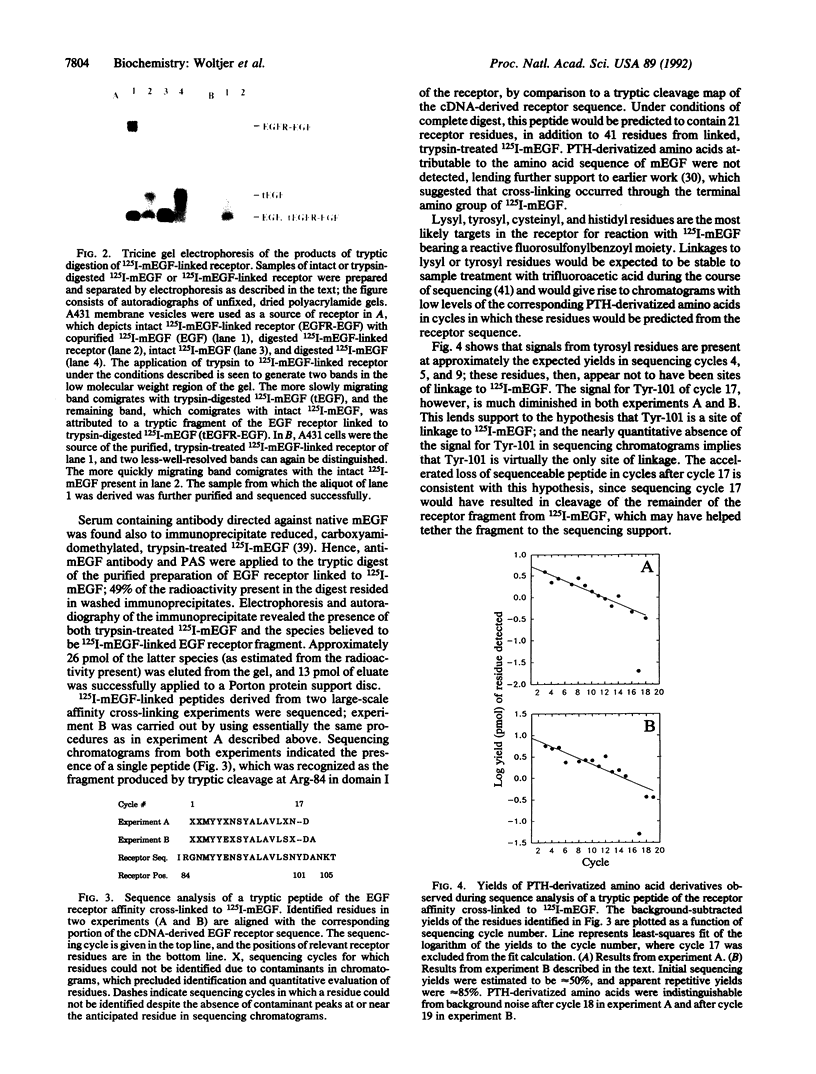
Abstract
We have recently developed a kinetically controlled, step-wise affinity cross-linking technique for specific, high-yield, covalent linkage of murine epidermal growth factor (mEGF) via its N terminus to the EGF receptor. EGF receptor from A431 cells was cross-linked to radiolabeled mEGF (125I-mEGF) by this technique and the 125I-mEGF-receptor complex was purified and denatured. Tryptic digestion of this preparation gave rise to a unique radiolabeled peptide that did not comigrate with trypsin-treated 125I-mEGF in SDS/Tricine gels but that could be immunoprecipitated with antibodies to mEGF. The immunoprecipitated peptide was isolated by electrophoresis in SDS/Tricine gels, eluted, and sequenced. The sequence was found to correspond to that of a tryptic peptide of the EGF receptor beginning with Gly-85, which is in domain I, a region N terminal to the first cysteine-rich region of the receptor. Selective loss of signal in the 17th sequencing cycle suggests that the point of attachment of N-terminally modified 125I-mEGF to the receptor is Tyr-101. The data presented here provide identification by direct protein microsequencing of a site of interaction of EGF and the EGF receptor.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Annamalai A. E., Colman R. F. Reaction of the adenine nucleotide analogue 5'-p-fluorosulfonylbenzoyl adenosine at distinct tyrosine and cysteine residues of rabbit muscle pyruvate kinase. J Biol Chem. 1981 Oct 25;256(20):10276–10283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basu A., Raghunath M., Bishayee S., Das M. Inhibition of tyrosine kinase activity of the epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor by a truncated receptor form that binds to EGF: role for interreceptor interaction in kinase regulation. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;9(2):671–677. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.2.671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellot F., Moolenaar W., Kris R., Mirakhur B., Verlaan I., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J., Felder S. High-affinity epidermal growth factor binding is specifically reduced by a monoclonal antibody, and appears necessary for early responses. J Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;110(2):491–502. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.2.491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buhrow S. A., Cohen S., Garbers D. L., Staros J. V. Characterization of the interaction of 5'-p-fluorosulfonylbenzoyl adenosine with the epidermal growth factor receptor/protein kinase in A431 cell membranes. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 25;258(12):7824–7827. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buhrow S. A., Cohen S., Staros J. V. Affinity labeling of the protein kinase associated with the epidermal growth factor receptor in membrane vesicles from A431 cells. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 25;257(8):4019–4022. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böni-Schnetzler M., Pilch P. F. Mechanism of epidermal growth factor receptor autophosphorylation and high-affinity binding. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(22):7832–7836. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.22.7832. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHEN S. Isolation of a mouse submaxillary gland protein accelerating incisor eruption and eyelid opening in the new-born animal. J Biol Chem. 1962 May;237:1555–1562. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter G., Cohen S. 125I-labeled human epidermal growth factor. Binding, internalization, and degradation in human fibroblasts. J Cell Biol. 1976 Oct;71(1):159–171. doi: 10.1083/jcb.71.1.159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter G., King L., Jr, Cohen S. Rapid enhancement of protein phosphorylation in A-431 cell membrane preparations by epidermal growth factor. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jun 10;254(11):4884–4891. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochet C., Kashles O., Chambaz E. M., Borrello I., King C. R., Schlessinger J. Demonstration of epidermal growth factor-induced receptor dimerization in living cells using a chemical covalent cross-linking agent. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 5;263(7):3290–3295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. PURIFICATION OF A NERVE-GROWTH PROMOTING PROTEIN FROM THE MOUSE SALIVARY GLAND AND ITS NEURO-CYTOTOXIC ANTISERUM. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1960 Mar;46(3):302–311. doi: 10.1073/pnas.46.3.302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S., Ushiro H., Stoscheck C., Chinkers M. A native 170,000 epidermal growth factor receptor-kinase complex from shed plasma membrane vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1982 Feb 10;257(3):1523–1531. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Defize L. H., Boonstra J., Meisenhelder J., Kruijer W., Tertoolen L. G., Tilly B. C., Hunter T., van Bergen en Henegouwen P. M., Moolenaar W. H., de Laat S. W. Signal transduction by epidermal growth factor occurs through the subclass of high affinity receptors. J Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;109(5):2495–2507. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.5.2495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fanger B. O., Stephens J. E., Staros J. V. High-yield trapping of EGF-induced receptor dimers by chemical cross-linking. FASEB J. 1989 Jan;3(1):71–75. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.3.1.2783412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill G. N., Bertics P. J., Santon J. B. Epidermal growth factor and its receptor. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1987 Jun;51(3):169–186. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(87)90027-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenfield C., Hiles I., Waterfield M. D., Federwisch M., Wollmer A., Blundell T. L., McDonald N. Epidermal growth factor binding induces a conformational change in the external domain of its receptor. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 20;8(13):4115–4123. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08596.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Günther N., Betzel C., Weber W. The secreted form of the epidermal growth factor receptor. Characterization and crystallization of the receptor-ligand complex. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 25;265(36):22082–22085. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HJERTEN S. Chromatographic separation according to size of macromolecules and cell particles on columns of agarose suspensions. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1962 Dec;99:466–475. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(62)90295-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lax I., Bellot F., Honegger A. M., Schmidt A., Ullrich A., Givol D., Schlessinger J. Domain deletion in the extracellular portion of the EGF-receptor reduces ligand binding and impairs cell surface expression. Cell Regul. 1990 Jan;1(2):173–188. doi: 10.1091/mbc.1.2.173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lax I., Bellot F., Howk R., Ullrich A., Givol D., Schlessinger J. Functional analysis of the ligand binding site of EGF-receptor utilizing chimeric chicken/human receptor molecules. EMBO J. 1989 Feb;8(2):421–427. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03393.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lax I., Burgess W. H., Bellot F., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J., Givol D. Localization of a major receptor-binding domain for epidermal growth factor by affinity labeling. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1831–1834. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1831. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lax I., Fischer R., Ng C., Segre J., Ullrich A., Givol D., Schlessinger J. Noncontiguous regions in the extracellular domain of EGF receptor define ligand-binding specificity. Cell Regul. 1991 May;2(5):337–345. doi: 10.1091/mbc.2.5.337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lax I., Mitra A. K., Ravera C., Hurwitz D. R., Rubinstein M., Ullrich A., Stroud R. M., Schlessinger J. Epidermal growth factor (EGF) induces oligomerization of soluble, extracellular, ligand-binding domain of EGF receptor. A low resolution projection structure of the ligand-binding domain. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 25;266(21):13828–13833. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsudaira P. Sequence from picomole quantities of proteins electroblotted onto polyvinylidene difluoride membranes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 25;262(21):10035–10038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murthy U., Basu A., Rodeck U., Herlyn M., Ross A. H., Das M. Binding of an antagonistic monoclonal antibody to an intact and fragmented EGF-receptor polypeptide. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1987 Feb 1;252(2):549–560. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(87)90062-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Northwood I. C., Davis R. J. Activation of the epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine protein kinase in the absence of receptor oligomerization. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 5;263(16):7450–7453. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pilch P. F., Czech M. P. Interaction of cross-linking agents with the insulin effector system of isolated fat cells. Covalent linkage of 125I-insulin to a plasma membrane receptor protein of 140,000 daltons. J Biol Chem. 1979 May 10;254(9):3375–3381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Savage C. R., Jr, Cohen S. Epidermal growth factor and a new derivative. Rapid isolation procedures and biological and chemical characterization. J Biol Chem. 1972 Dec 10;247(23):7609–7611. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schägger H., von Jagow G. Tricine-sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis for the separation of proteins in the range from 1 to 100 kDa. Anal Biochem. 1987 Nov 1;166(2):368–379. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90587-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Coussens L., Hayflick J. S., Dull T. J., Gray A., Tam A. W., Lee J., Yarden Y., Libermann T. A., Schlessinger J. Human epidermal growth factor receptor cDNA sequence and aberrant expression of the amplified gene in A431 epidermoid carcinoma cells. 1984 May 31-Jun 6Nature. 309(5967):418–425. doi: 10.1038/309418a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. Signal transduction by receptors with tyrosine kinase activity. Cell. 1990 Apr 20;61(2):203–212. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90801-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ushiro H., Cohen S. Identification of phosphotyrosine as a product of epidermal growth factor-activated protein kinase in A-431 cell membranes. J Biol Chem. 1980 Sep 25;255(18):8363–8365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl M. I., Daniel T. O., Carpenter G. Antiphosphotyrosine recovery of phospholipase C activity after EGF treatment of A-431 cells. Science. 1988 Aug 19;241(4868):968–970. doi: 10.1126/science.2457254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch J. W., Fogel S., Cathala G., Karin M. Industrial yeasts display tandem gene iteration at the CUP1 region. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Aug;3(8):1353–1361. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.8.1353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu D. G., Wang L. H., Chi Y., Sato G. H., Sato J. D. Human epidermal growth factor receptor residue covalently cross-linked to epidermal growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(8):3151–3155. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.8.3151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu D. G., Wang L. H., Sato G. H., West K. A., Harris W. R., Crabb J. W., Sato J. D. Human epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor sequence recognized by EGF competitive monoclonal antibodies. Evidence for the localization of the EGF-binding site. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 15;264(29):17469–17475. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarden Y., Schlessinger J. Epidermal growth factor induces rapid, reversible aggregation of the purified epidermal growth factor receptor. Biochemistry. 1987 Mar 10;26(5):1443–1451. doi: 10.1021/bi00379a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarden Y., Schlessinger J. Self-phosphorylation of epidermal growth factor receptor: evidence for a model of intermolecular allosteric activation. Biochemistry. 1987 Mar 10;26(5):1434–1442. doi: 10.1021/bi00379a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]