Abstract
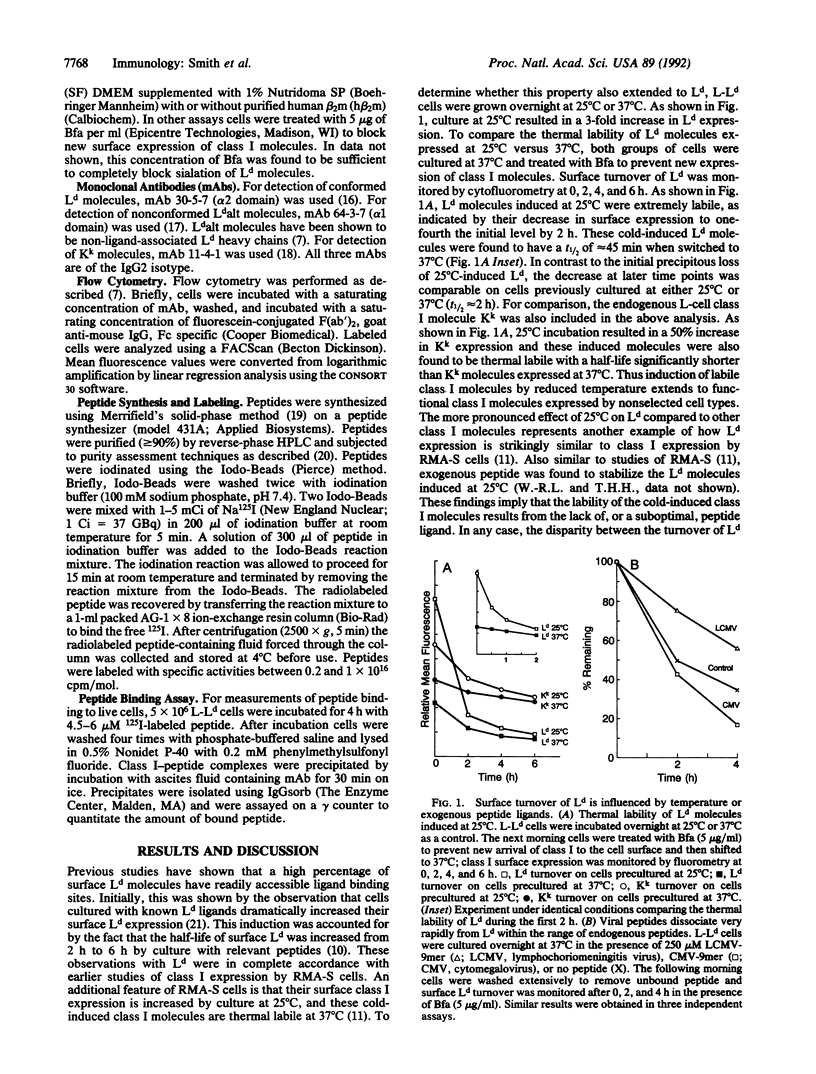
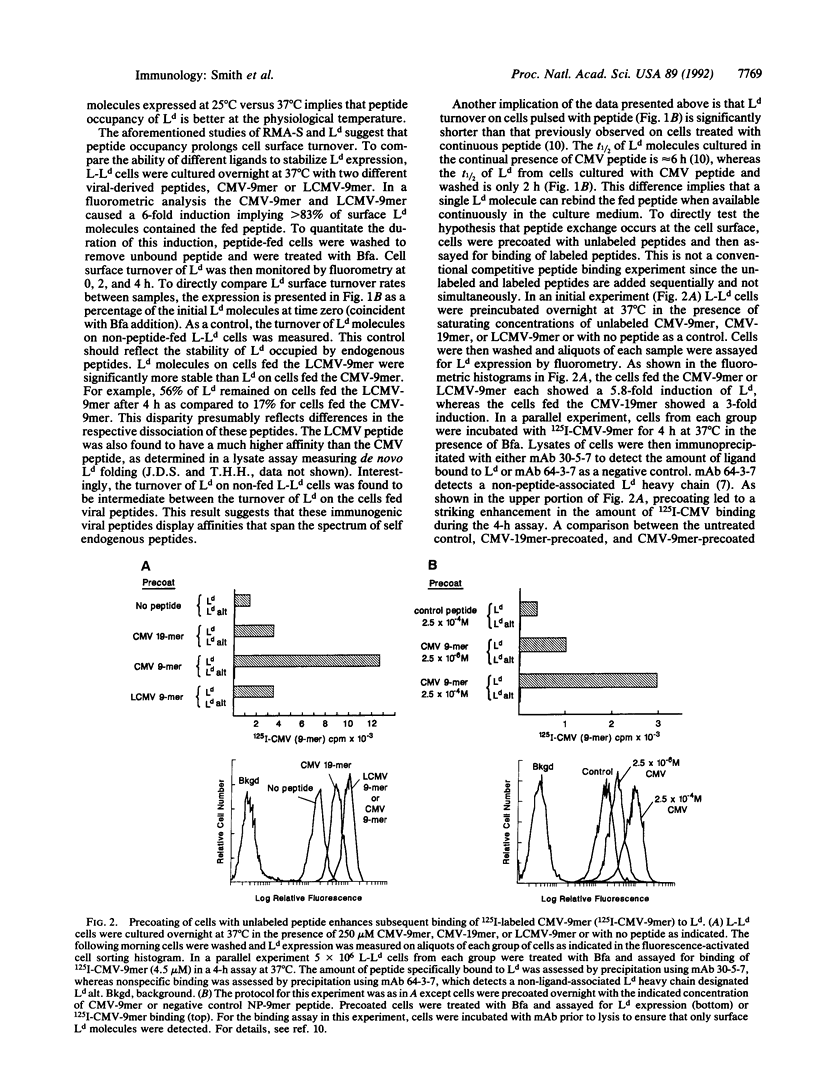
Certain class I major histocompatibility complex molecules expressed on live cells have been shown to bind exogenous peptide ligands. However, it remains controversial whether this binding occurs by peptide exchange or to empty surface class I molecules. In this report we compare the surface binding and dissociation of two virus-derived ligands of the Ld class I molecule of the mouse. The peptide ligands were previously identified in immune responses to cytomegalovirus or lymphochoriomeningitis virus as immunodominant, optimally sized, and Ld restricted. Ligand dissociation was monitored on live cells indirectly by measuring the surface turnover of Ld-peptide complexes or directly by using labeled peptides. The cytomegalovirus-derived and lymphochoriomeningitis virus-derived peptides appeared to dissociate relatively rapidly; however, the cytomegalovirus-derived peptide had a more rapid off-rate than the lymphochoriomeningitis-derived peptide. Furthermore, these rates of dissociation appear to span that seen with endogenous Ld-associated peptides expressed by cells at 37 degrees C. Exploiting the extraordinary accessibility of the surface Ld ligand binding site we developed an assay to quantitate peptide ligand exchange. Cells were precoated with saturating amounts of unlabeled peptide by overnight incubation and were then tested for secondary binding of labeled peptides in a 4-h assay. Our results unequivocally demonstrate the potential for surface class I molecules to undergo peptide exchange. Furthermore, peptide exchange was found to be largely independent of exogenous beta 2-microglobulin. This result implies that beta 2-microglobulin association and not beta 2-microglobulin exchange is the critical factor in peptide exchange by surface class I molecules. Because of the exquisite ability of T cells to discriminate different amounts of ligand bound to class I, the binding of exogenous peptides could play a critical role in normal or aberrant immune responses.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexander M. A., Damico C. A., Wieties K. M., Hansen T. H., Connolly J. M. Correlation between CD8 dependency and determinant density using peptide-induced, Ld-restricted cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1991 Apr 1;173(4):849–858. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.4.849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benjamin R. J., Madrigal J. A., Parham P. Peptide binding to empty HLA-B27 molecules of viable human cells. Nature. 1991 May 2;351(6321):74–77. doi: 10.1038/351074a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd L. F., Kozlowski S., Margulies D. H. Solution binding of an antigenic peptide to a major histocompatibility complex class I molecule and the role of beta 2-microglobulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 15;89(6):2242–2246. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.6.2242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen B. P., Parham P. Direct binding of influenza peptides to class I HLA molecules. Nature. 1989 Feb 23;337(6209):743–745. doi: 10.1038/337743a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christinck E. R., Luscher M. A., Barber B. H., Williams D. B. Peptide binding to class I MHC on living cells and quantitation of complexes required for CTL lysis. Nature. 