Abstract
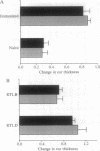
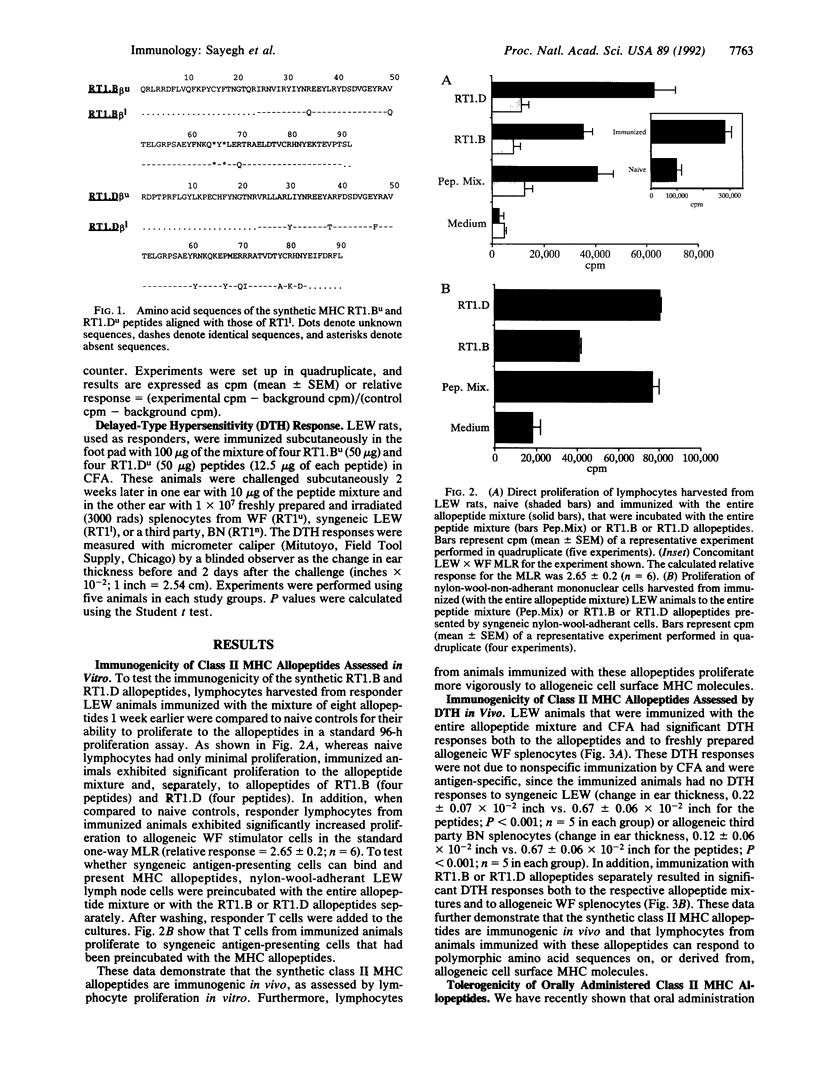
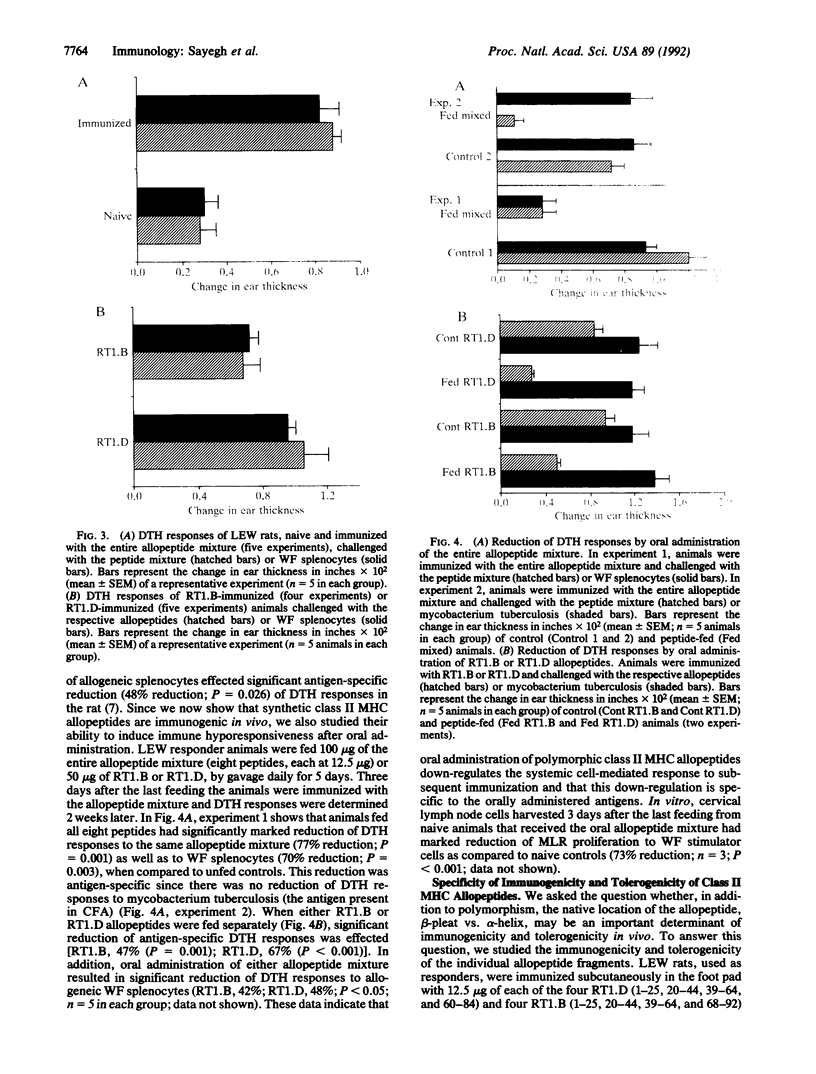
We studied the immunogenicity and tolerogenicity of class II major histocompatibility complex (MHC) allopeptides in the rat. Inbred LEW (RT1l) rats, used as responders, were immunized in the foot pad with a mixture of eight synthetic class II MHC allopeptides emulsified in complete Freund's adjuvant. These sequences represent the full-length second domain of RT1.Bu and RT1.Du (WF) beta chains. In vitro, responder lymphocytes harvested from popliteal and inguinal lymph nodes of immunized animals exhibited significant proliferation to the MHC allopeptide mixture. In addition, these responder lymphocytes had significantly increased proliferation to allogeneic WF (RT1u) stimulator cells, when compared to naive controls in the standard one-way mixed lymphocyte response. In vivo, peptide-immunized LEW animals were challenged in the ear 2 weeks after immunization with the allopeptide mixture, the individual allopeptide sequences, or allogeneic WF splenocytes. When compared to controls, these animals had significant delayed-type hypersensitivity responses to the allopeptide mixture, to the beta-pleated sheet allopeptide sequences, and to allogeneic WF splenocytes but not to the alpha-helix allopeptide sequences, to syngeneic LEW splenocytes, or to third party allogeneic BN splenocytes. Oral administration of the allopeptide mixture to LEW responder rats daily for 5 days before immunization effected significant reduction of delayed-type hypersensitivity responses both to the allopeptide mixture and to allogeneic splenocytes. This reduction was antigen-specific, since there was no reduction of delayed-type hypersensitivity responses to mycobacterium tuberculosis. These data demonstrate that lymphocytes from animals immunized with polymorphic class II MHC allopeptides can recognize and proliferate to the same amino acid sequences on allogeneic cell surface MHC molecules. In addition, oral administration of these peptides down-regulates the systemic cell-mediated immune response in a specific fashion. Synthetic MHC allopeptides should allow the study of alloimmunity in vivo, including induction of immune tolerance.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benichou G., Takizawa P. A., Ho P. T., Killion C. C., Olson C. A., McMillan M., Sercarz E. E. Immunogenicity and tolerogenicity of self-major histocompatibility complex peptides. J Exp Med. 1990 Nov 1;172(5):1341–1346. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.5.1341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chao N. J., Timmerman L., McDevitt H. O., Jacob C. O. Molecular characterization of MHC class II antigens (beta 1 domain) in the BB diabetes-prone and -resistant rat. Immunogenetics. 