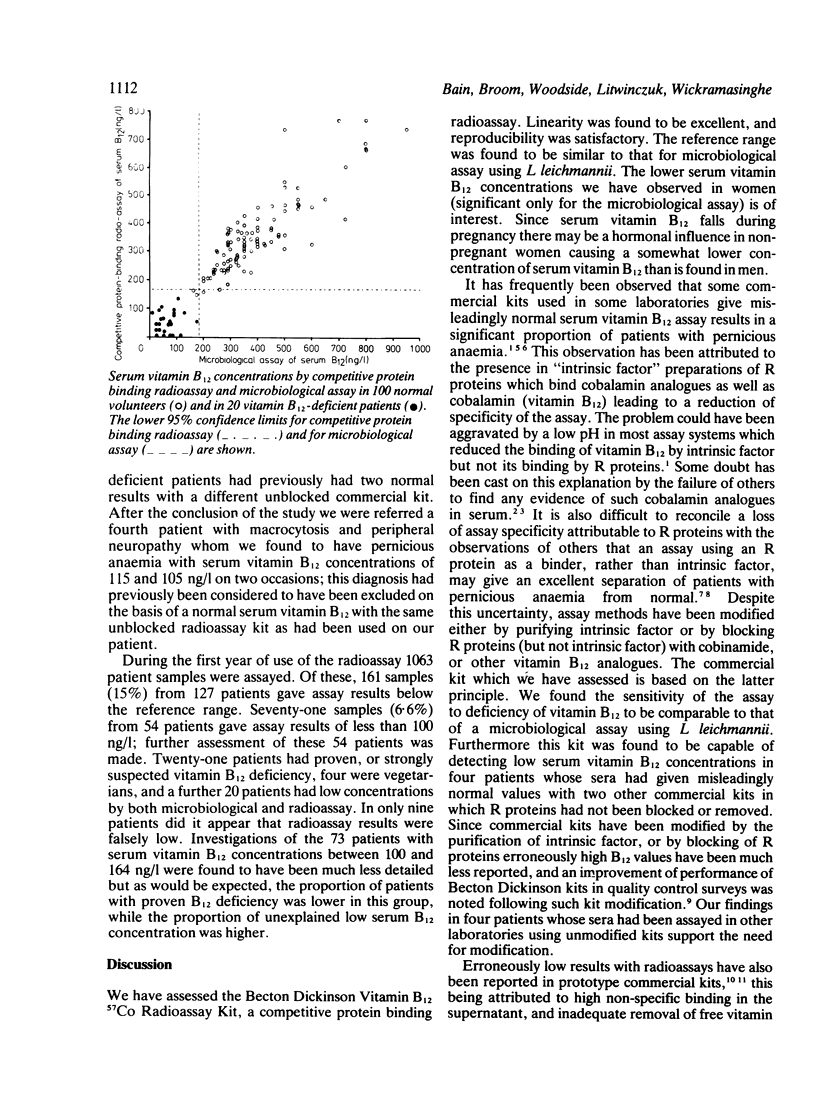
Abstract
A competitive protein binding radioassay kit for serum vitamin B12 has been assessed. Precision, linearity, sensitivity, and specificity have been found to be satisfactory. Falsely-normal assay results in patients with vitamin B12 deficiency have not been observed.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Begley J. A., Hall C. A. Forms of vitamin B12 in radioisotope dilution assays. J Clin Pathol. 1981 Jun;34(6):630–636. doi: 10.1136/jcp.34.6.630. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen I. W., Silberstein E. B., Maxon H. R., Sperling M., Barnes E. Clinical significance of serum vitamin B12 measured by radioassay using pure intrinsic factor. J Nucl Med. 1981 May;22(5):447–451. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper B. A., Whitehead V. M. Evidence that some patients with pernicious anemia are not recognized by radiodilution assay for cobalamin in serum. N Engl J Med. 1978 Oct 12;299(15):816–818. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197810122991506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson D. W., Fish D. I., Frew I. D., Orton B., Roome T. Vitamin B12 quality control trials. Clin Lab Haematol. 1981;3(4):323–330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green R., Newmark P. A., Musso A. M., Mollin D. L. The use of chicken serum for measurement of serum vitamin B12 concentration by radioisotope dilution: discription of method and comparison with microbiological assay results. Br J Haematol. 1974 Jul;27(3):507–526. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1974.tb06816.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolhouse J. F., Kondo H., Allen N. C., Podell E., Allen R. H. Cobalamin analogues are present in human plasma and can mask cobalamin deficiency because current radioisotope dilution assays are not specific for true cobalamin. N Engl J Med. 1978 Oct 12;299(15):785–792. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197810122991501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeFebvre R. J., Virji A. S., Mertens B. F. Erroneously low results due to high nonspecific binding encountered with a radioassay kit that measures true serum vitamin B12. Am J Clin Pathol. 1980 Aug;74(2):209–213. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/74.2.209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sourial N. A. Use of an improved E. coli method for the measurement of cobalamin in serum: comparison with the E. gracilis assay results. J Clin Pathol. 1981 Apr;34(4):351–356. doi: 10.1136/jcp.34.4.351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturgeon M. F. Erroneously low results due to high nonspecific binding encountered with a radioassay kit that measures "true" serum vitamin B12. Am J Clin Pathol. 1981 May;75(5):767–768. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/75.5.767a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickramasinghe S. N., Saunders J. E. A fault in the design of the deoxyuridine suppression test. Clin Lab Haematol. 1979;1(1):69–71. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2257.1979.tb00593.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zacharakis R., Muir M., Chanarin I. Comparison of serum vitamin B12 estimation by saturation analysis with intrinsic factor and with R-protein as binding agents. J Clin Pathol. 1981 Apr;34(4):357–360. doi: 10.1136/jcp.34.4.357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