1991 Jul 4;352(6330):67–70. doi: 10.1038/352067a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Del Val M., Schlicht H. J., Ruppert T., Reddehase M. J., Koszinowski U. H. Efficient processing of an antigenic sequence for presentation by MHC class I molecules depends on its neighboring residues in the protein. Cell. 1991 Sep 20;66(6):1145–1153. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90037-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorka J., McCourt D. W., Schwartz B. D. Automated synthesis of a C-terminal photoprobe using combined Fmoc and t-Boc synthesis strategies on a single automated peptide synthesizer. Pept Res. 1989 Nov-Dec;2(6):376–380. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kane K. P., Sherman L. A., Mescher M. F. Exogenous beta 2-microglobulin is required for antigenic peptide binding to isolated class I major histocompatibility complex molecules. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Sep;21(9):2289–2292. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830210945. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozlowski S., Takeshita T., Boehncke W. H., Takahashi H., Boyd L. F., Germain R. N., Berzofsky J. A., Margulies D. H. Excess beta 2 microglobulin promoting functional peptide association with purified soluble class I MHC molecules. Nature. 1991 Jan 3;349(6304):74–77. doi: 10.1038/349074a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee D. R., Rubocki R. J., Lie W. R., Hansen T. H. The murine MHC class I genes, H-2Dq and H-2Lq, are strikingly homologous to each other, H-2Ld, and two genes reported to encode tumor-specific antigens. J Exp Med. 1988 Nov 1;168(5):1719–1739. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.5.1719. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lie W. R., Myers N. B., Connolly J. M., Gorka J., Lee D. R., Hansen T. H. The specific binding of peptide ligand to Ld class I major histocompatibility complex molecules determines their antigenic structure. J Exp Med. 1991 Feb 1;173(2):449–459. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.2.449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lie W. R., Myers N. B., Gorka J., Rubocki R. J., Connolly J. M., Hansen T. H. Peptide ligand-induced conformation and surface expression of the Ld class I MHC molecule. Nature. 1990 Mar 29;344(6265):439–441. doi: 10.1038/344439a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ljunggren H. G., Stam N. J., Ohlén C., Neefjes J. J., Höglund P., Heemels M. T., Bastin J., Schumacher T. N., Townsend A., Kärre K. Empty MHC class I molecules come out in the cold. Nature. 1990 Aug 2;346(6283):476–480. doi: 10.1038/346476a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luescher I. F., Romero P., Cerottini J. C., Maryanski J. L. Specific binding of antigenic peptides to cell-associated MHC class I molecules. Nature. 1991 May 2;351(6321):72–74. doi: 10.1038/351072a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madden D. R., Gorga J. C., Strominger J. L., Wiley D. C. The structure of HLA-B27 reveals nonamer self-peptides bound in an extended conformation. Nature. 1991 Sep 26;353(6342):321–325. doi: 10.1038/353321a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nuchtern J. G., Bonifacino J. S., Biddison W. E., Klausner R. D. Brefeldin A implicates egress from endoplasmic reticulum in class I restricted antigen presentation. Nature. 