Abstract
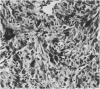
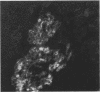
Antisera to the intermediate filaments vimentin and desmin react with fixed paraffin embedded tissue. Benign uterine myomas contain both classes of filaments. Gastrointestinal “smooth muscle tumours” however often lack desmin even when they appear histologically benign. In the sarcomas examined vimentin was the only class of intermediate filament present. The diagnostic and histogenetic implications of these findings are discussed.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashton N., Morgan G. Embryonal sarcoma and embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma of the orbit. J Clin Pathol. 1965 Nov;18(6):699–714. doi: 10.1136/jcp.18.6.699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Badley R. A., Lloyd C. W., Woods A., Carruthers L., Allcock C., Rees D. A. Mechanisms of cellular adhesion. III. Preparation and preliminary characterisation of adhesions. Exp Cell Res. 1978 Dec;117(2):231–244. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(78)90136-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke W. W., Schmid E., Winter S., Osborn M., Weber K. Widespread occurrence of intermediate-sized filaments of the vimentin-type in cultured cells from diverse vertebrates. Exp Cell Res. 1979 Oct 1;123(1):25–46. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(79)90418-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabbiani G., Schmid E., Winter S., Chaponnier C., de Ckhastonay C., Vandekerckhove J., Weber K., Franke W. W. Vascular smooth muscle cells differ from other smooth muscle cells: predominance of vimentin filaments and a specific alpha-type actin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):298–302. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarides E. Intermediate filaments as mechanical integrators of cellular space. Nature. 1980 Jan 17;283(5744):249–256. doi: 10.1038/283249a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid E., Tapscott S., Bennett G. S., Croop J., Fellini S. A., Holtzer H., Franke W. W. Differential location of different types of intermediate-sized filaments in various tissues of the chicken embryo. Differentiation. 1979;15(1):27–40. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1979.tb01031.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Virtanen I., Lehto V. P., Lehtonen E., Vartio T., Stenman S., Kurki P., Wager O., Small J. V., Dahl D., Badley R. A. Expression of intermediate filaments in cultured cells. J Cell Sci. 1981 Aug;50:45–63. doi: 10.1242/jcs.50.1.45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]