1989;29(4):231–234. doi: 10.1007/BF00717906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen B. P., Madrigal A., Parham P. Cytotoxic T cell recognition of an endogenous class I HLA peptide presented by a class II HLA molecule. J Exp Med. 1990 Sep 1;172(3):779–788. doi: 10.1084/jem.172.3.779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eckels D. D. Alloreactivity: allogeneic presentation of endogenous peptide or direct recognition of MHC polymorphism? A review. Tissue Antigens. 1990 Feb;35(2):49–55. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1990.tb01755.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falk K., Rötzschke O., Stevanović S., Jung G., Rammensee H. G. Allele-specific motifs revealed by sequencing of self-peptides eluted from MHC molecules. Nature. 1991 May 23;351(6324):290–296. doi: 10.1038/351290a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frankel A. H., Sayegh M. H., Rothstein D. M., Milford E. L., Carpenter C. B. Requirements for the induction of allospecific CD8+ suppressor T cells in the rat primary mixed lymphocyte response. CD4+, CD45R+ T cells, or supernatant factor. Transplantation. 1989 Oct;48(4):639–646. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins P. J., Weiner H. L. Suppression of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by oral administration of myelin basic protein and its fragments. J Immunol. 1988 Jan 15;140(2):440–445. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khoury S. J., Lider O., al-Sabbagh A., Weiner H. L. Suppression of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by oral administration of myelin basic protein. III. Synergistic effect of lipopolysaccharide. Cell Immunol. 1990 Dec;131(2):302–310. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(90)90256-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lider O., Santos L. M., Lee C. S., Higgins P. J., Weiner H. L. Suppression of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis by oral administration of myelin basic protein. II. Suppression of disease and in vitro immune responses is mediated by antigen-specific CD8+ T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1989 Feb 1;142(3):748–752. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A., Lider O., Roberts A. B., Sporn M. B., Weiner H. L. Suppressor T cells generated by oral tolerization to myelin basic protein suppress both in vitro and in vivo immune responses by the release of transforming growth factor beta after antigen-specific triggering. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jan 1;89(1):421–425. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.1.421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagler-Anderson C., Bober L. A., Robinson M. E., Siskind G. W., Thorbecke G. J. Suppression of type II collagen-induced arthritis by intragastric administration of soluble type II collagen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(19):7443–7446. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.19.7443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nuchtern J. G., Biddison W. E., Klausner R. D. Class II MHC molecules can use the endogenous pathway of antigen presentation. Nature. 1990 Jan 4;343(6253):74–76. doi: 10.1038/343074a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nussenblatt R. B., Caspi R. R., Mahdi R., Chan C. C., Roberge F., Lider O., Weiner H. L. Inhibition of S-antigen induced experimental autoimmune uveoretinitis by oral induction of tolerance with S-antigen. J Immunol. 1990 Mar 1;144(5):1689–1695. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson C. A., Williams L. C., McLaughlin-Taylor E., McMillan M. Creation of H-2 class I epitopes using synthetic peptides: recognition by alloreactive cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(3):1031–1035. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.3.1031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parham P., Clayberger C., Zorn S. L., Ludwig D. S., Schoolnik G. K., Krensky A. M. Inhibition of alloreactive cytotoxic T lymphocytes by peptides from the alpha 2 domain of HLA-A2. Nature. 1987 Feb 12;325(6105):625–628. doi: 10.1038/325625a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudensky AYu, Preston-Hurlburt P., Hong S. C., Barlow A., Janeway C. A., Jr Sequence analysis of peptides bound to MHC class II molecules. Nature. 1991 Oct 17;353(6345):622–627. doi: 10.1038/353622a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sayegh M. H., Zhang Z. J., Hancock W. W., Kwok C. A., Carpenter C. B., Weiner H. L. Down-regulation of the immune response to histocompatibility antigens and prevention of sensitization by skin allografts by orally administered alloantigen. Transplantation. 1992 Jan;53(1):163–166. doi: 10.1097/00007890-199201000-00033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherer M. T., Chan B. M., Ria F., Smith J. A., Perkins D. L., Gefter M. L. Control of cellular and humoral immune responses by peptides containing T-cell epitopes. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1989;54(Pt 1):497–504. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1989.054.01.059. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitacre C. C., Gienapp I. E., Orosz C. G., Bitar D. M. Oral tolerance in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. III. Evidence for clonal anergy. J Immunol. 1991 Oct 1;147(7):2155–2163. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Z. J., Davidson L., Eisenbarth G., Weiner H. L. Suppression of diabetes in nonobese diabetic mice by oral administration of porcine insulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 15;88(22):10252–10256. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.22.10252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Z. Y., Lee C. S., Lider O., Weiner H. L. Suppression of adjuvant arthritis in Lewis rats by oral administration of type II collagen. J Immunol. 1990 Oct 15;145(8):2489–2493. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]