1989 May 18;339(6221):223–226. doi: 10.1038/339223a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oi V. T., Jones P. P., Goding J. W., Herzenberg L. A., Herzenberg L. A. Properties of monoclonal antibodies to mouse Ig allotypes, H-2, and Ia antigens. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1978;81:115–120. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-67448-8_18. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozato K., Hansen T. H., Sachs D. H. Monoclonal antibodies to mouse MHC antigens. II. Antibodies to the H-2Ld antigen, the products of a third polymorphic locus of the mouse major histocompatibility complex. J Immunol. 1980 Dec;125(6):2473–2477. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedrazzini T., Sette A., Albertson M., Grey H. M. Free ligand-induced dissociation of MHC-antigen complexes. J Immunol. 1991 May 15;146(10):3496–3501. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rock K. L., Rothstein L. E., Gamble S. R., Benacerraf B. Reassociation with beta 2-microglobulin is necessary for Kb class I major histocompatibility complex binding of exogenous peptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(19):7517–7521. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.19.7517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulz M., Aichele P., Vollenweider M., Bobe F. W., Cardinaux F., Hengartner H., Zinkernagel R. M. Major histocompatibility complex--dependent T cell epitopes of lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus nucleoprotein and their protective capacity against viral disease. Eur J Immunol. 1989 Sep;19(9):1657–1667. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830190921. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schumacher T. N., De Bruijn M. L., Vernie L. N., Kast W. M., Melief C. J., Neefjes J. J., Ploegh H. L. Peptide selection by MHC class I molecules. Nature. 1991 Apr 25;350(6320):703–706. doi: 10.1038/350703a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiroishi T., Evans G. A., Appella E., Ozato K. In vitro mutagenesis of a mouse MHC class I gene for the examination of structure-function relationships. J Immunol. 1985 Jan;134(1):623–629. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. D., Lie W. R., Gorka J., Kindle C. S., Myers N. B., Hansen T. H. Disparate interaction of peptide ligand with nascent versus mature class I major histocompatibility complex molecules: comparisons of peptide binding to alternative forms of Ld in cell lysates and the cell surface. J Exp Med. 1992 Jan 1;175(1):191–202. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.1.191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsomides T. J., Walker B. D., Eisen H. N. An optimal viral peptide recognized by CD8+ T cells binds very tightly to the restricting class I major histocompatibility complex protein on intact cells but not to the purified class I protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 15;88(24):11276–11280. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.24.11276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yewdell J. W., Bennink J. R. Brefeldin A specifically inhibits presentation of protein antigens to cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Science. 1989 Jun 2;244(4908):1072–1075. doi: 10.1126/science.2471266. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]






